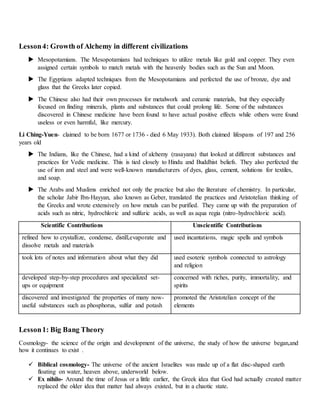
The document discusses several nuclear fusion reactions that occur in stars, including the proton-proton chain reaction, alpha process, CNO cycle, and triple-alpha process. The proton-proton chain reaction fuses hydrogen into helium. The alpha process fuses helium into heavier elements. The CNO cycle is another reaction that fuses hydrogen into helium using carbon, nitrogen, and oxygen as catalysts. The triple-alpha process fuses three helium nuclei into carbon.
![Lesson5: 2xProton, CNO & Alpha
The proton–proton chain reaction is one of two
known sets of nuclear fusion reactions by
which stars convert hydrogen to helium.
The first step in all the branches is the fusion of
two protons into deuterium. As the protons fuse one
of them undergoes beta decay, converting into
a neutron by emitting a positron and an electron
neutrino.[6]
The alpha process, also known as the alpha
ladder, is one of two classes of nuclear
fusion reactions by which stars convert helium into
heavier elements, the other being the triple-alpha
process.[1] The triple-alpha process consumes only
helium, and produces carbon. After enough carbon
has accumulated, the reactions below take place, all
consuming only helium and the product of the
previous reaction.
The CNO cycle (for carbon–nitrogen–oxygen) is
one of the two known sets of fusion reactions by
which stars convert hydrogento helium, the other
being the proton–proton chain reaction (pp-chain
reaction). Unlike the latter, the CNO cycle is
a catalytic cycle.
In the CNO cycle, four protons fuse, using carbon,
nitrogen, and oxygen isotopes as catalysts, to
produce one alpha particle, two positrons and
two electron neutrinos.
The triple-alpha process is a set of nuclear
fusion reactions by which three helium-4 nuclei
(alpha particles) are transformed into carbon.
Beta plus decay- releases neutrino and positron
𝑝 → 𝑣 + 𝑒 = 𝑛
Beta minus decay- releases anti-neutrino and
electron](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/physicalscience-190630065515/75/Physical-science-module-1-2048.jpg)