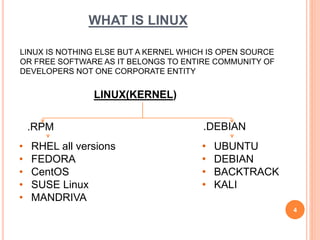
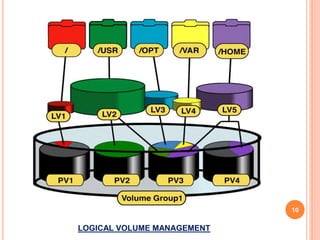
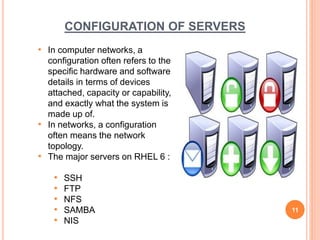
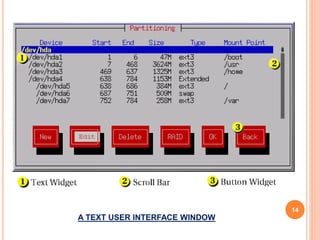
This document outlines a seminar presentation on Linux system administration certification (RHCSA/RHCE). The presentation covers topics such as what Linux is, features of Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6.4, user and file system management, logical volume management, server configuration, shell scripting, and text user interfaces. It provides an introduction to the RHCSA/RHCE certification and its focus on competencies for senior Linux system administrators. An agenda with timing is included, as well as conclusions about the benefits of Linux being an open source, customizable, portable, and stable operating system.