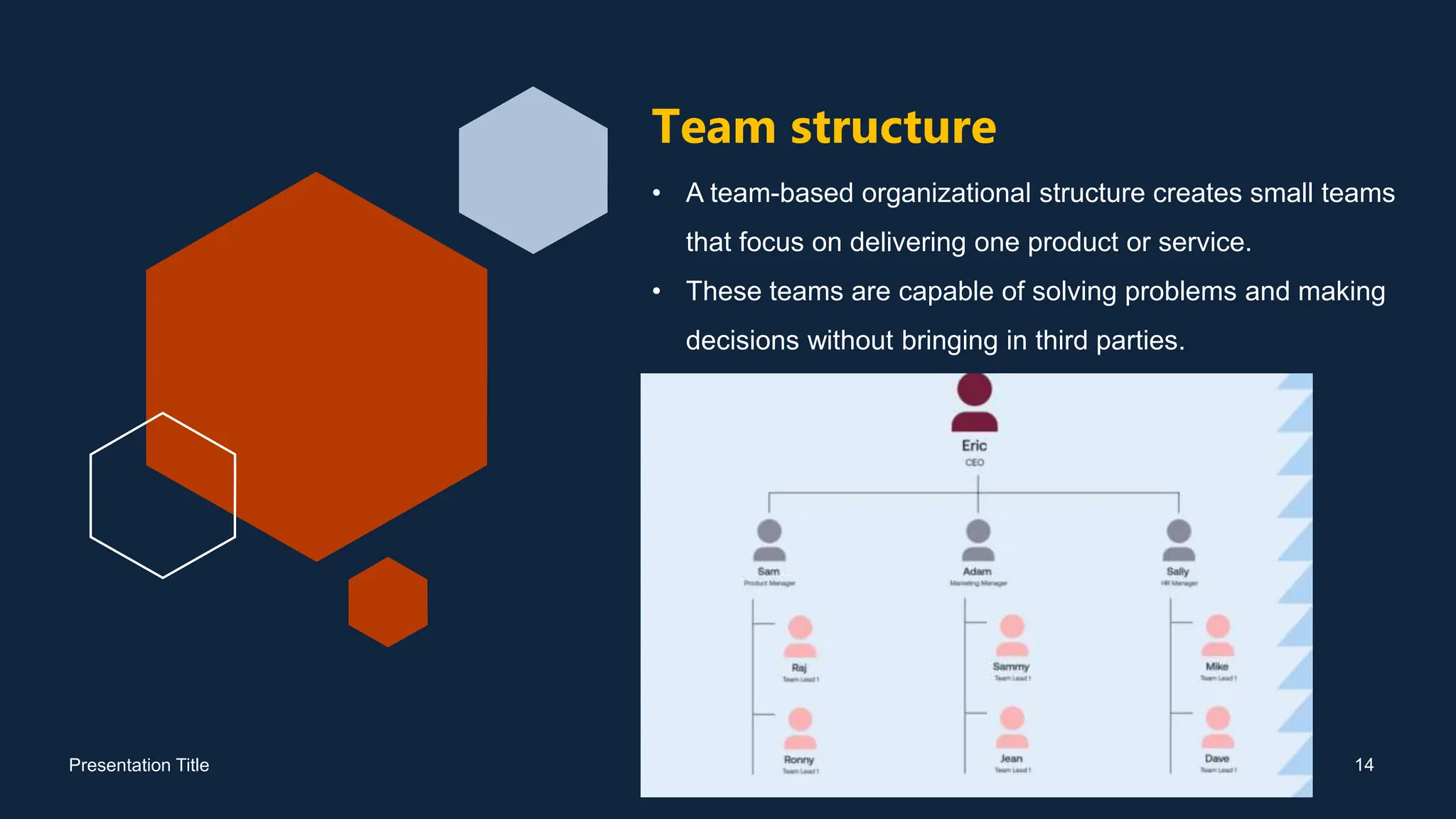
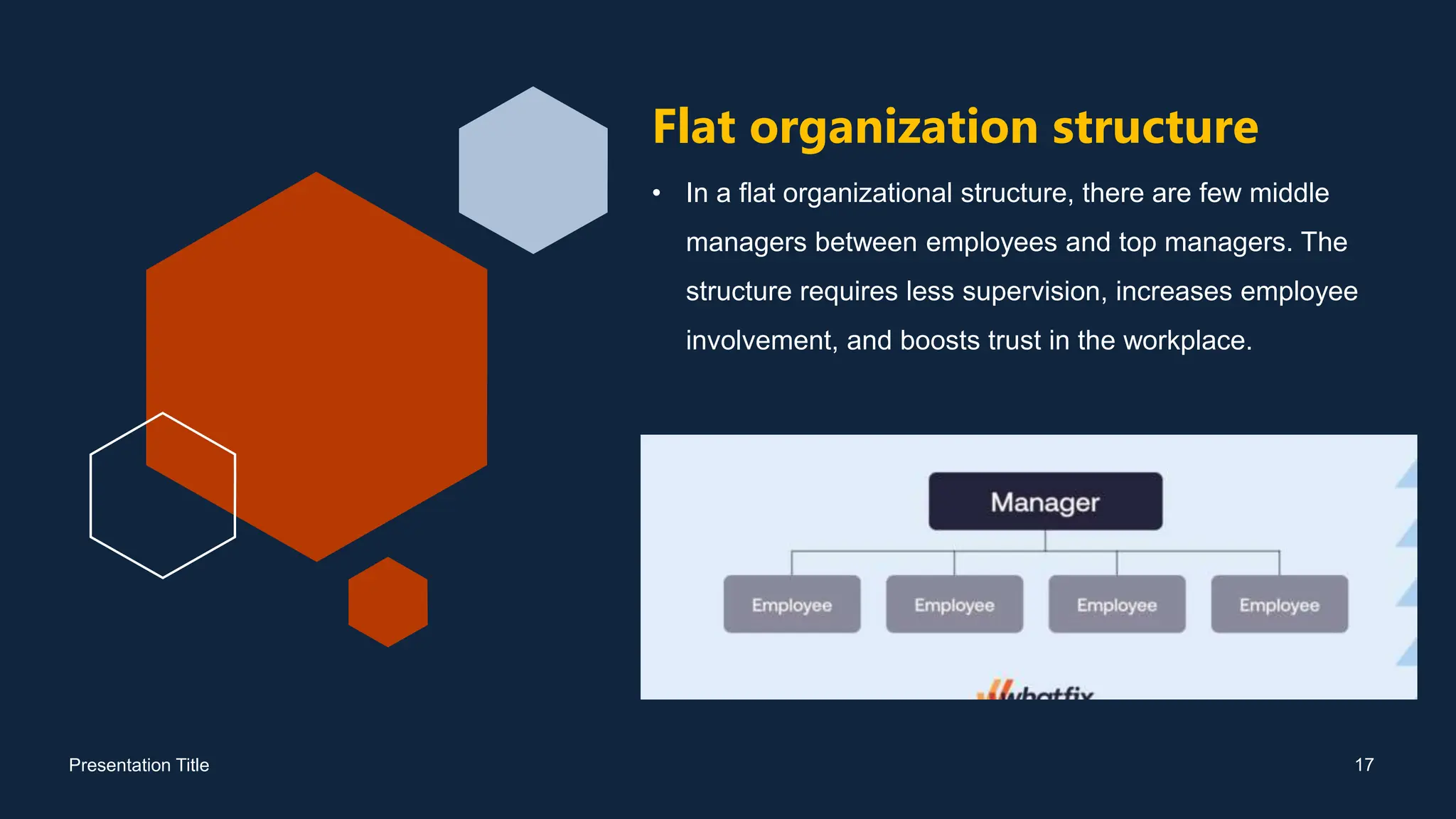
The document discusses the concept of organizational structure, which defines the framework for how activities are organized and supervised within an organization. It outlines key elements including work specialization, departmentalization, chain of command, and various structure types such as functional, divisional, and flat organizations. Additionally, it highlights the objectives, importance, and advantages of having a well-defined organizational structure, as well as the limitations it may encounter.