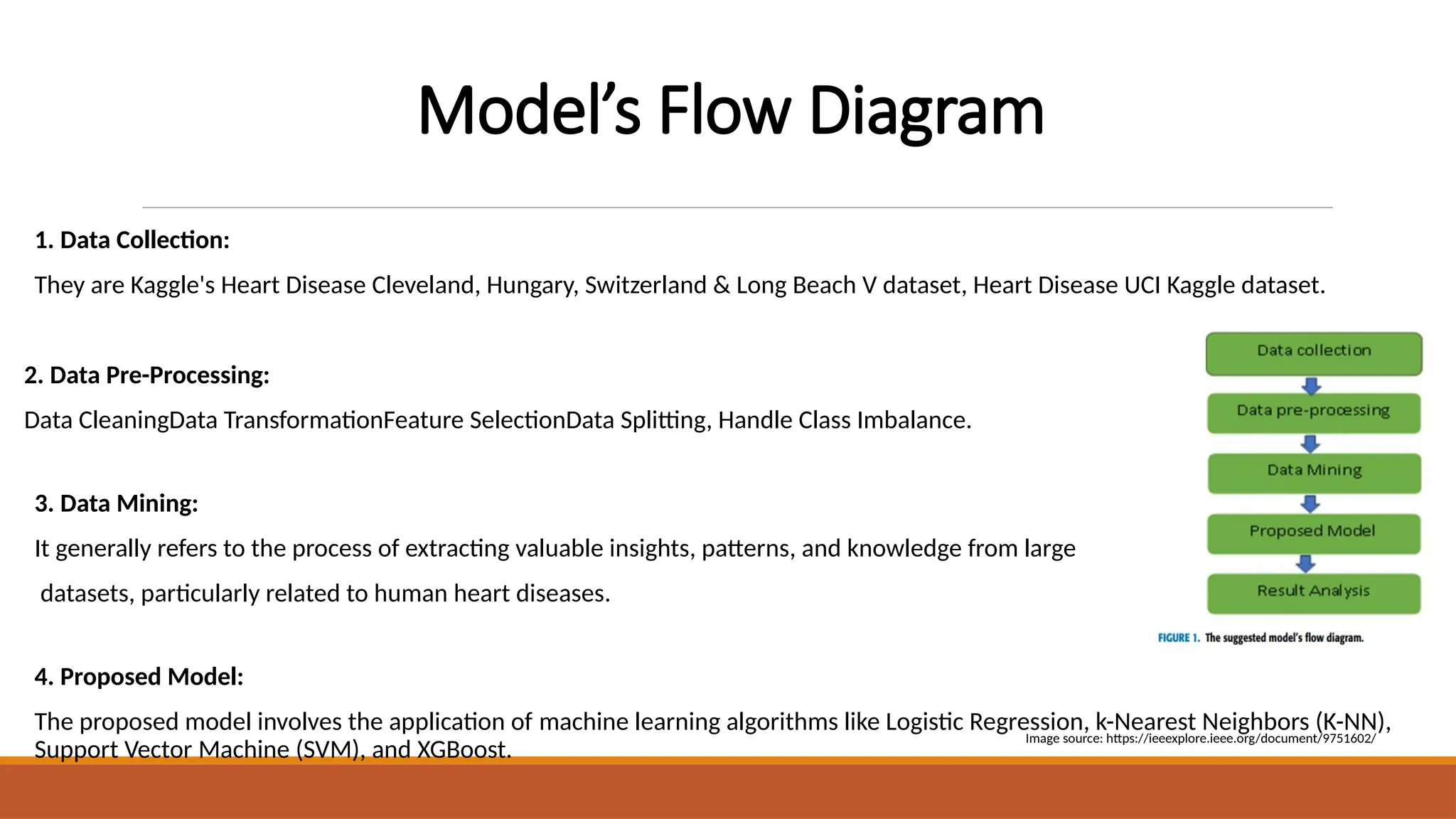
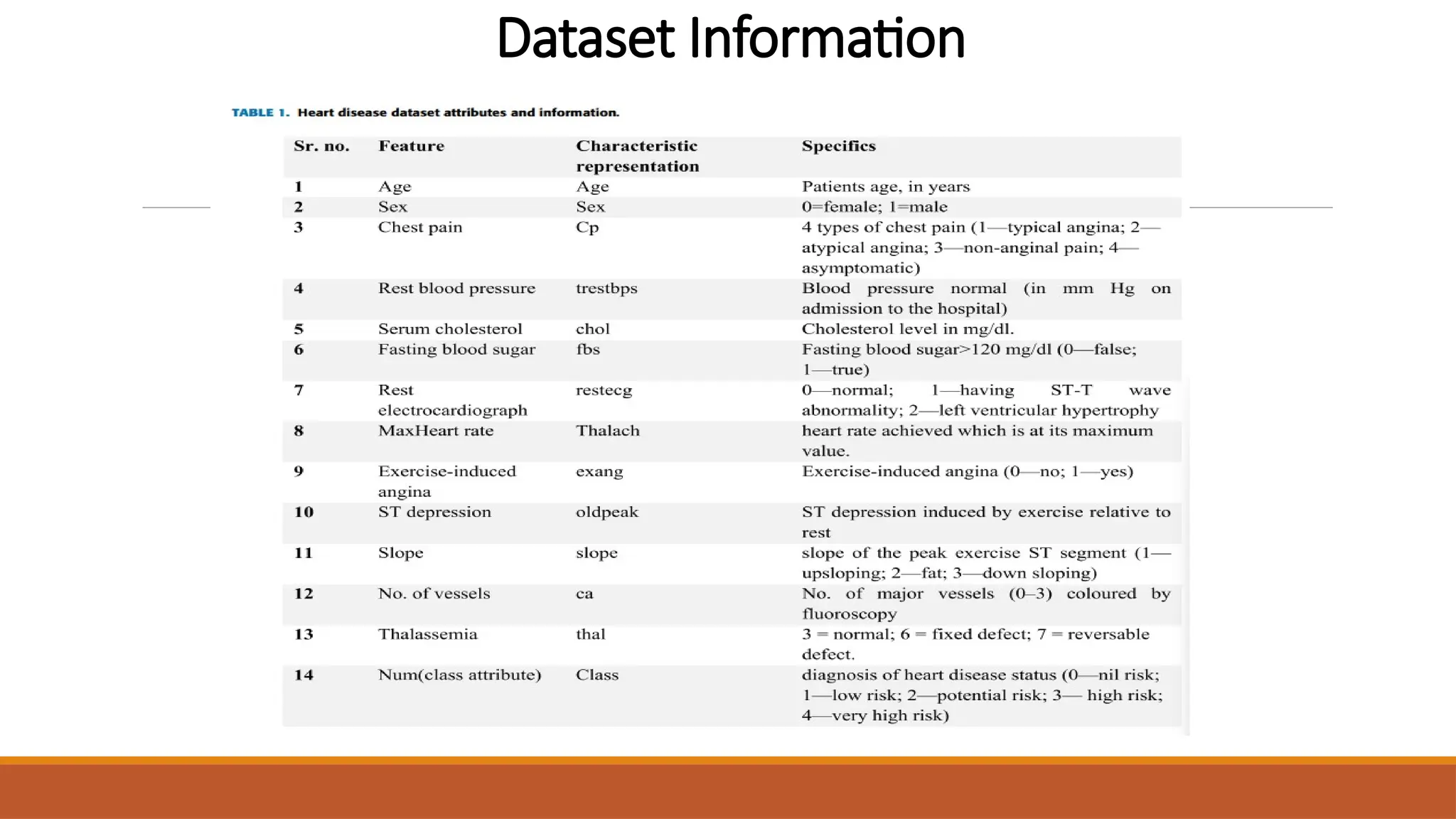
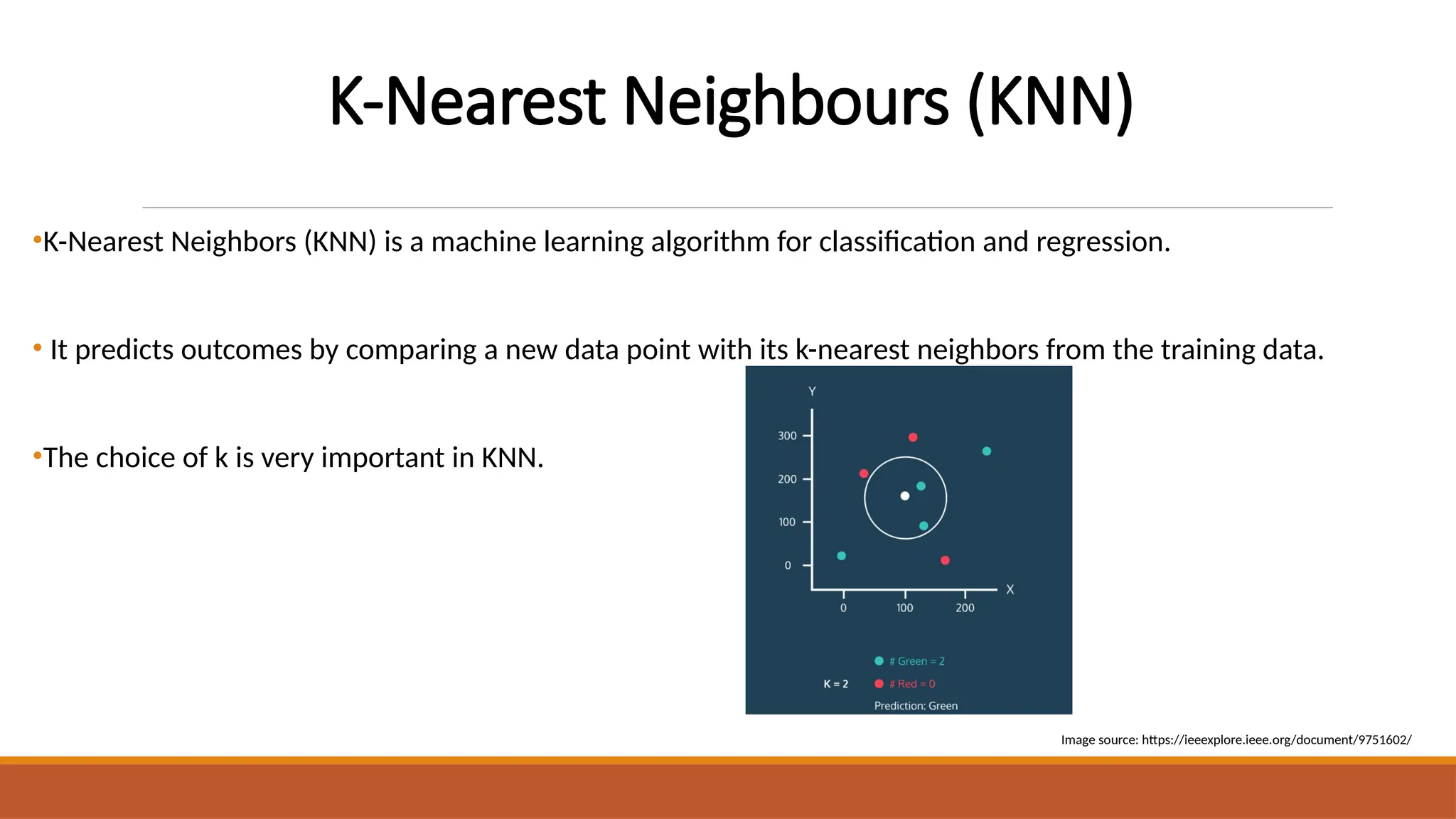
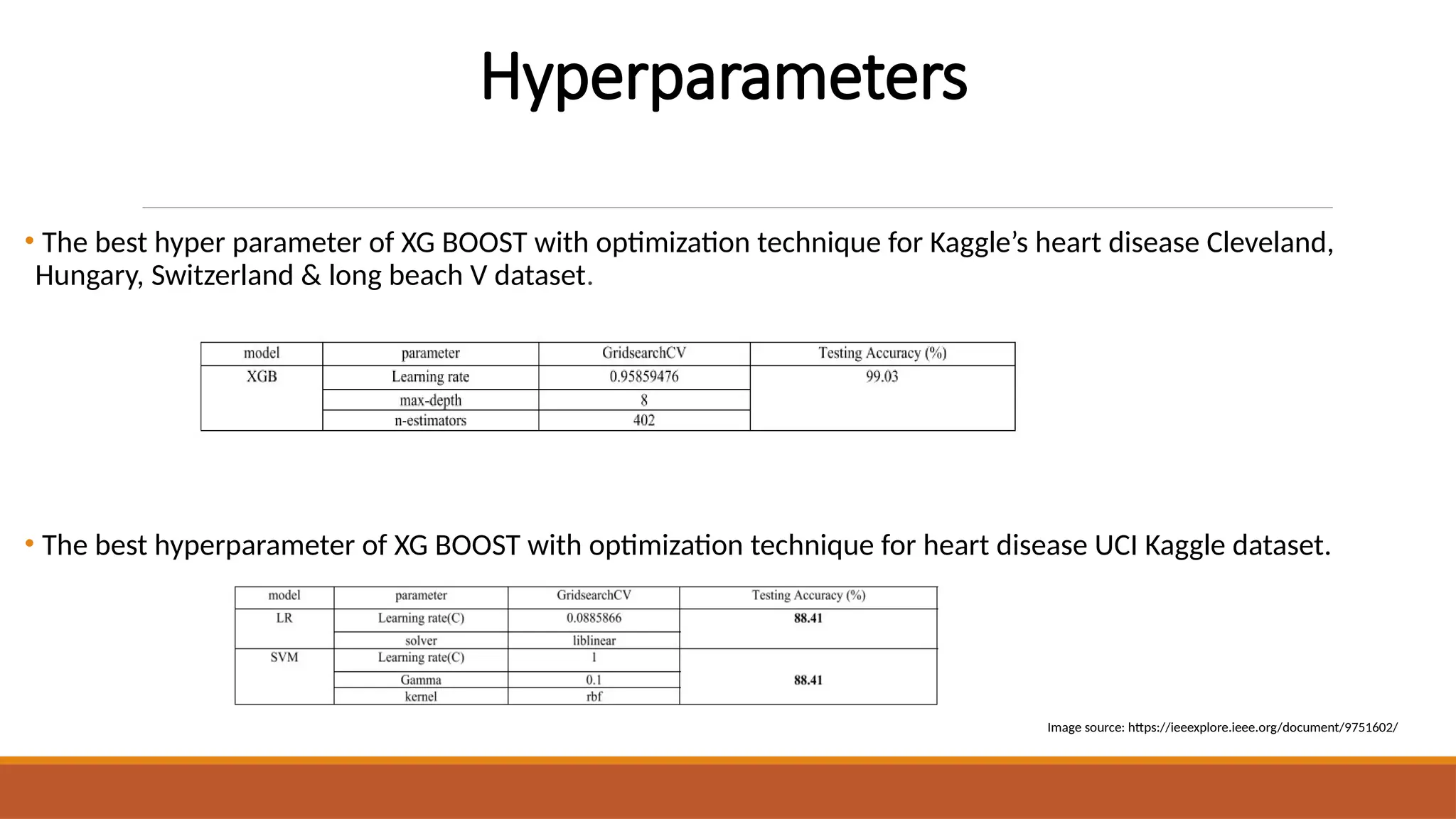
