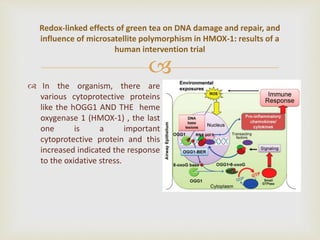
The document discusses DNA repair mechanisms in human lymphocytes. It describes how oxidized purines in DNA are repaired through the base excision repair pathway involving the OGG1 glycosylase. This repair requires activation by the transcription factor NF-YA, which upregulates OGG1 expression when DNA is at risk of oxidation. The repair of oxidized bases by OGG1 in human lymphocytes is slow but can be activated by phytohemagglutinin. Disruption of this global repair of oxidized purines may be due to downregulation of OGG1. A second document discusses how green tea acts as an antioxidant to protect against oxidative stress and influence DNA damage and repair through activation of the Nrf2 transcription factor and upreg