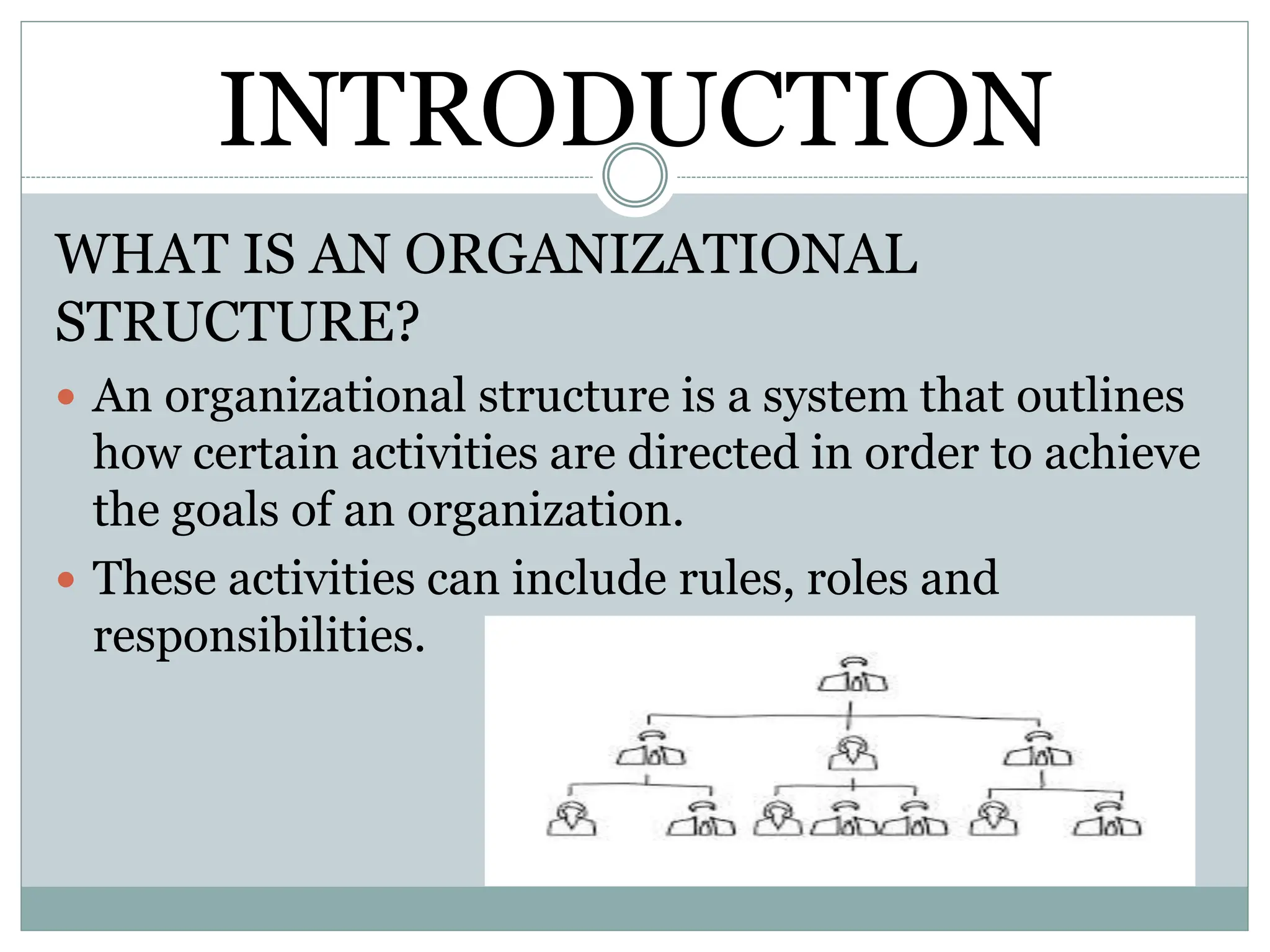
The document discusses organizational structure and the delegation of authority, defining organizational structure as a system that directs activities to achieve goals. It highlights various types of structures (functional, divisional, matrix, and network) and factors influencing them, along with the importance of delegation, barriers to effective delegation, and its principles. Ultimately, it emphasizes how proper structure and delegation foster efficiency, clear communication, and employee development within organizations.