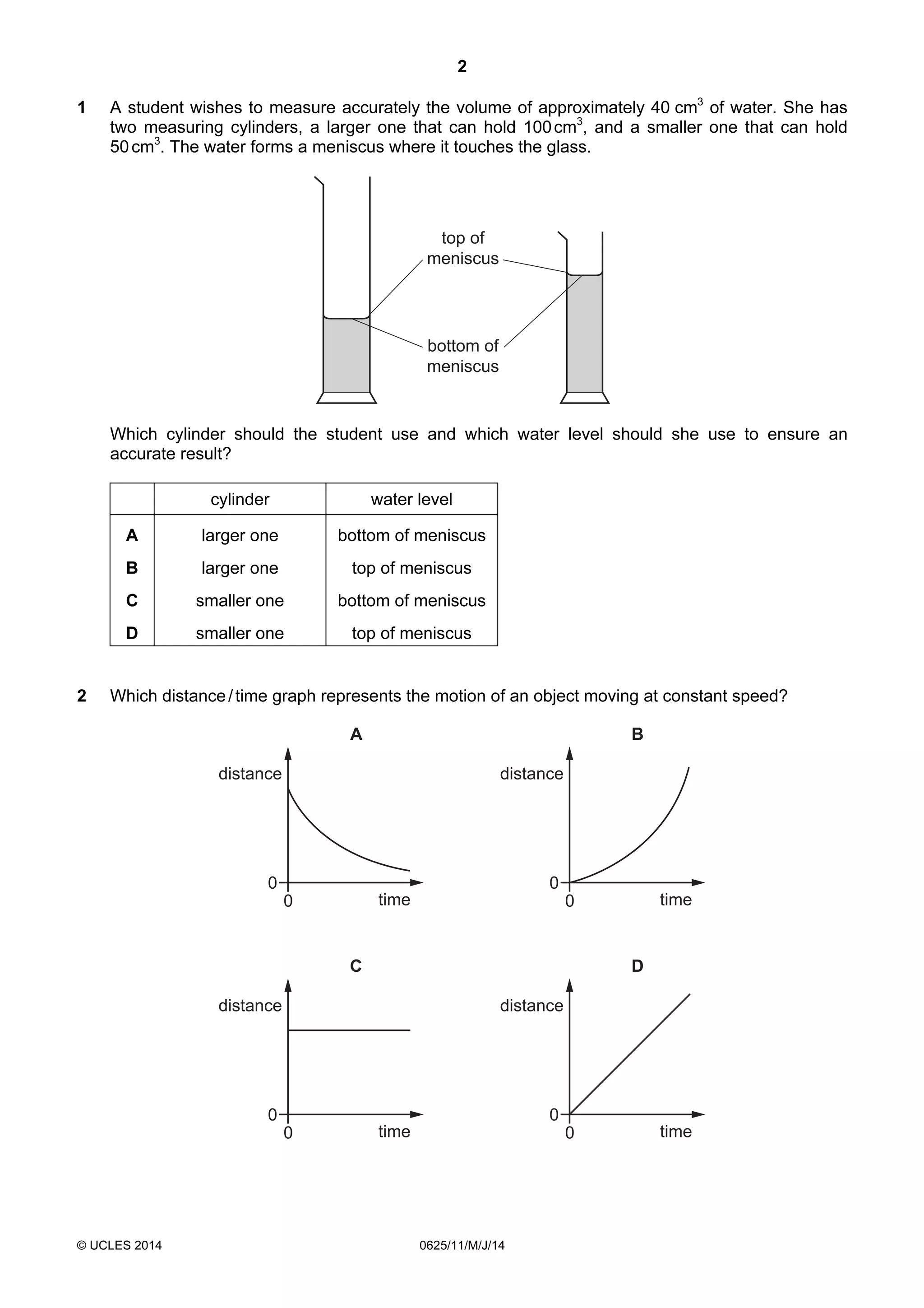
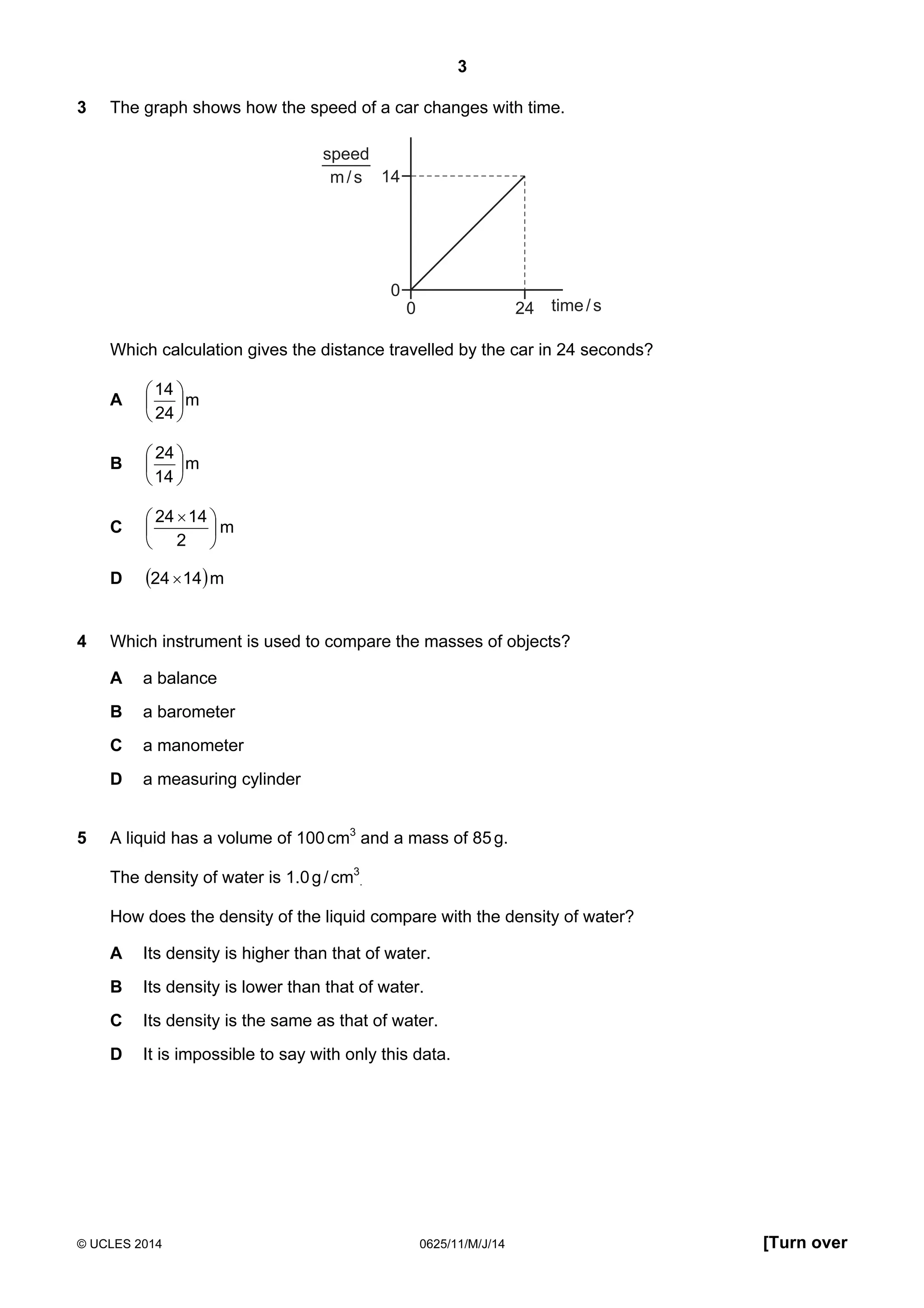
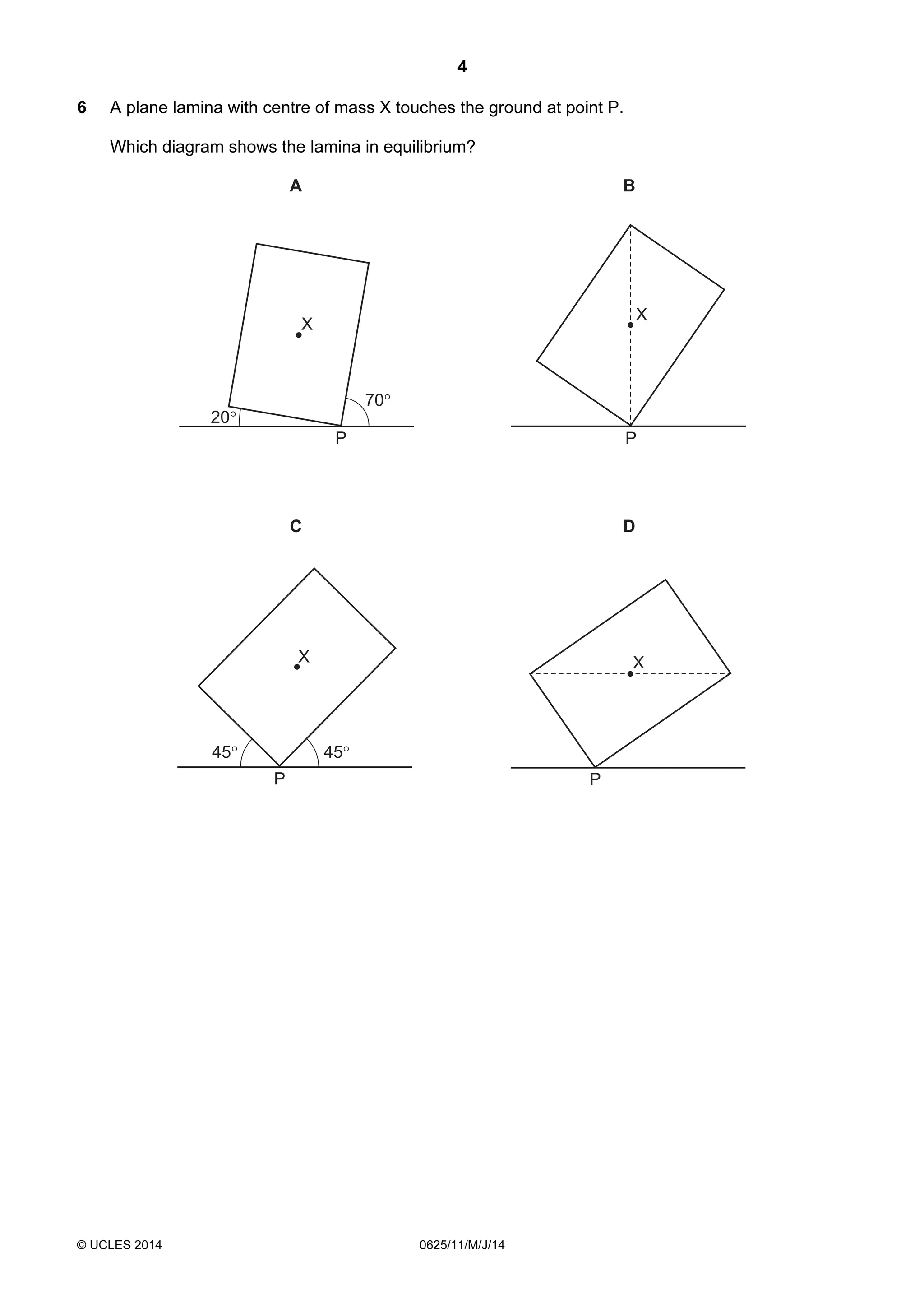
