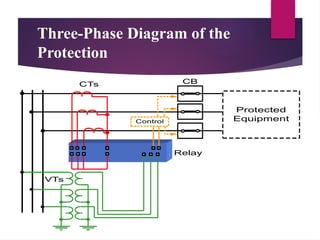
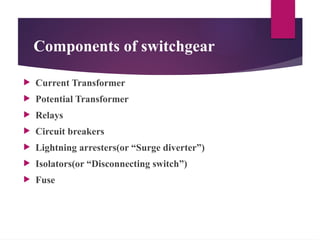
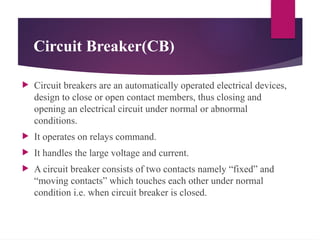
The seminar presentation on substation protection devices outlines the importance of protecting electrical power systems from faults to maintain stability and safety. It details various protection devices such as current transformers, potential transformers, relays, circuit breakers, and lightning arresters, explaining their functions and roles in the protection scheme. The conclusion emphasizes the automation of modern substation protection systems.