For any year student basically chemical engineering students seminar project presentation or report they can easily do presentation *Pharmaceutical Aqueous Solution Treatment*
Pharmaceutical aqueous solutions are a crucial component of many medicinal products, including injections, eye drops, and oral liquids. However, these solutions can be susceptible to contamination, degradation, and instability, which can compromise their efficacy and safety. To address these challenges, various treatment methods are employed to ensure the quality and stability of pharmaceutical aqueous solutions.
*Types of Aqueous Solutions*
1. *Injectable Solutions*: These are sterile solutions intended for parenteral administration, such as intravenous (IV) fluids, vaccines, and antibiotics.
2. *Oral Liquids*: These are solutions or suspensions intended for oral administration, such as cough syrups, antacids, and pediatric formulations.
3. *Eye Drops*: These are sterile solutions intended for ocular administration, such as antibiotics, anti-inflammatory agents, and lubricants.
*Common Contaminants and Degradation Products*
1. *Microbial Contamination*: Bacteria, fungi, and viruses can contaminate aqueous solutions, leading to infection, spoilage, or degradation.
2. *Chemical Degradation*: Aqueous solutions can undergo chemical reactions, such as hydrolysis, oxidation, or photolysis, leading to the formation of impurities or degradation products.
3. *Particulate Matter*: Particles, such as dust, fibers, or precipitates, can contaminate aqueous solutions, leading to physical instability or toxicity.
*Treatment Methods*
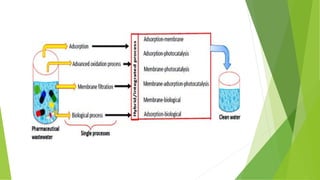
1. *Sterilization*: Methods, such as autoclaving, filtration, or gamma radiation, are used to eliminate microbial contamination.
2. *Filtration*: Membrane filtration, such as 0.2 μm or 0.45 μm filters, is used to remove particulate matter and microorganisms.
3. *pH Adjustment*: pH adjustment is used to optimize the stability and solubility of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs).
4. *Antioxidants and Preservatives*: Antioxidants, such as ascorbic acid or tocopherol, and preservatives, such as parabens or benzyl alcohol, are used to prevent chemical degradation and microbial growth.
5. *Lyophilization*: Freeze-drying is used to remove water and improve the stability of aqueous solutions.
6. *Encapsulation*: Techniques, such as liposomes or nanoparticles, are used to encapsulate APIs and improve their stability and bioavailability.
*Quality Control and Assurance*
1. *In-Process Testing*: Testing is performed during manufacturing to ensure the quality and stability of the aqueous solution.
2. *Finished Product Testing*: Testing is performed on the final product to ensure compliance with specifications and regulatory requirements.
3. *Stability Studies*: Studies are conducted to evaluate the stability of the aqueous solution under various conditions, such as temperature, humidity, and light.
*Regulatory Requirements*
1. *Good Manufacturing Practice