This document outlines key points about modern project management:
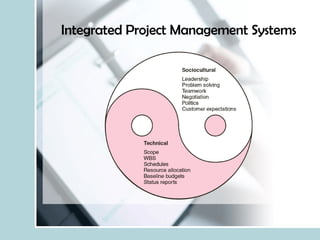
- It describes the importance of project management in society and organizations, and in executing strategy.
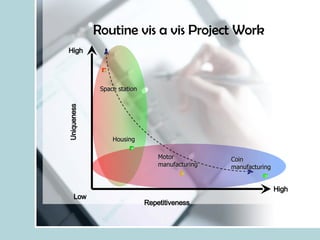
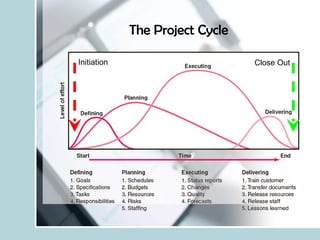
- It explains that projects are multi-disciplinary, non-routine efforts with defined time/budget constraints to meet customer needs.
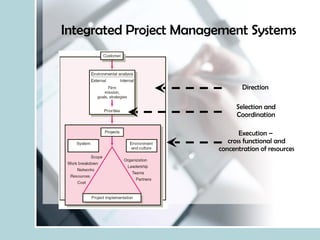
- It discusses what differentiates projects from routine work, and how programs relate to multiple coordinated projects targeting a common goal.
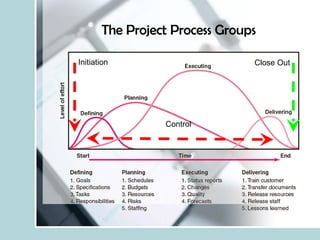
- It describes the role of a project manager in leading temporary and independent project teams to success.