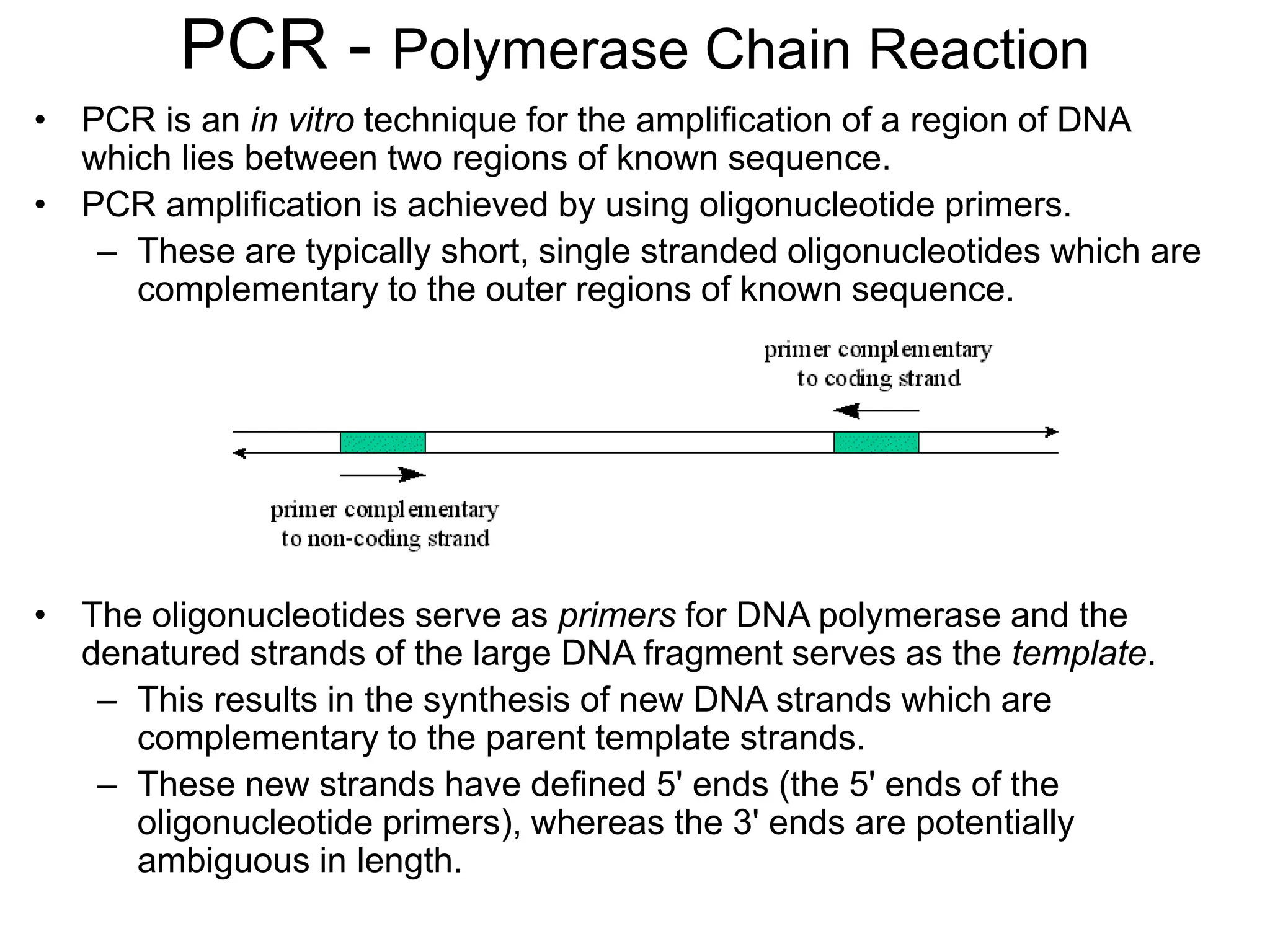
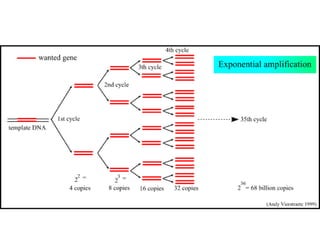
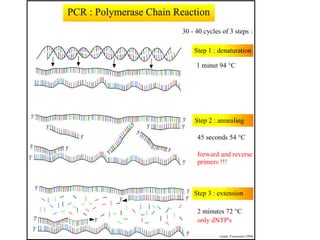
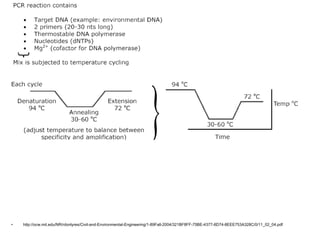
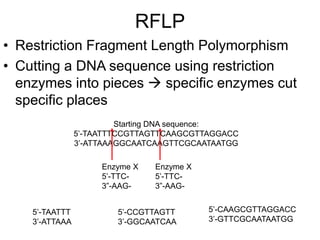
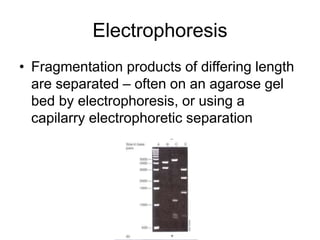
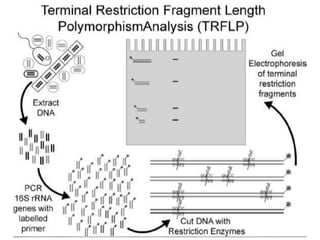
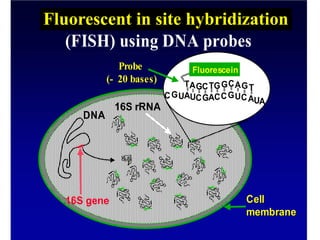
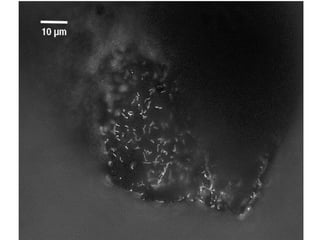
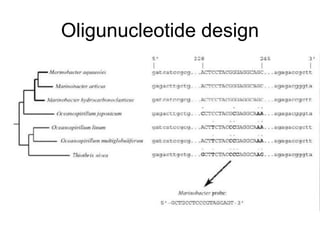
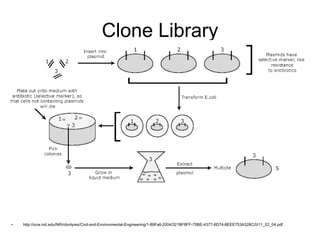
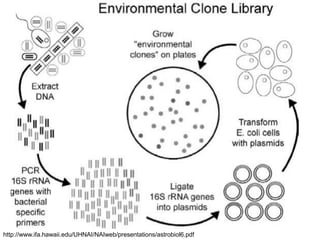
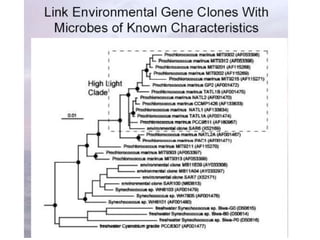
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) is a technique that amplifies specific DNA sequences using oligonucleotide primers and DNA polymerase, crucial for laboratory DNA analysis. It is often paired with methods like Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism (RFLP) and Denaturing Gradient Gel Electrophoresis (DGGE) for DNA separation and characterization. Fluorescent in-situ hybridization (FISH) is another method to image specific organisms in samples using tagged oligonucleotide probes.