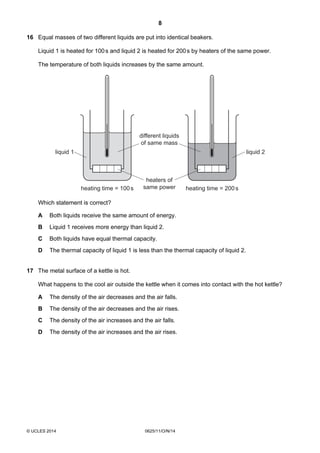
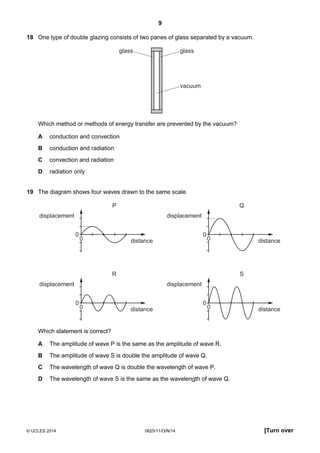
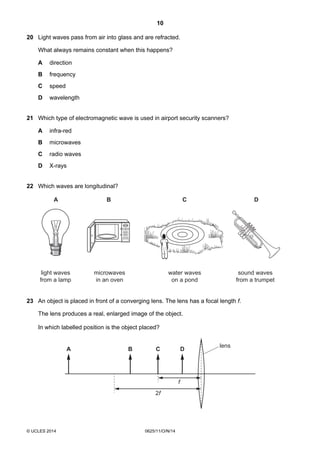
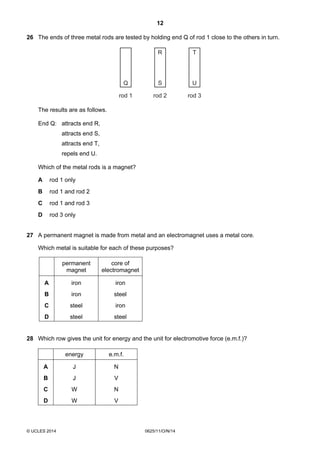
1. This document consists of 17 printed pages and 3 blank pages for the Cambridge International Level 1/2 Certificate in Physics.
2. The document is approved for use in England, Wales and Northern Ireland and contains a multiple choice exam from October/November 2014 with 40 questions on topics related to physics.
3. Students are instructed to choose the correct answer for each question and record their choice on an answer sheet within 45 minutes, with each correct answer scoring one mark.