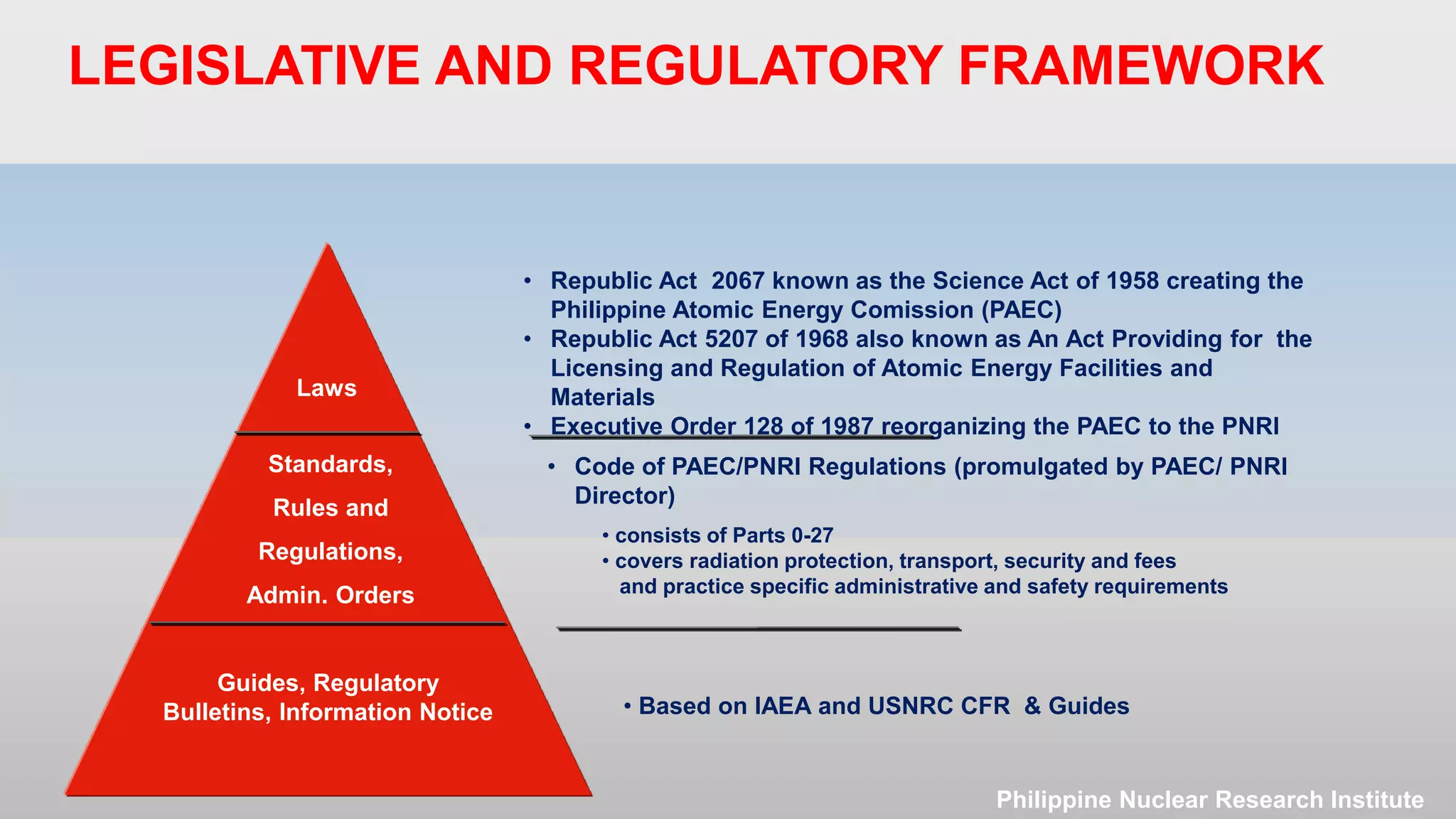
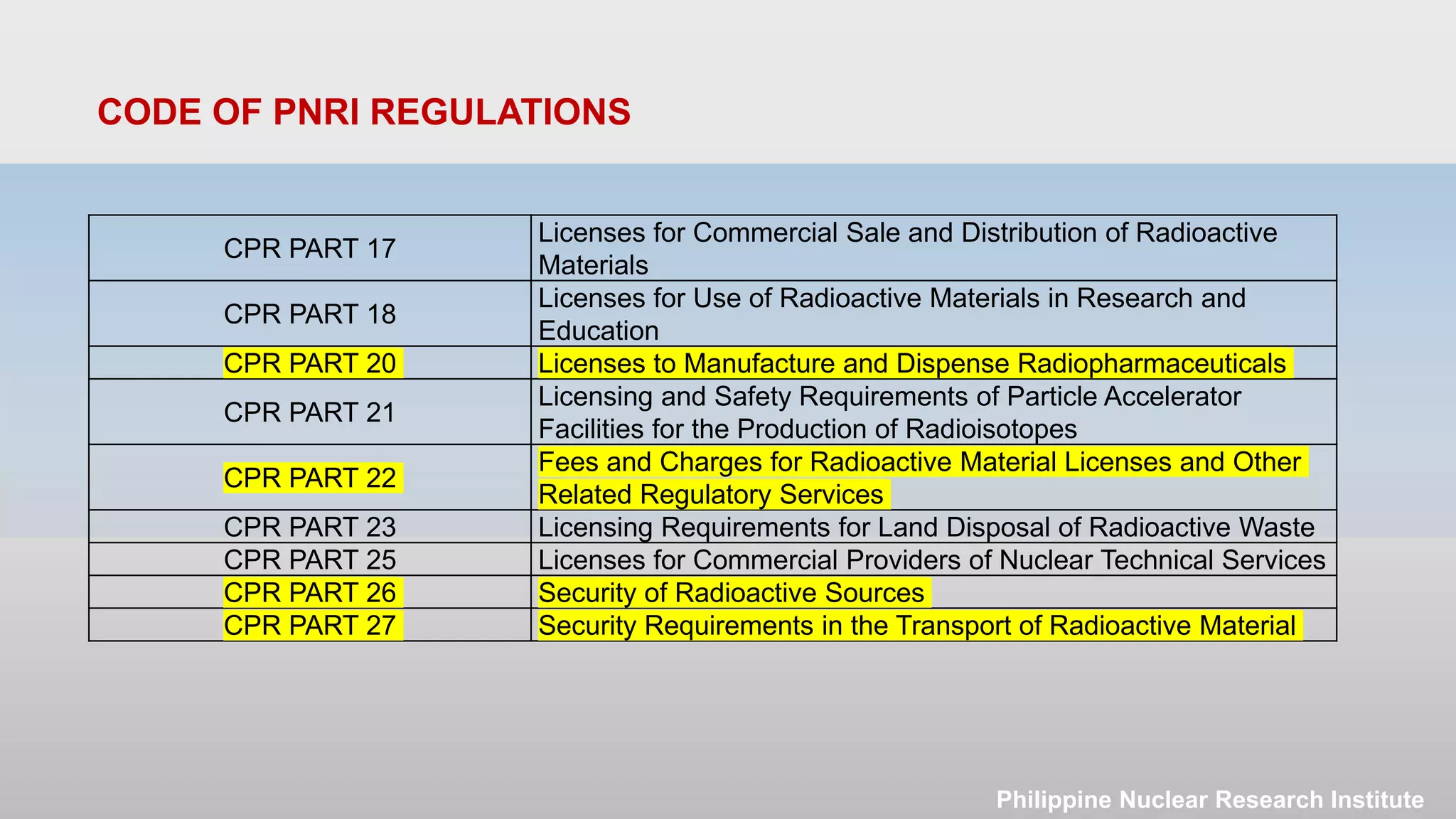
The document outlines the legislative and regulatory framework for licensing radioactive materials in the Philippines. It describes the laws and regulations governing the Philippine Nuclear Research Institute (PNRI) and its mandate to license radioactive material. The document reviews the Code of PNRI Regulations, which consists of 27 parts establishing the regulatory requirements. It discusses the basic licensing process and requirements for obtaining, renewing, amending, and terminating a radioactive materials license in the Philippines.