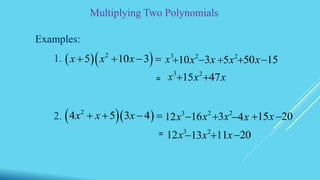
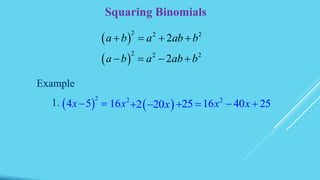
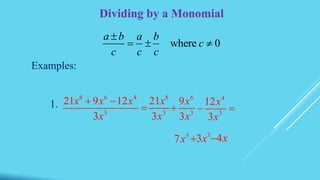
This document defines key terms related to polynomials including monomial, binomial, trinomial, constant, coefficient, and degree. It also describes methods for multiplying polynomials including multiplying monomials, multiplying polynomials using FOIL, squaring binomials, and multiplying the sum and difference of binomials. Finally, it provides examples of dividing monomials.