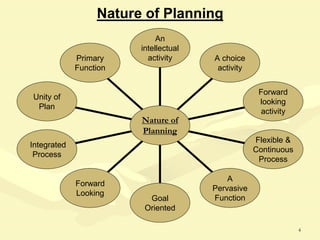
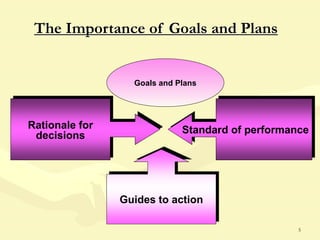
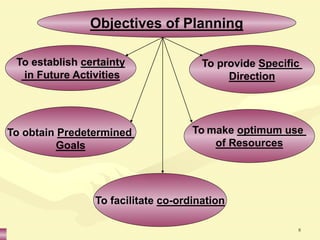
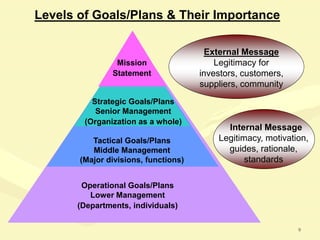
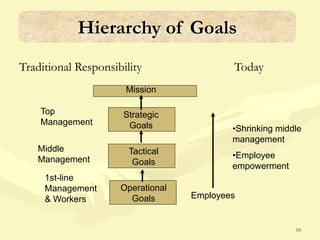
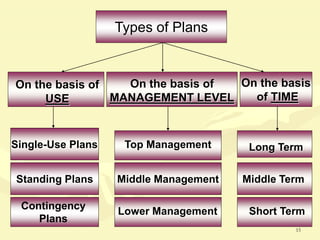
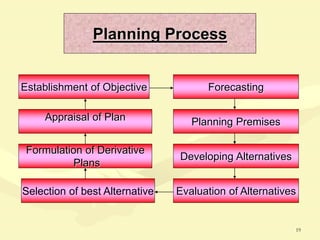
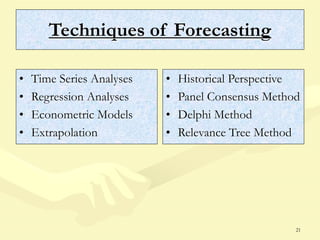
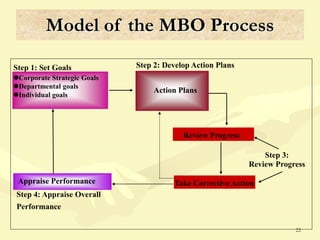
This document discusses various aspects of planning, including definitions of planning, the importance and benefits of goals and plans, different types of plans, and planning techniques and processes. Specifically, it defines planning as determining an organization's goals and means to achieve them. It also outlines the benefits of goals and plans such as providing rationale for decisions, guiding action, and establishing performance standards. The document discusses strategic, tactical, and operational goals and plans at different management levels.