Embed presentation
Download to read offline





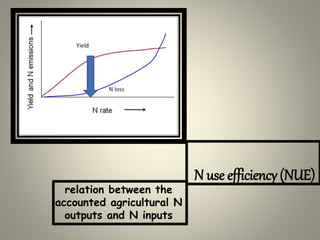



This document discusses the pre-processing of groundwater data from monitoring points over eight years to measure nitrate levels. Specific water samples are selected based on nitrate, iron, and oxygen concentrations to minimize uncertainty and enable nitrate sampling years to be converted to groundwater recharge years. This allows for comparison of long-term changes in nitrogen surplus from agriculture to changes in groundwater nitrate levels. Agricultural nitrogen balances of inputs and outputs are also calculated as an indicator of nitrogen lost to the environment. Nitrate pollution levels in groundwater are then evaluated against economic growth rates to examine an environmental curve.







