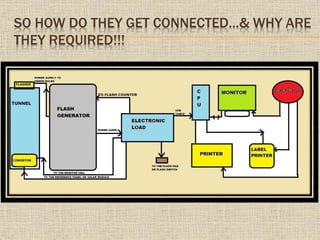
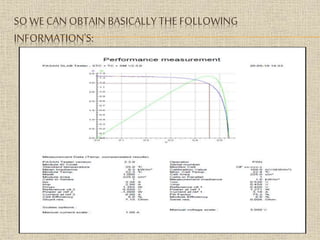
The document provides an overview of the module line process for manufacturing solar panels. It describes the key components in a module line - the stringer, layup unit, laminator, and module tester. The stringer connects solar cells into strings through soldering. The layup unit arranges the strings on glass. The laminator applies heat and pressure to laminate the solar panel. Lastly, the module tester measures the panel's performance through a computer system connected to sensors. Taken together, these components form the manufacturing line that converts solar cells into completed solar panels.










![LAMINATOR CHAMBER’S WORKING….
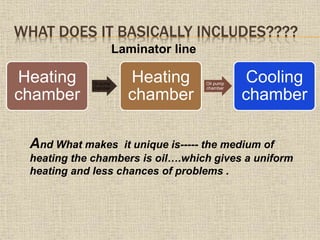
CONTINUED…
Heating chamber 2:
Once the above process is over module moves on
from 1st heating chamber to 2nd.
Here the only difference is that, no pin-up position
is there.
In this chamber, the complete 480 seconds(pin up+
pressing time + sync. time) the upper chamber
presses and the suction takes place in lower
chamber.
After this the module moves into the cooling
chamber.
[note: the pressure is applied by the membrane fixed
to the upper chamber]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentationonmoduleline-copy-150224232743-conversion-gate01/85/Presentation-on-module-line-18-320.jpg)