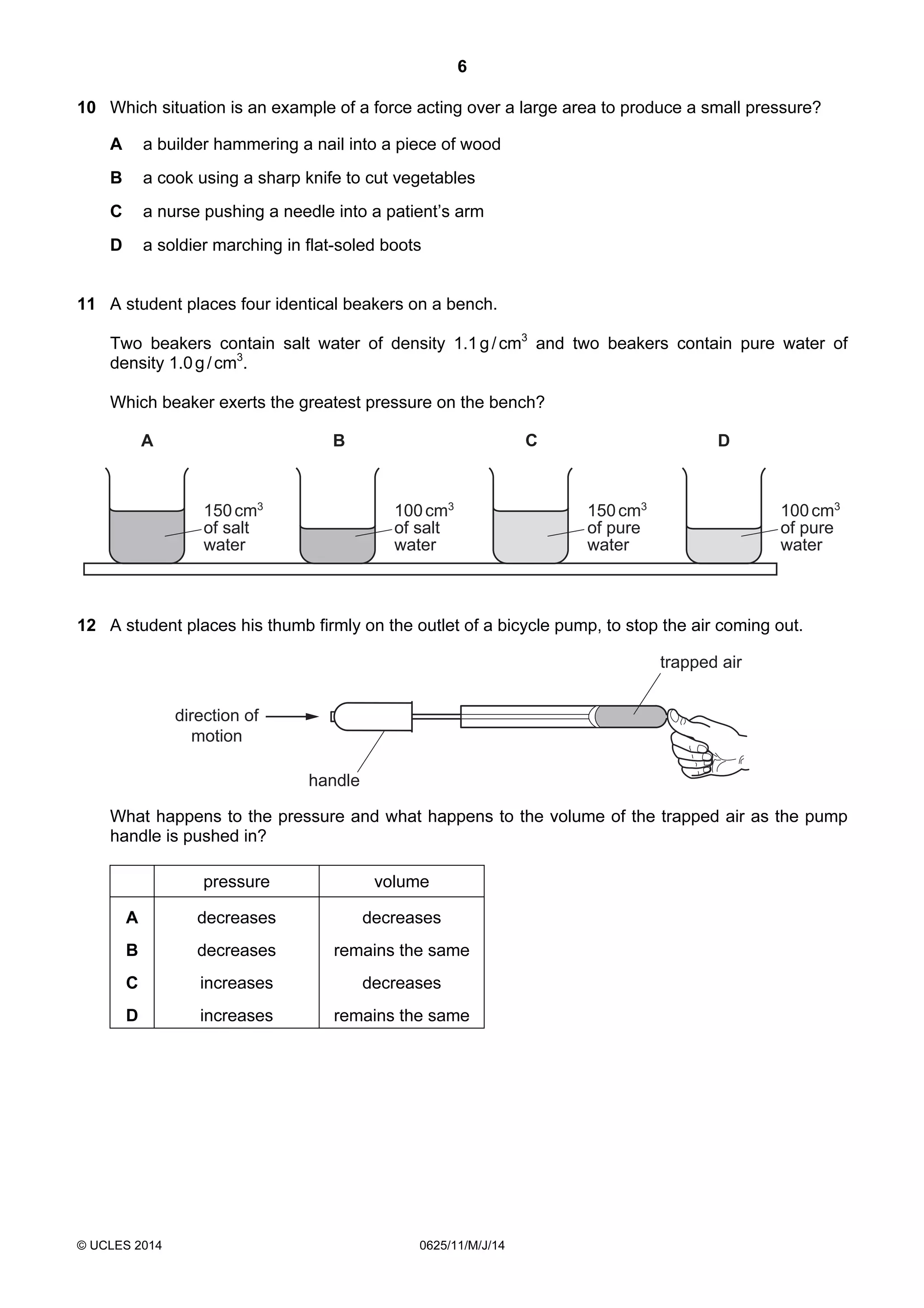
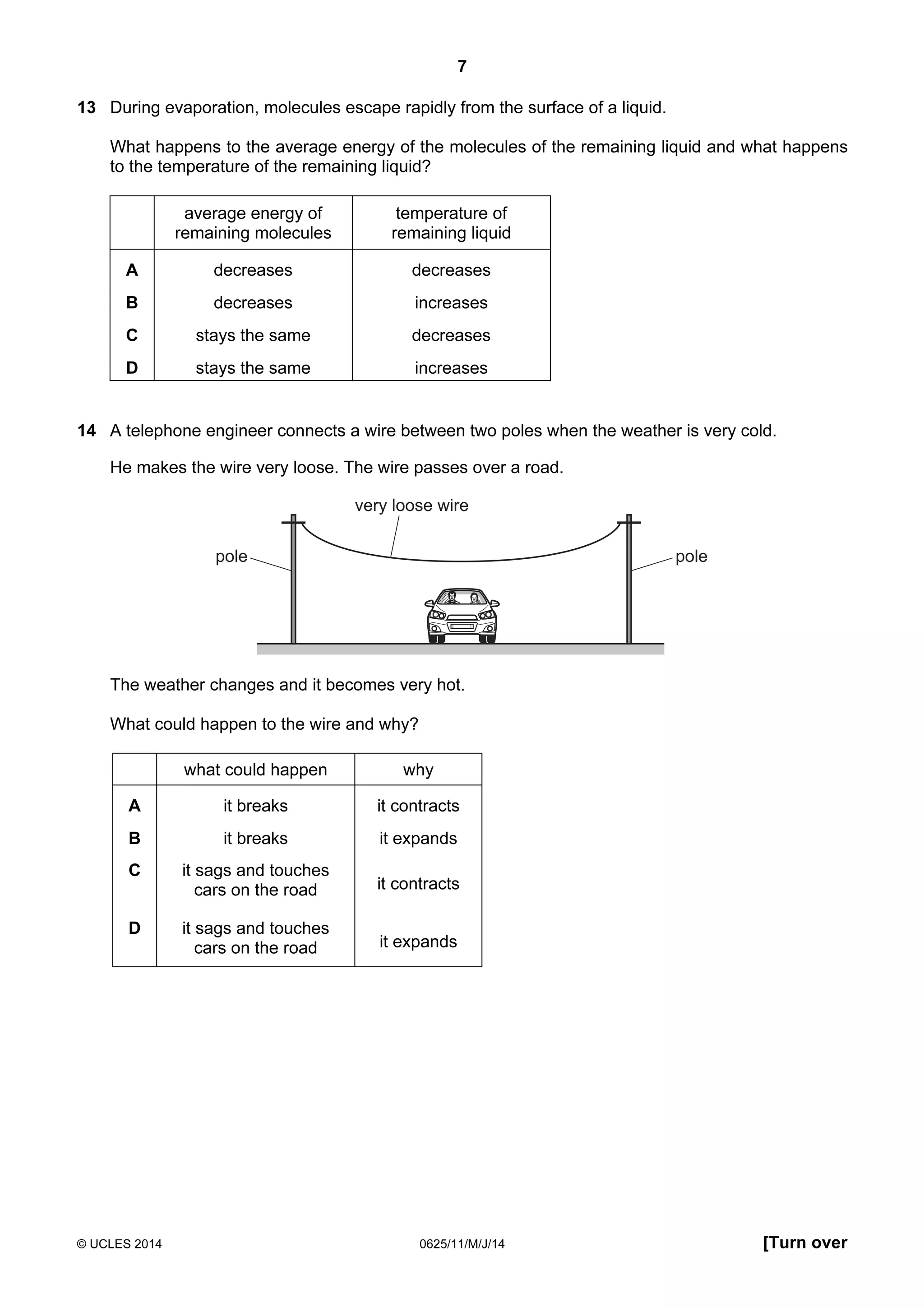
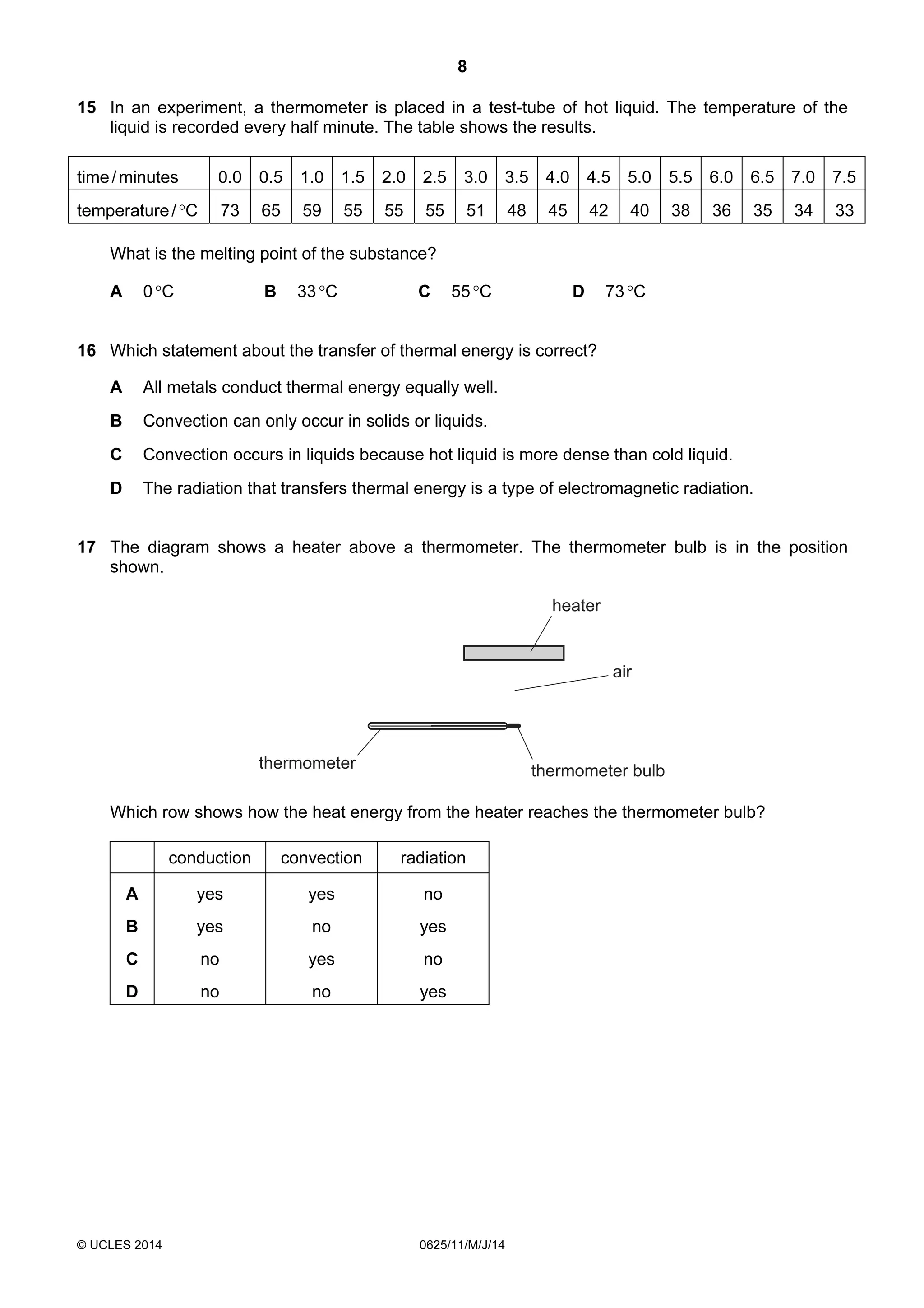
