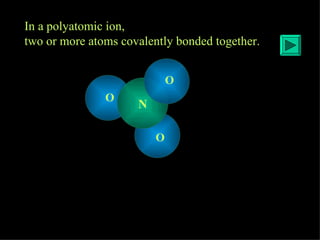
Polyatomic ions are groups of atoms that are covalently bonded together and carry an overall electric charge. They behave as a single unit of charge when balancing equations for ionic compounds. Common examples include the nitrate ion (NO3-), which has one more electron than protons overall. Polyatomic ions are different from monatomic ions which involve a single atom with an electric charge due to having more or fewer electrons than protons.