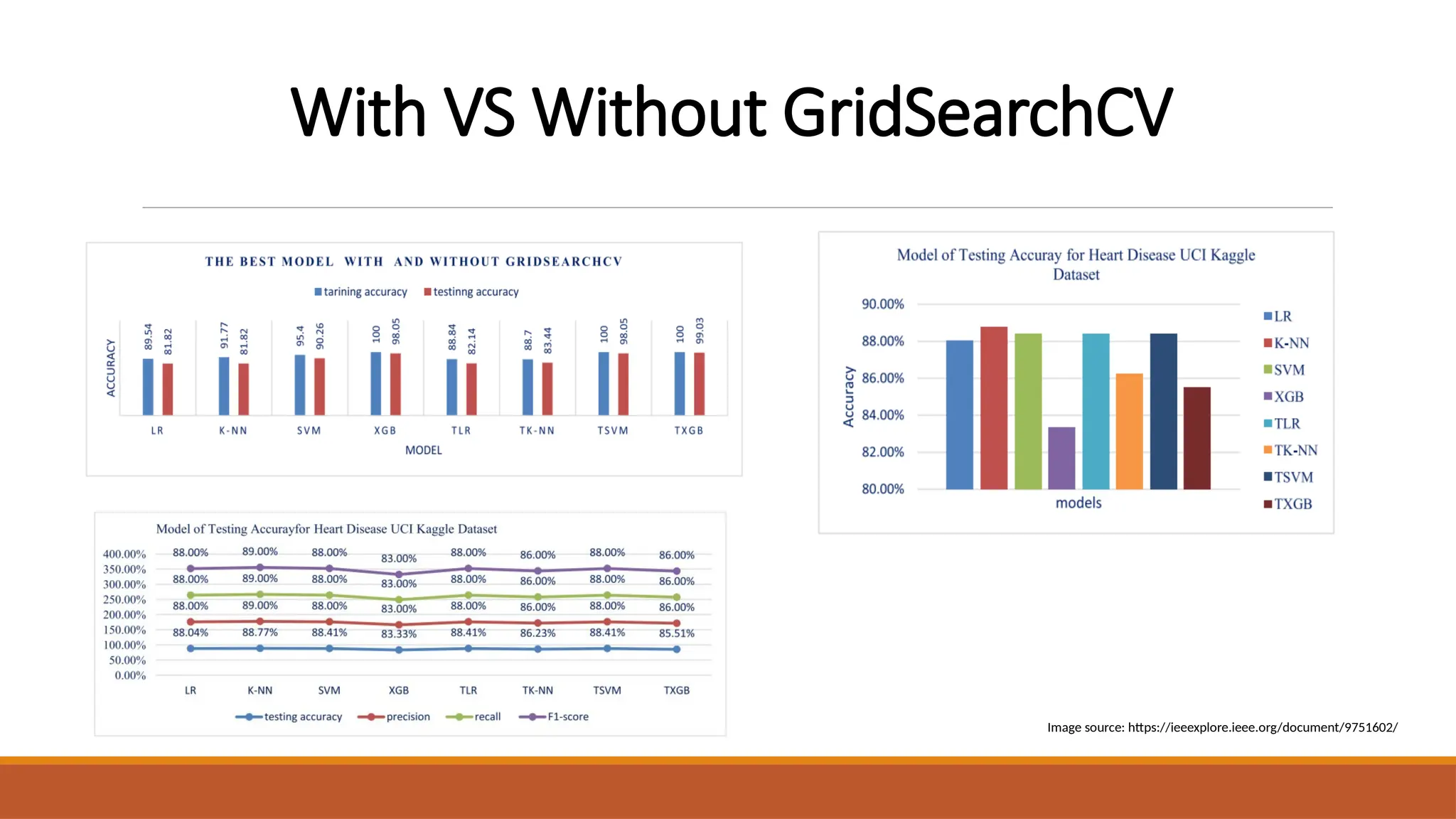
The document discusses the application of machine learning techniques, including logistic regression, k-nearest neighbors, support vector machines, and extreme gradient boosting, to improve the diagnosis of cardiovascular diseases. It emphasizes the importance of early and accurate diagnosis for effective treatment and highlights the role of hyperparameter optimization through GridSearchCV in enhancing model performance. The research utilizes various datasets to enhance diagnostic accuracy and address class imbalances in heart disease prediction.