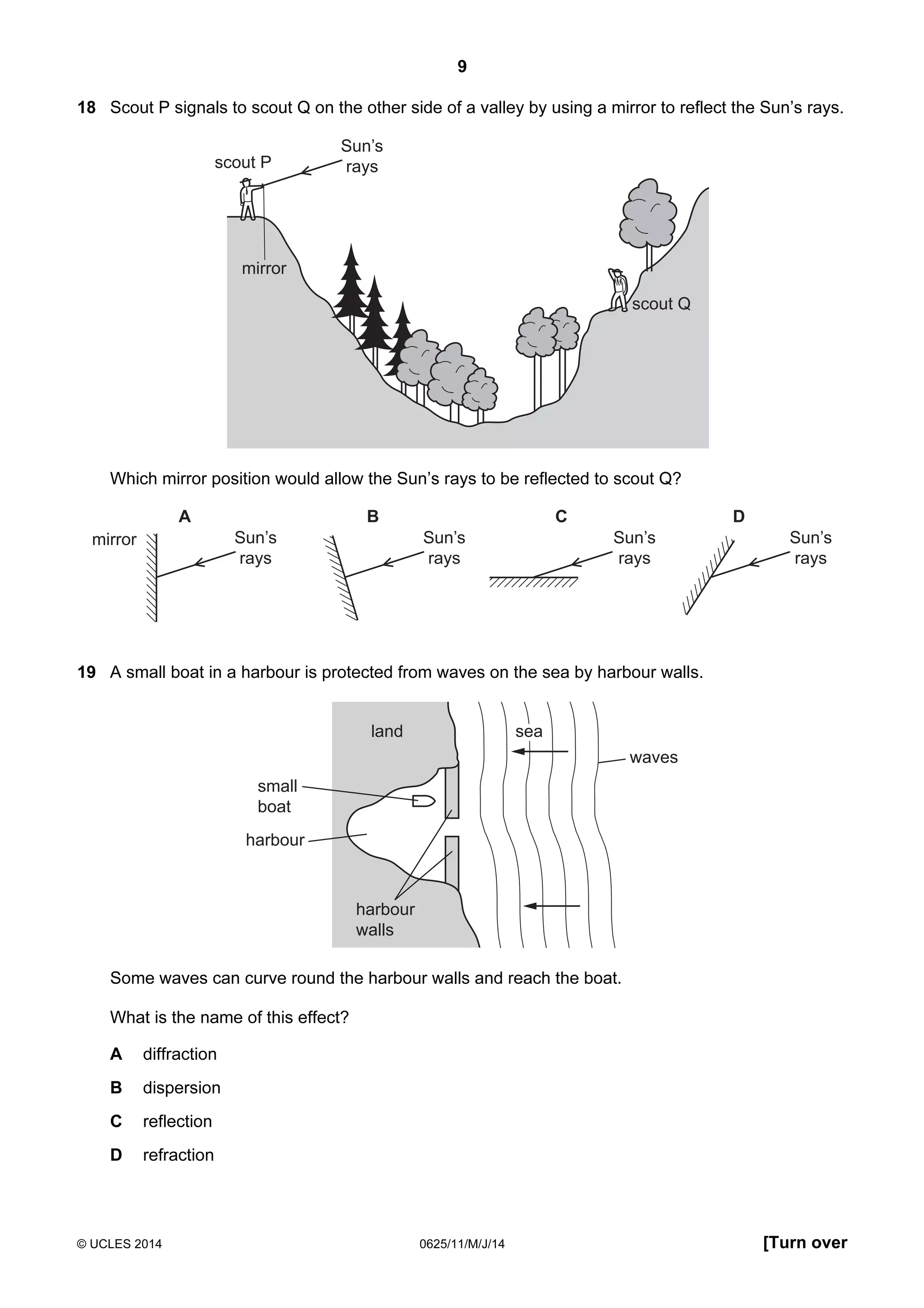
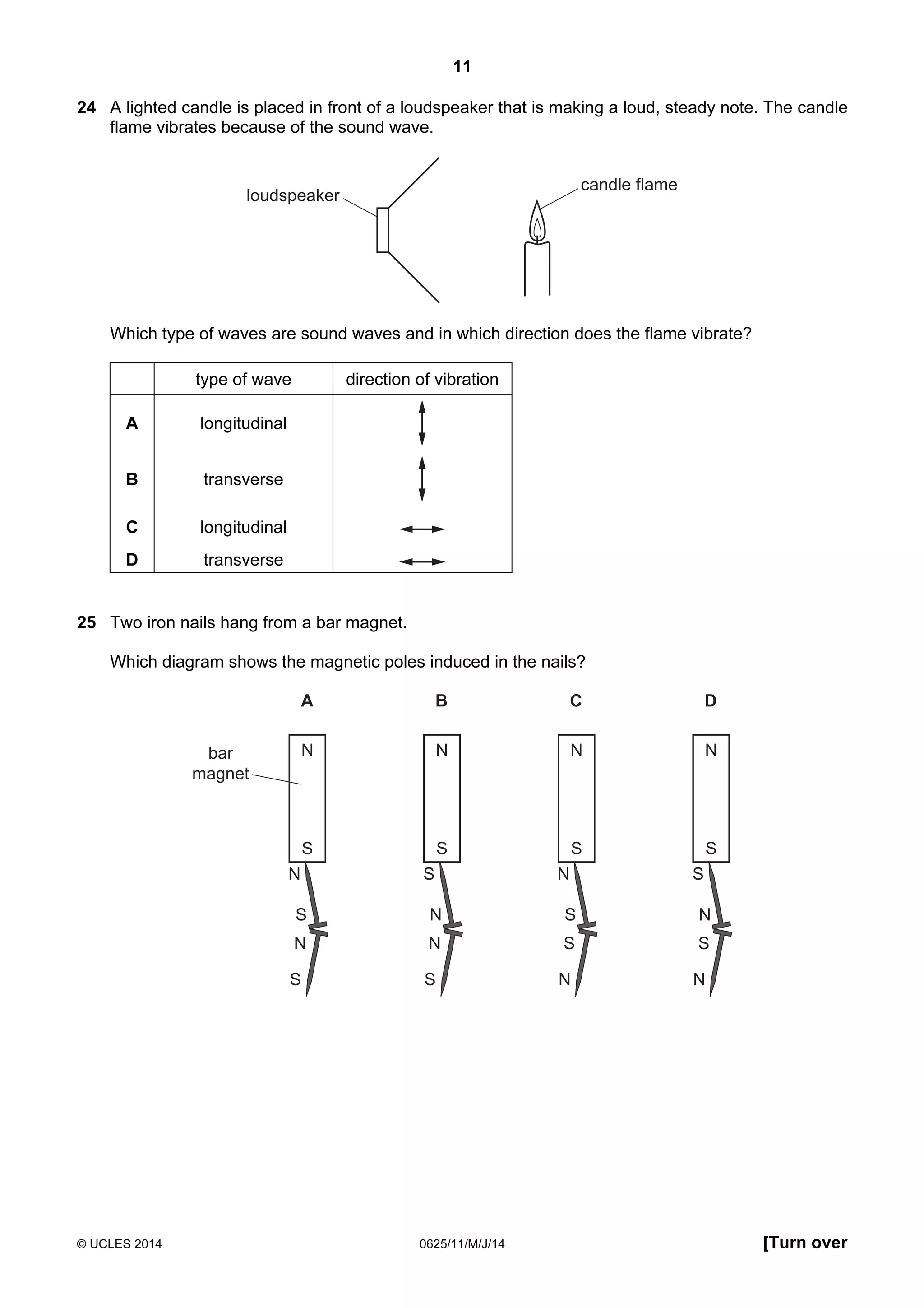
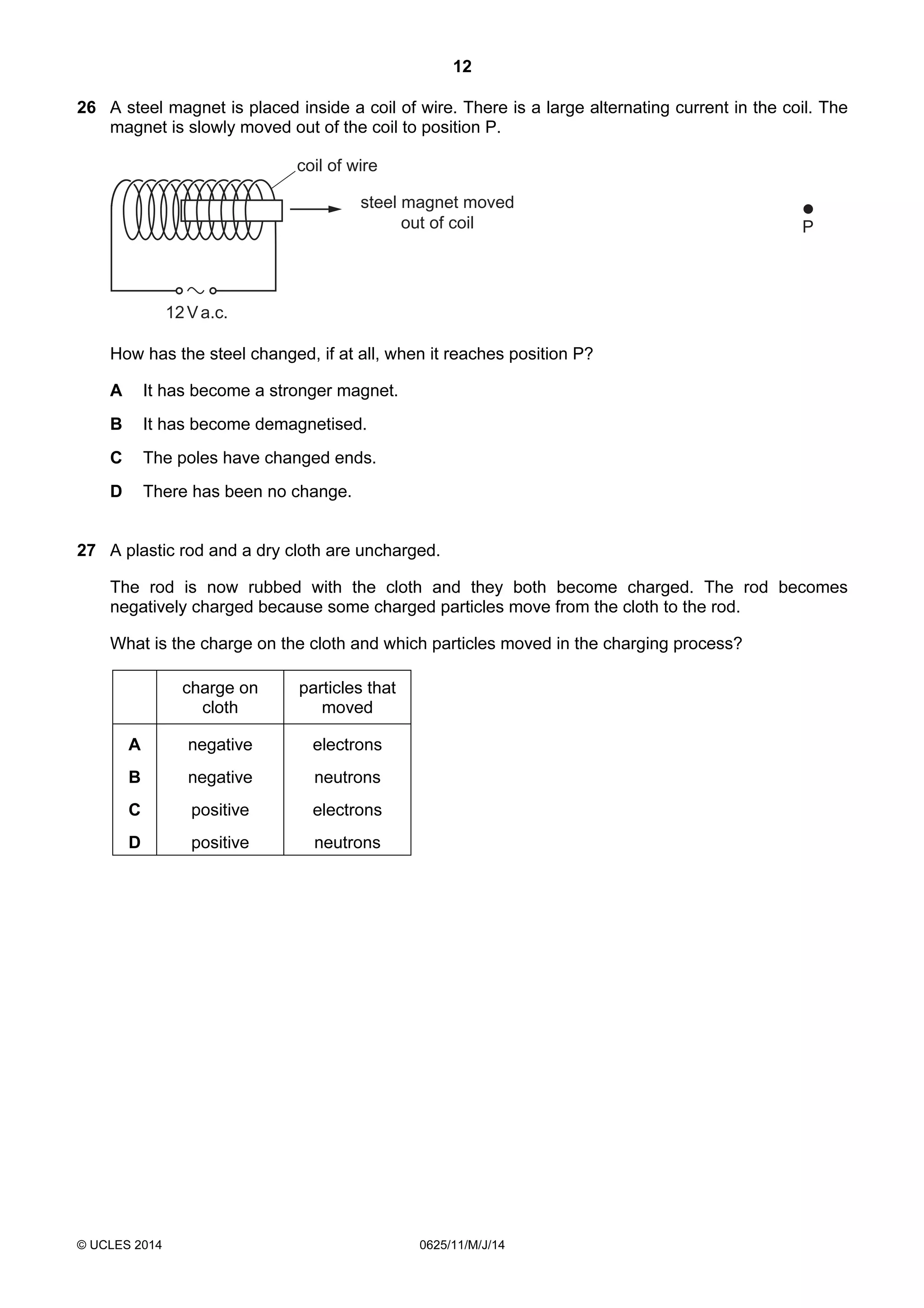
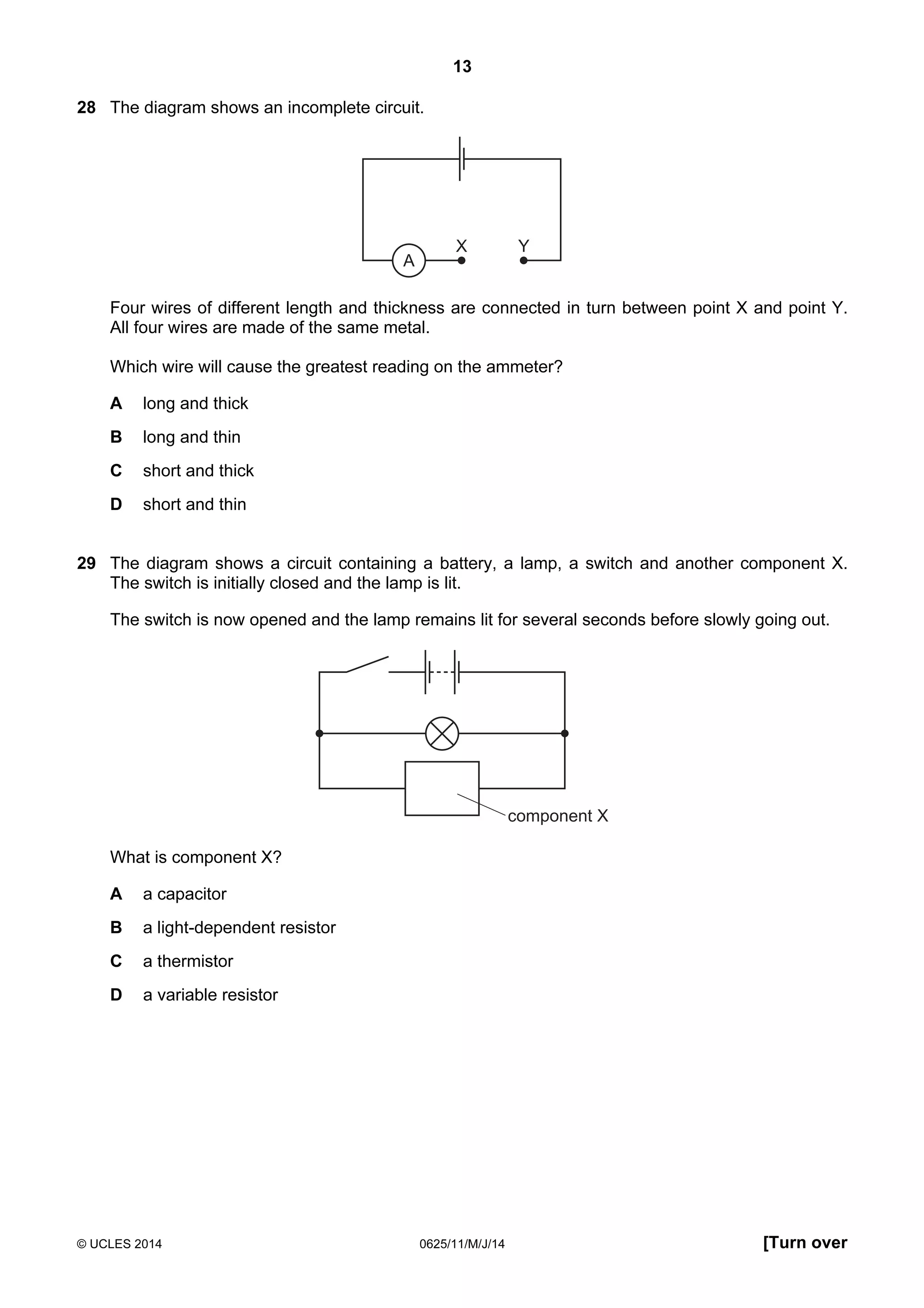
