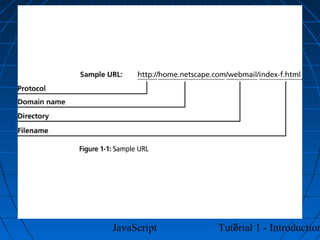
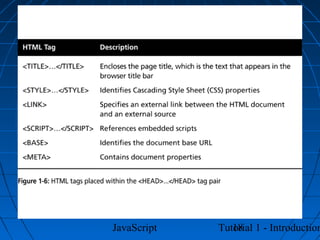
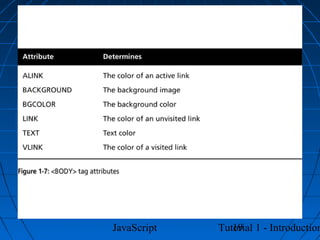
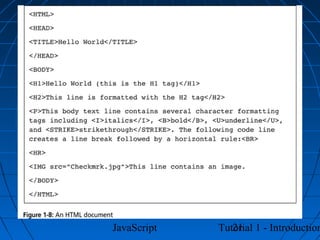
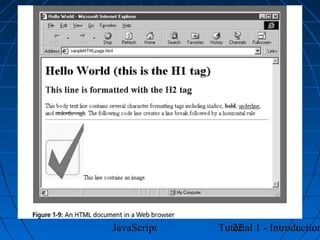
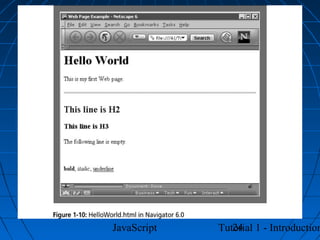
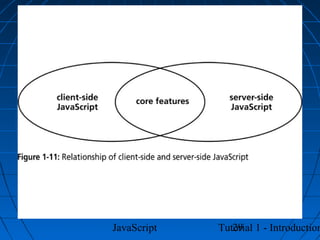
This document provides an introduction to JavaScript programming through a tutorial. Section A discusses programming, HTML, and JavaScript. It covers the history and purpose of the World Wide Web, how HTML is used to design web pages, and JavaScript's role in making web pages interactive. It also explains how to create basic HTML documents and introduces JavaScript syntax and logic.