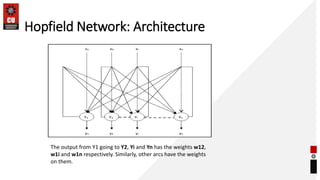
The Hopfield network is a type of recurrent neural network model that is able to store memory as associations between input patterns and target patterns. It consists of neurons with one inverting and one non-inverting output that are fully connected to each other in both directions with symmetrical weights. The network can operate in either synchronous or asynchronous mode. It is a linear model that can only model linearly separable data and its stability and behavior over time can be analyzed by developing a state table listing all possible subsequent states of the network.