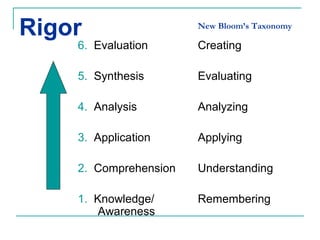
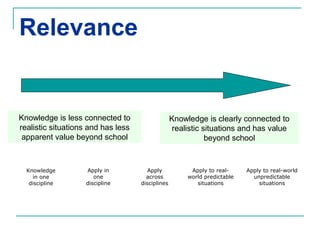
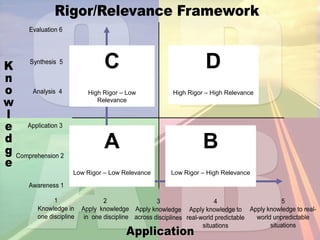
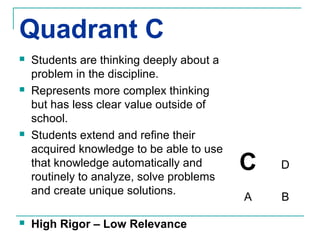
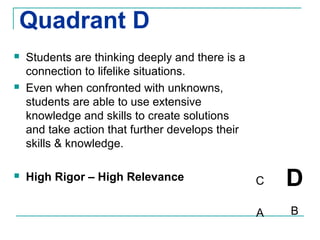
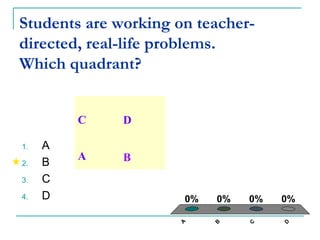
The Rigor/Relevance framework is a model used by many Iowa schools to improve instruction. It focuses on engaging teachers in school-wide efforts and providing a common vocabulary to discuss teaching and learning. Rigor refers to deep, complex thinking using higher order cognitive processes like analysis, synthesis, and evaluation. Relevance refers to knowledge and skills that can be applied beyond the classroom. Tasks are mapped onto a quadrant chart based on their level of rigor and relevance, with the goal of designing lessons that fall in the high rigor/high relevance quadrant D.