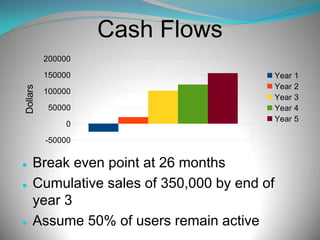
This document outlines a business plan for a mobile app called GymCrowd that tracks gym crowding in real-time. The app founders are Filip Kik, Taron Kephart, Will Schoellkopf, and Brad Shoemaker. GymCrowd will allow users to check gym crowding levels and waitlists for equipment. It will have basic and premium versions available on iOS, Android and Windows platforms. The business aims to target college students and busy areas with a $0.99 basic version and $2.99 premium version including advertisements. Marketing strategies include social media, gym posters, and partnerships. The team plans to obtain initial funding, hire additional staff, and begin app development.