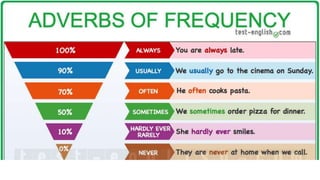
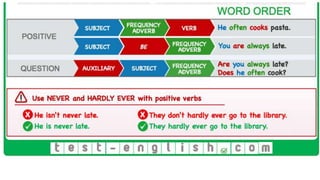
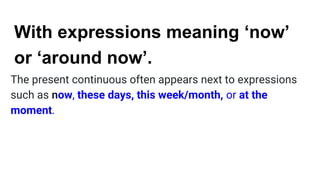
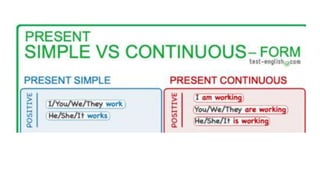
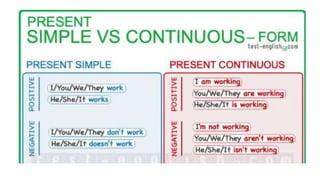
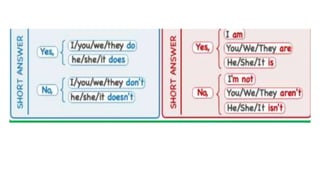
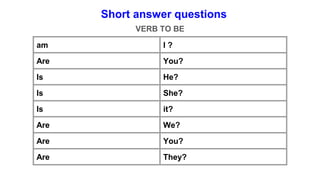
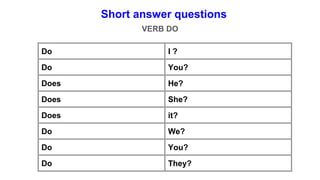
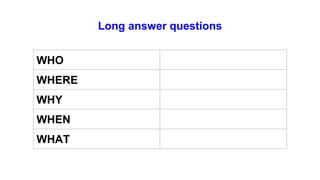
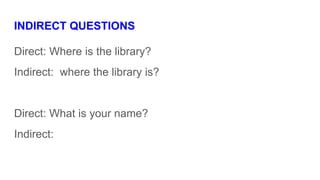
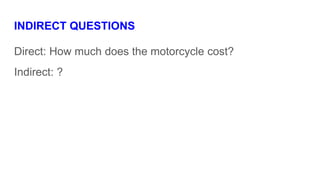
The document provides information about using the present simple and present continuous tenses. It includes examples of when to use each tense, such as using the present simple for habits and schedules, and the present continuous for temporary actions. It also provides practice exercises and links to online resources for further practice with these tenses.