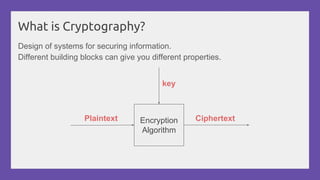
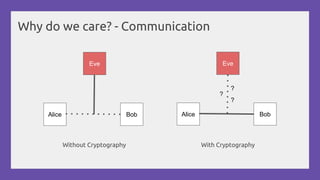
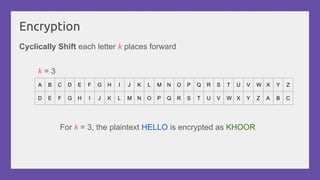
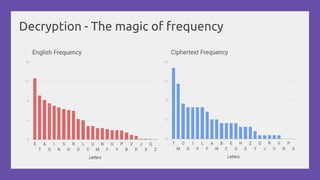
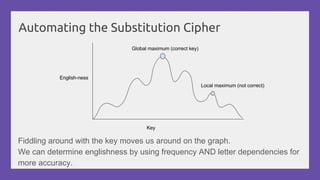
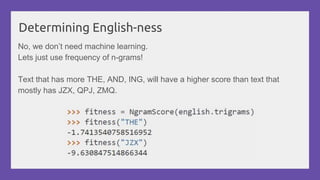
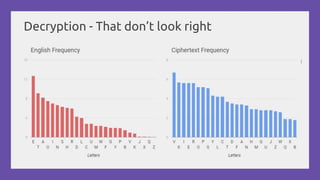
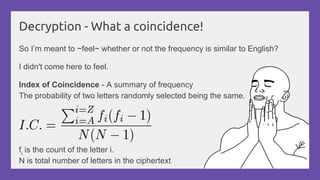
This document provides a practical introduction to cryptanalysis, defining cryptography as the design of systems for securing information and cryptanalysis as recovering plaintext without the key. It discusses various types of cryptanalysis attacks, their utility, and principles such as frequency analysis, brute force, and substitution ciphers, using examples to illustrate these concepts. The document also mentions tools for learning and practicing cryptanalysis, encouraging exploration of additional resources for deeper understanding.