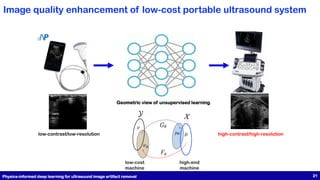
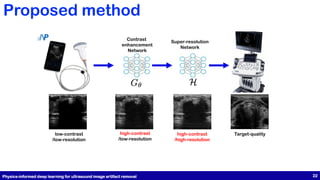
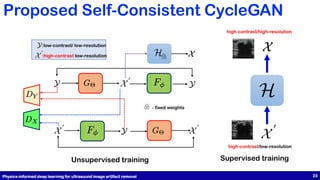
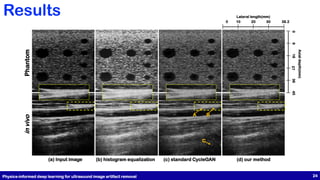
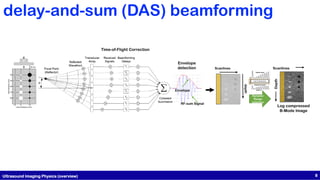
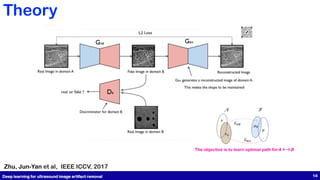
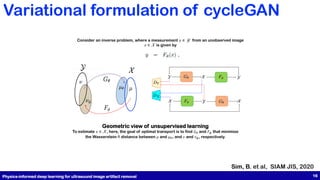
This document presents a study on physics-informed deep learning techniques for improving b-mode ultrasound imaging, focusing on artifact removal using various deep learning methodologies. It details the implementation of deep learning models like U-Net and CycleGAN for image quality enhancement and proposes a novel approach based on optimal transport theory. The findings suggest effective applications of these techniques for enhancing the performance of low-cost ultrasound systems.







![Image domain (deconvolution-filter)
Input
(DAS)
Label
(DeepBF
[1])
U-NET model is trained to mimic DeepBF (Deconvolution) results using image data.
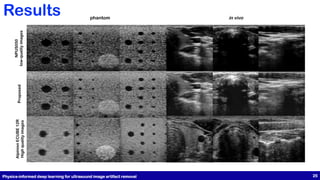
Results (in-vivo) Results (phantom)
Input Label Output Input Label Output
Deep learning for ultrasound image artifact removal 11
[1] Khan et al, IEEE TUFFC, 2021](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/physics-informeddeeplearningforefficientb-modeultrasoundimaging-220228150324/85/Physics-informed-deep-learning-for-efficient-b-mode-ultrasound-imaging-11-320.jpg)
![Image domain (speckle de-noising filter)
Input
(DAS)
Noise-Free
Label
[1]
U-NET model is trained to mimic noise-free results of [1] Zhu, Lei, et al, IEEE CVPR 2017
Input Label Output Label-Input Output-Input
Deep learning for ultrasound image artifact removal 12](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/physics-informeddeeplearningforefficientb-modeultrasoundimaging-220228150324/85/Physics-informed-deep-learning-for-efficient-b-mode-ultrasound-imaging-12-320.jpg)


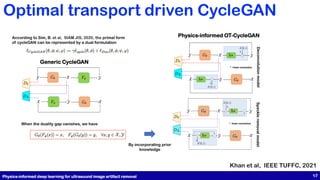

![Physics-informed deep learning for ultrasound image artifact removal 19
Deconvolution
Improved resolution (FWHM)
Physics-informed OT-CycleGAN for
deconvolution
𝑦𝑦 = ℎ ∗ 𝑥𝑥 +N
Deconvolution model
Point spread function
(PSF)
Tissue reflectivity
function (TRF)
RF-Image
[1] Khan et al, IEEE TUFFC, 2021
[1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/physics-informeddeeplearningforefficientb-modeultrasoundimaging-220228150324/85/Physics-informed-deep-learning-for-efficient-b-mode-ultrasound-imaging-19-320.jpg)
![Physics-informed deep learning for ultrasound image artifact removal 20
Speckle denoising
Physics-informed OT-CycleGAN
Multiplicative noise model for
speckle denoising
[1] Zhu, Lei, et al, IEEE CVPR 2017
[1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/physics-informeddeeplearningforefficientb-modeultrasoundimaging-220228150324/85/Physics-informed-deep-learning-for-efficient-b-mode-ultrasound-imaging-20-320.jpg)