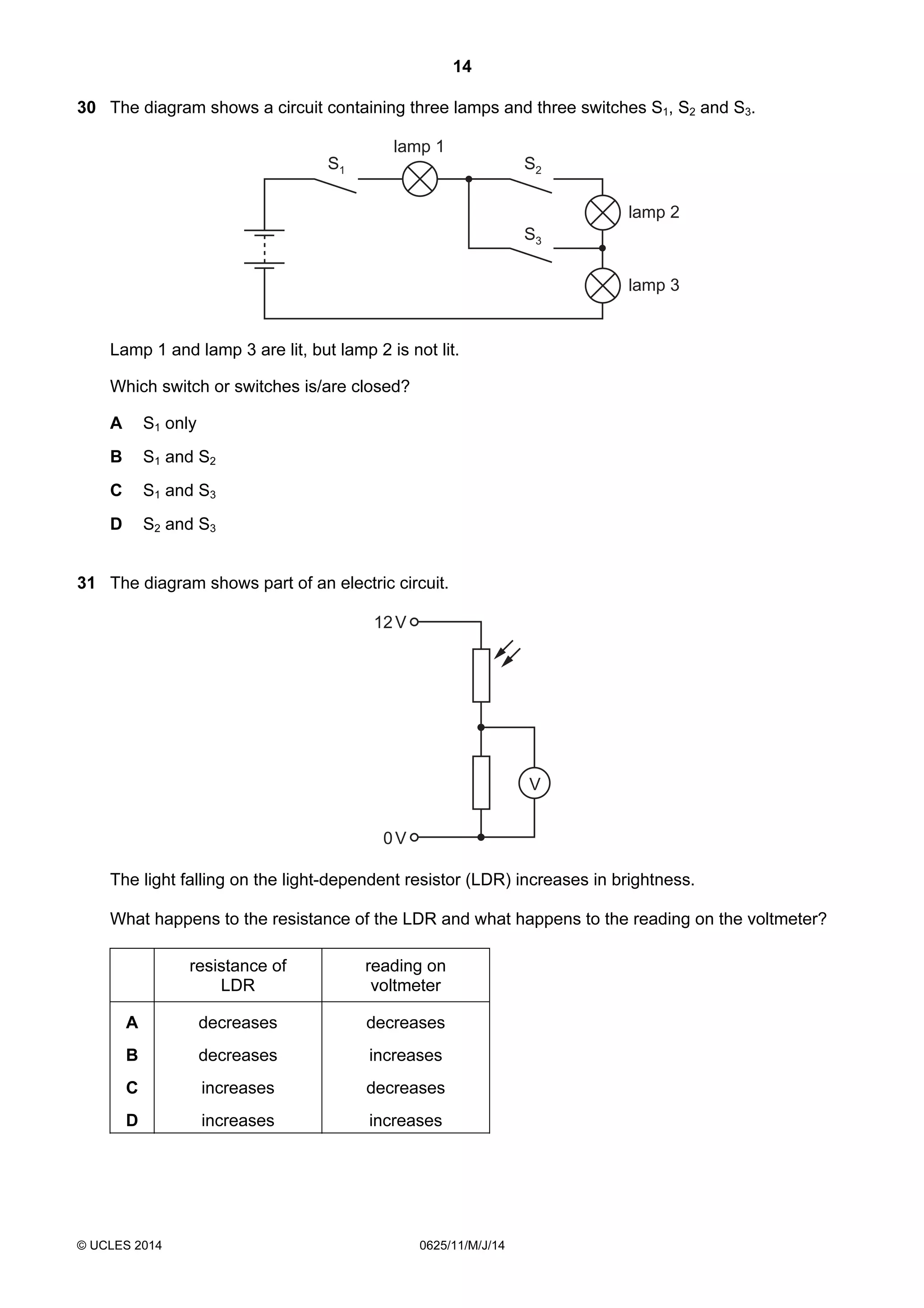
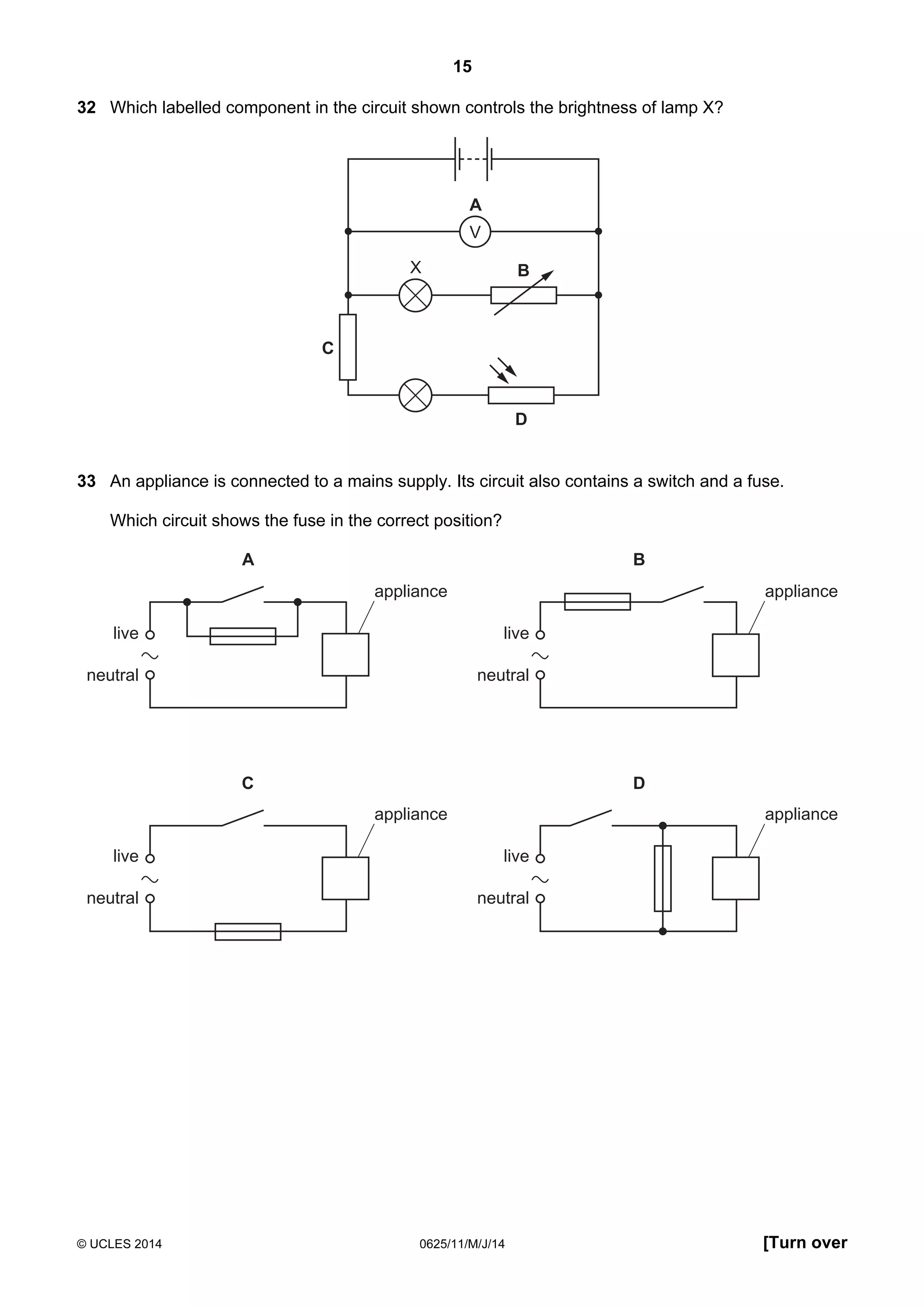
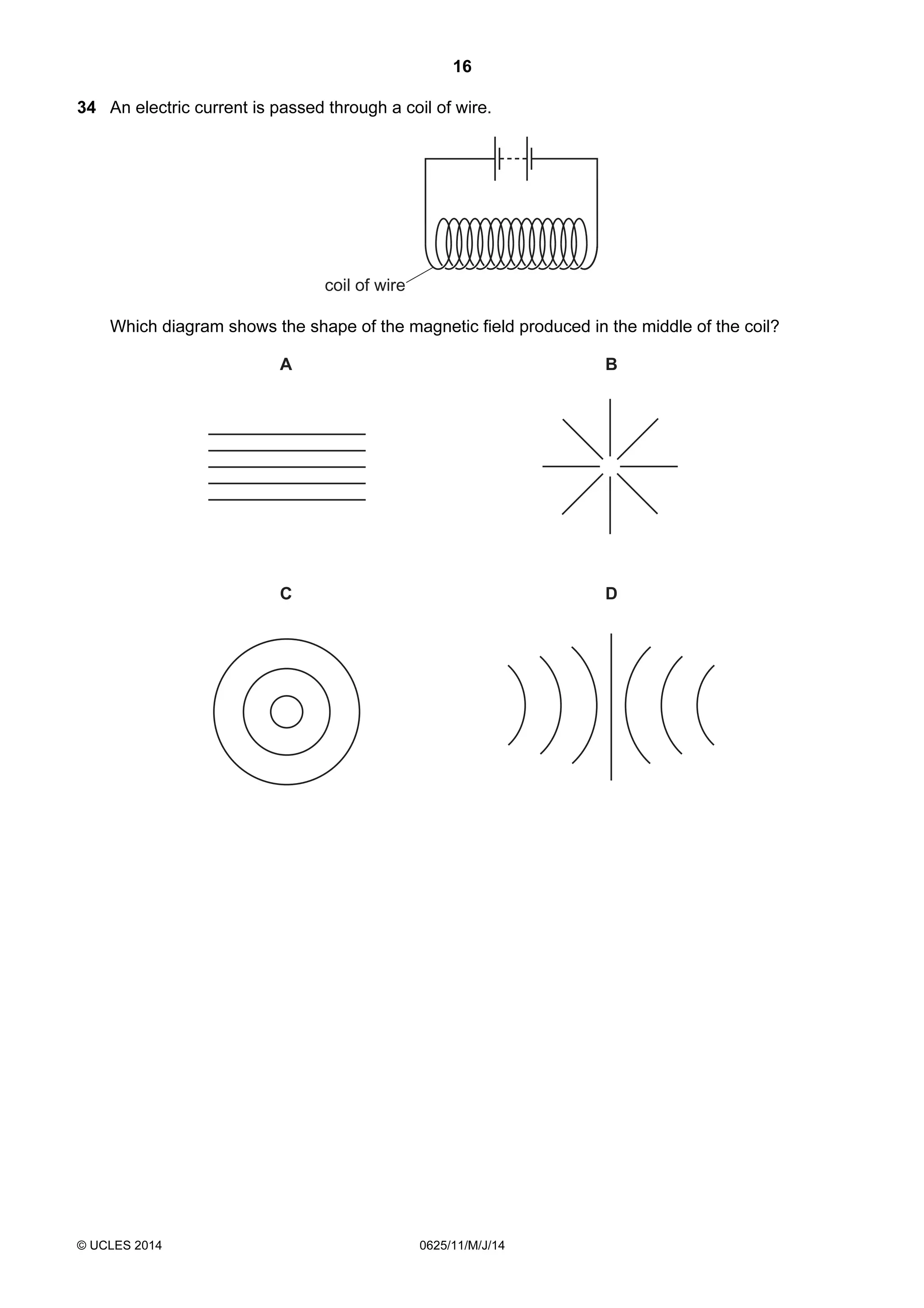
