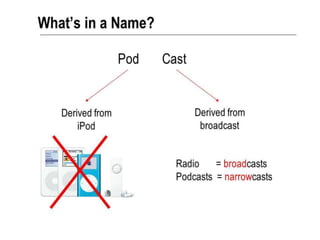
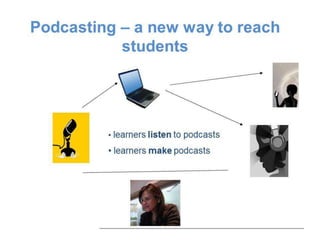
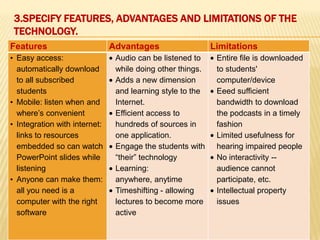
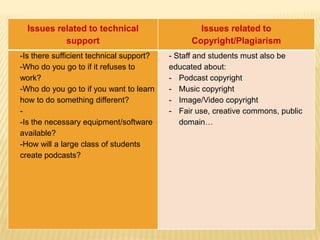
This document discusses podcasting and its use in distance education. It begins by defining podcasting as the publishing of audio files, typically MP3s, on the internet for download to portable devices. It notes podcasting can supplement lecture materials and accommodate different learning styles. The document outlines features like automatic downloading and mobile access. It explores how podcasting supports learning by making education student-centered and drawing students to the technology. It also discusses concerns for students and teachers regarding access, learning objectives, and copyright issues. Examples of universities using podcasting are provided.