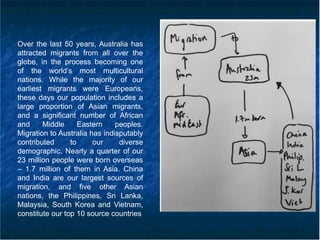
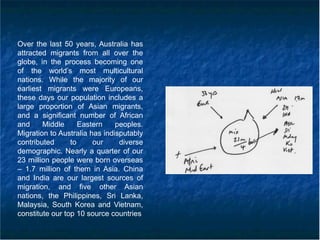
The document discusses effective note-taking skills, emphasizing the importance of summarizing speeches into manageable components for analysis and recall. It highlights techniques such as creating mind maps and using abbreviations to enhance memory and understanding during interpreting tasks. Additionally, it explores the multicultural demographics of Australia, attributing the nation's diversity to significant migration patterns over the last fifty years.

























![Links
//
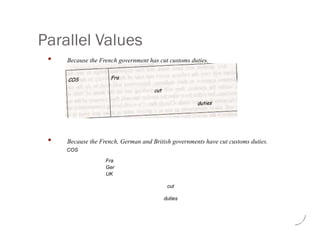
Britain and Germany are among those countries pushing most
for an ambitious new WTO round.
—
So, for both the UK and Germany, the failure of the trade
talks in Cancun was a huge disappointment.
// A successful trade round would be a massive prize.
if If we could halve world tariffs,
then
[then] that would add as much as $400 billion annually to
world incomes, of which at least 150 billion will flow to
developing countries.
// Thafs more than 3 times what they currently get in aid.
BUT But to achieve this we need to reform the CAP.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ppt-241205125350-8ca22603/85/PPT-pptx-interpreting-note-taking-29-320.jpg)













































![■ para = paragraph
■ part = particular; partner
■ pass = passive; passenger
■ PAT = patent
■ payt = payment
■ pc = piece; personal computer
■ pd.= paid (钱款)已付
■ perf = perform; performance
■ Ph.D. = Doctor of Philosophy
■ pk= park; peak (备注:pk
这个符号大家可以根据时髦的用语来灵活拓展其含义 )
■ pkg = package
■ PLS = please
■ p.m. = post meridiem = [w]afternoon
■ POB = post-office box
■ pop = popular; population
■ pr. = pair; preferred
■ prec = preceding](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ppt-241205125350-8ca22603/85/PPT-pptx-interpreting-note-taking-78-320.jpg)