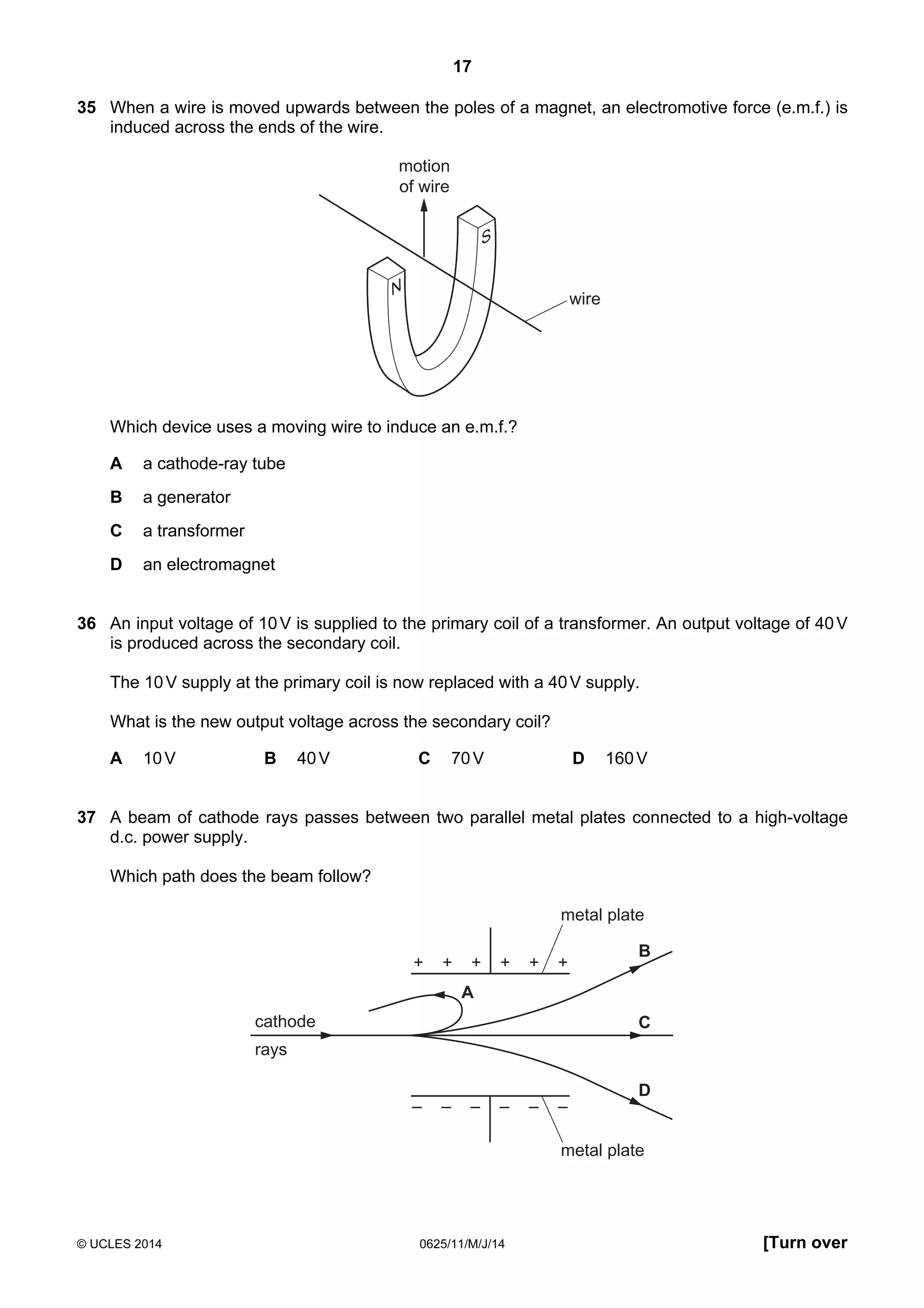
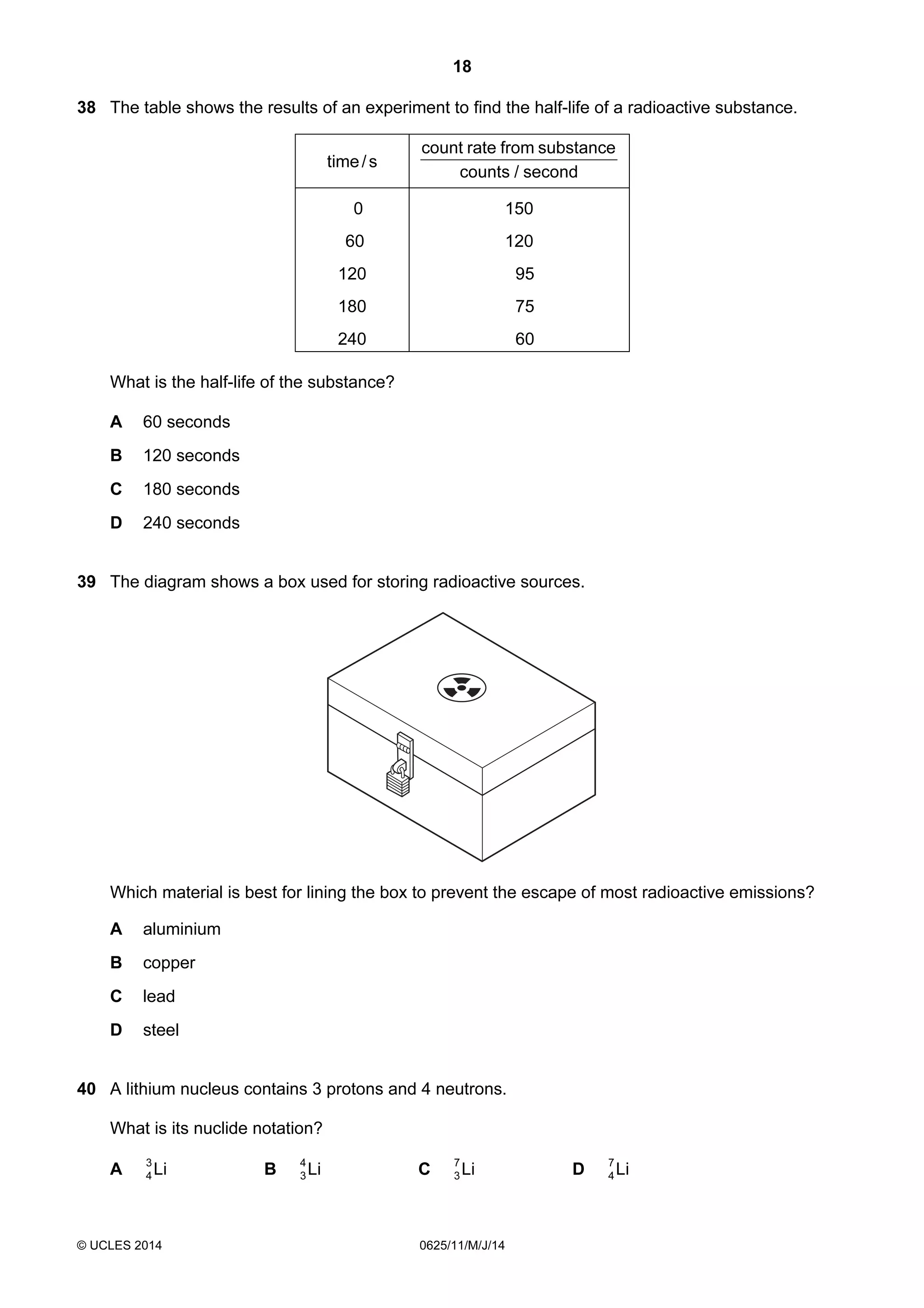
This document consists of 18 printed pages and 2 blank pages. It is the syllabus for Cambridge International Level 1/Level 2 Certificate in Physics, which is approved for use in England, Wales and Northern Ireland. The document contains the syllabus content and examination information. It also provides a sample multiple choice exam paper with 40 questions on topics such as measurement, motion, energy, electricity, magnetism and atomic physics.