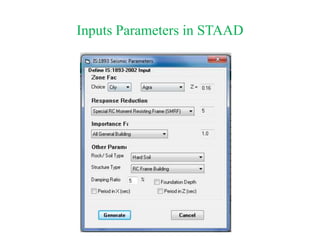
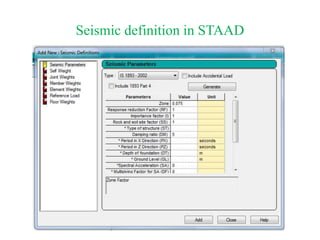
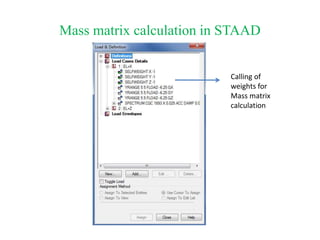
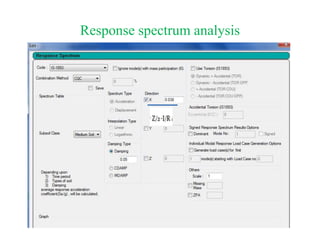
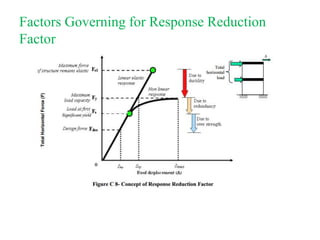
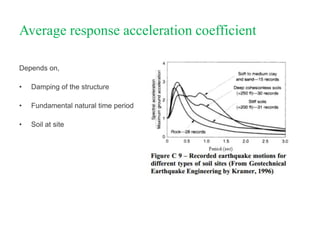
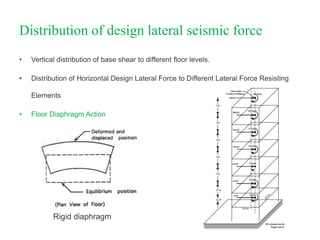
The document outlines the methods for seismic analysis of building structures, including static and dynamic analyses, and detailed calculations for seismic forces influenced by factors such as zone and importance. It discusses the significance of the design basis earthquake, maximum considered earthquake, and factors affecting response reduction and average response acceleration. Additionally, it highlights considerations for structural performance during earthquakes and the distribution of seismic forces across different elements.