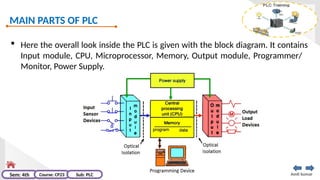
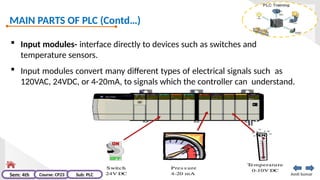
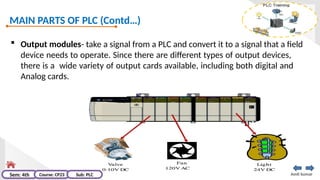
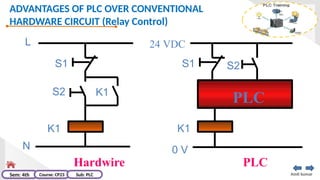
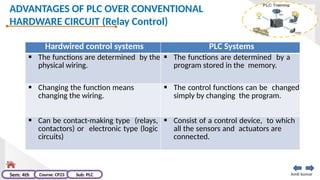
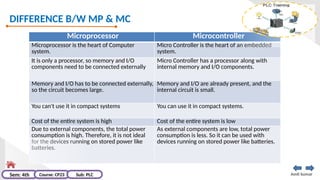
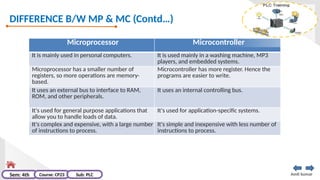
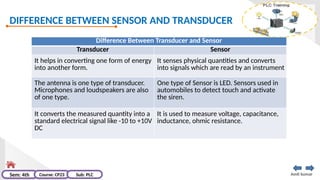
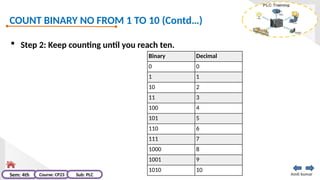
The document provides an extensive overview of programmable logic controllers (PLCs), detailing their definition, main components, advantages over relay-based systems, and programming languages. It also covers the differences between microprocessors and microcontrollers, sensor and transducer distinctions, and guidelines for designing PLC programs. Additionally, it addresses PLC troubleshooting methods and selection criteria for different applications.