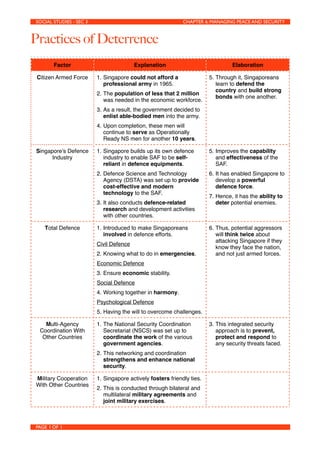
Singapore has developed several practices to manage peace and security with limited resources:
1) It implements a citizen armed force called National Service where able-bodied men serve in the army and afterwards continue to serve as operationally ready reservists for 10 years.
2) It builds up its own defense industry through agencies like DSTA to develop cost-effective technologies and enable the SAF to be self-reliant.
3) It practices the concept of "Total Defence" which involves defending the country through military, civil, economic, social, psychological means and gaining the support of citizens.