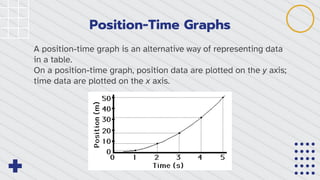
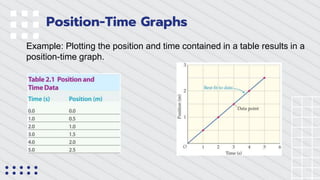
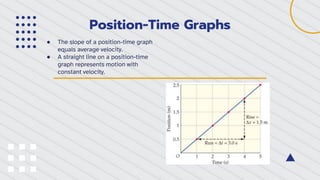
Position-time graphs plot an object's position on the y-axis against time on the x-axis, providing an alternative way to represent position and time data compared to a table. Key features of position-time graphs include using the slope of a best-fit line to learn about an object's motion, where the slope equals average velocity for constant velocity motion. The slope can be used to determine position, velocity, and whether velocity is positive, negative, or zero at any point along the graph.