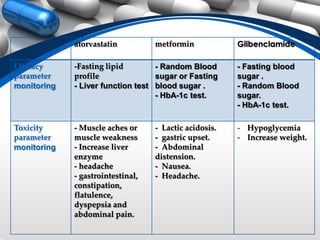
The document presents a case study of a 69-year-old male patient with hypercholesterolemia, diabetes, hypertension, and ischemic heart disease, outlining his medical history, current medications, lab results, and a pharmaceutical care plan to monitor and control his conditions through lifestyle changes, medication management, and treatment goals. Risk factors for his conditions included obesity, family history, smoking, physical inactivity, and age. His diseases were assessed as uncontrolled despite medications due to additional risk factors.