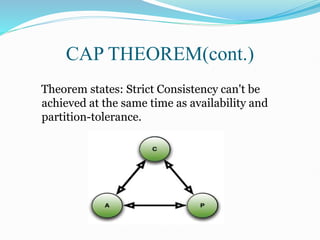
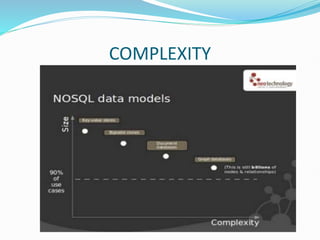
The document discusses NoSQL databases, emphasizing their ability to scale and manage large datasets in modern applications like Facebook and eBay. It outlines various NoSQL types, including key-value stores, document stores, graph databases, and Bigtable implementations, while comparing them with traditional RDBMS. The author also explains architectural principles, such as the CAP theorem, which prioritizes availability and partition tolerance over strict consistency.