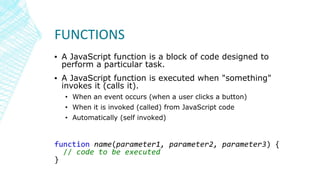
This document provides an overview and plan for learning JavaScript. It covers introductory topics like variables, operators, functions, loops, and events. It also explains why JavaScript is important for web development as one of the three main languages, along with HTML and CSS. The document outlines how to integrate JavaScript into HTML pages and defines common JavaScript concepts.