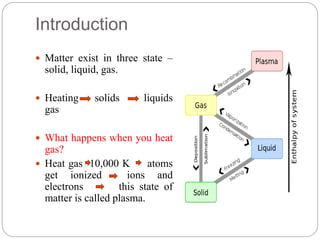
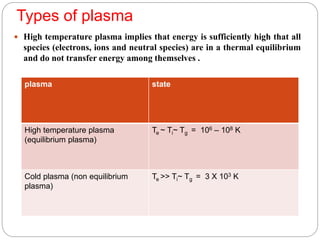
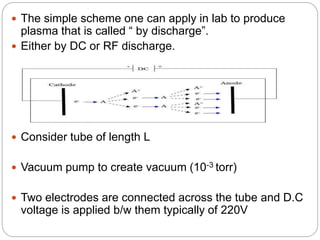
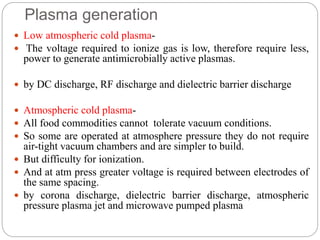
Plasma is the fourth state of matter created when a gas is heated to high temperatures, ionizing its atoms. Cold plasma is generated at near room temperatures and does not cause thermal damage to foods. It inactivates microbes through chemical reactions with cell membranes from reactive species, UV damage to DNA and membranes, and breaks DNA strands. Applications include surface decontamination of meats, produce, and packaging. It improves properties of cereals and dairy. Limitations include potential oxidation and effects on color and firmness of some foods.