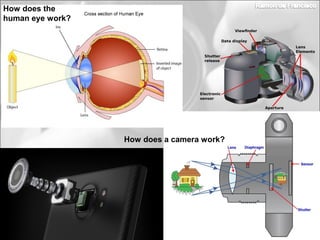
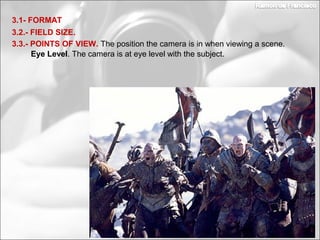
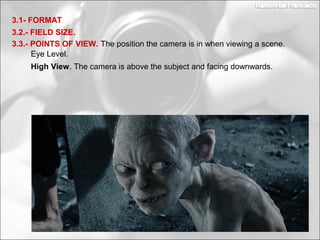
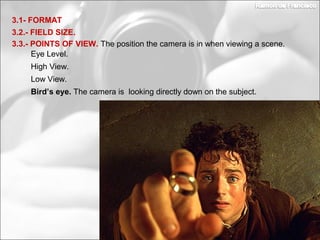
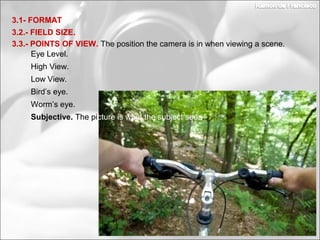
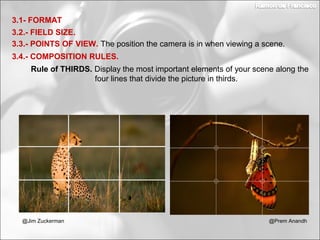
This document discusses photography techniques. It begins with a brief history of photography from ancient Greece to modern times. It then covers how the human eye and cameras work similarly to capture images. The bulk of the document focuses on techniques for taking pictures, including format, field size, points of view, and composition rules. Field size refers to how much of the subject and surroundings are captured in shots ranging from very extreme long shots to extreme close-ups. Points of view include eye level, high, low, bird's eye, worm's eye, and subjective. Composition rules discuss the rule of thirds and rule of gaze.