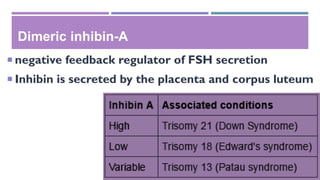
This document discusses prenatal diagnosis techniques including screening tests and diagnostic tests. Screening tests include ultrasonography, maternal serum screening which tests biomarkers, and alpha-fetoprotein. Diagnostic tests include invasive techniques like amniocentesis and chorionic villus sampling, as well as non-invasive techniques using cell-free fetal DNA in the mother's bloodstream which can be used to detect genetic disorders as early as 6 weeks into the pregnancy. Cell-free fetal DNA is isolated from maternal plasma through size fractionation methods and can be used for applications like fetal sex determination and rhesus blood grouping.






![BLOOD TEST
maternal serum human chorionic
gonadotropin [βhCG],
pregnancy-associated plasma
protein [PAPP-A]
Human placental lactogen [HPL]
Rh factor
HIV
HBV
Rubella
Syphlis
Biomarkers and blood test](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/prenataldiagnosistest-180608005221/85/Prenatal-diagnosis-test-7-320.jpg)
![MATERNAL SERUM HUMAN CHORIONIC
GONADOTROPIN [ΒHCG]
Quantitative?? Qualitative??
immunometric assay](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/prenataldiagnosistest-180608005221/85/Prenatal-diagnosis-test-8-320.jpg)