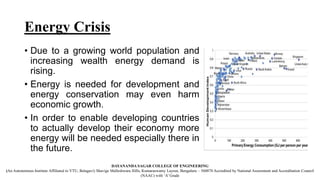
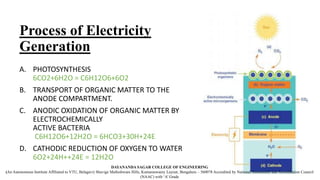
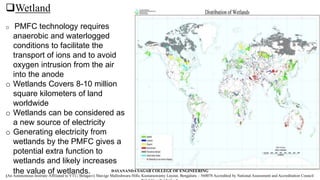
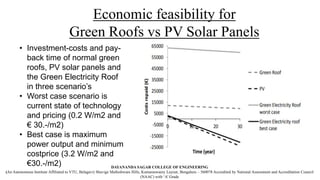
The document discusses the innovative Plant-Microbial Fuel Cell (P-MFC) technology developed at Wageningen University, which generates electricity by utilizing naturally occurring processes in plants and their root-associated microorganisms. It highlights the growing global energy demand and the potential of P-MFC as a sustainable alternative to fossil fuels and conventional solar energy systems, emphasizing its environmental benefits and applicability in various contexts such as wetlands and green roofs. Although still in development, P-MFC technology promises renewable energy production with low environmental impacts and cost efficiency.