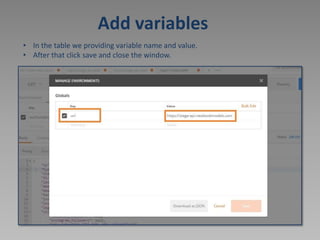
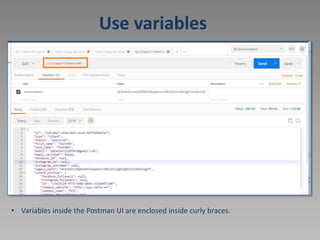
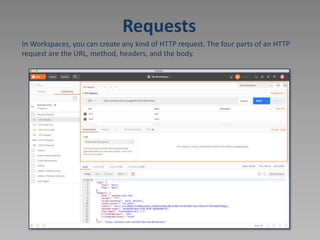
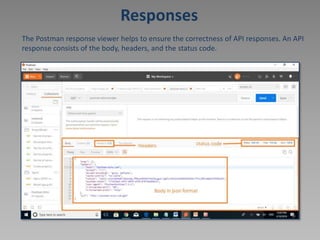
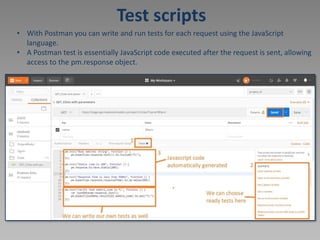
The document discusses using Postman to test REST APIs. Postman is an HTTP client that allows users to create and test HTTP requests. It provides a multi-window interface to work on APIs. Users can create requests, view responses, add variables, write test scripts, and view test results in Postman. The document also provides an example of testing the Newbook API, including GET, POST, PATCH, and other requests.







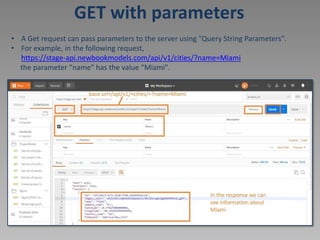
![GET list of cities [GET /cities/]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/14294674-221107012322-59c510c8/85/Postman-ppt-10-320.jpg)
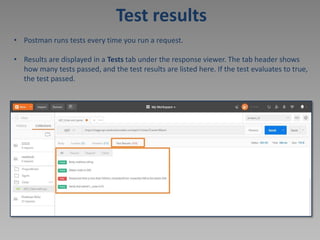
![Signin [POST /auth/signin/]
• The HTTP POST request method is meant to transfer data to a server (and elicit a
response). What data is returned depends on the implementation of the server.
• To send POST request we need:
URL: https://stage-api.newbookmodels.com/api/v1/auth/signin/
Body: example of request body provided in documentation
{
"email": "a@a.aa",
"password": "qwer1234"
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/14294674-221107012322-59c510c8/85/Postman-ppt-14-320.jpg)
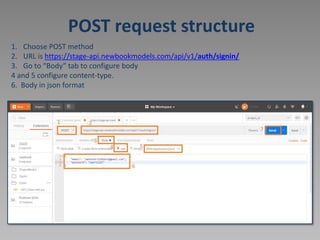
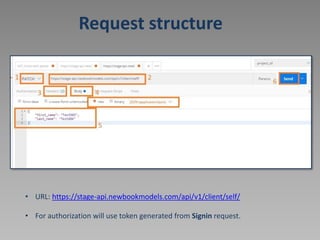
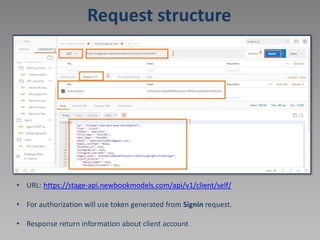
![Get self data [GET /client/self/]
• URL: https://stage-api.newbookmodels.com/api/v1/client/self/
• For authorization will use token generated from Signin request.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/14294674-221107012322-59c510c8/85/Postman-ppt-17-320.jpg)
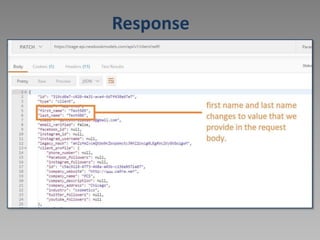
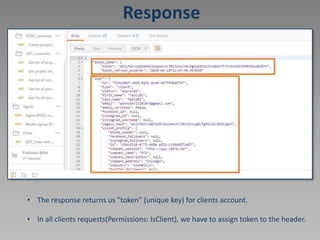
![Update self user data
[PATCH /client/self/]
• URL: https://stage-api.newbookmodels.com/api/v1/client/self/
• For authorization will use token generated from Signin request.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/14294674-221107012322-59c510c8/85/Postman-ppt-19-320.jpg)