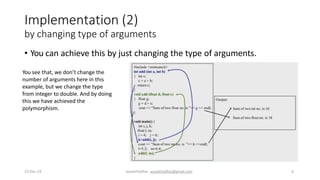
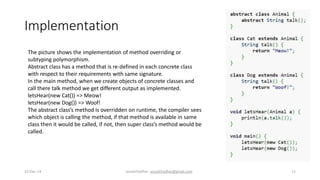
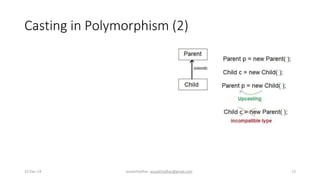
This document discusses different types of polymorphism including ad-hoc polymorphism, parametric polymorphism, and subtyping polymorphism. It defines each type and provides examples of their implementation in code. Ad-hoc polymorphism includes function overloading and operator overloading which can be achieved by changing argument types, number of arguments, or argument order. Parametric polymorphism allows functions and data types to work with different types through generics. Subtyping polymorphism involves method overriding where a subclass redefines a parent class method.