PolyMath is a numeric framework for Pharo written entirely in Pharo. It provides functionality for ordinary differential equations, linear algebra, matrices, random number generation, and more. Recent updates include the release of version 1.0, adding PCA and t-SNE dimensionality reduction methods, and improvements to code quality. PolyMath is open source under the MIT license and contributors are working to expand its capabilities in scientific domains.

















![:= [ :x| x sin ].
:= 1/2.
iffForward := [:h| (((f value: (x+h)) - (f value: x)) / h)].
rror := [:h| ((diffForward value: h) - x cos) abs].
rror value: 0.1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/3-polymath1-191104144754/85/Polymath-Version-1-0-and-Beyond-18-320.jpg)
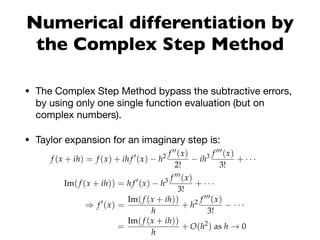
![f := [ :x| (x*x) sin ].
pi := Float pi.
x := pi /2.
h := 0.001.
((f value: (h*1i +x )) imaginary) / h.
pi * ((pi*pi/4) cos)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/3-polymath1-191104144754/85/Polymath-Version-1-0-and-Beyond-20-320.jpg)













