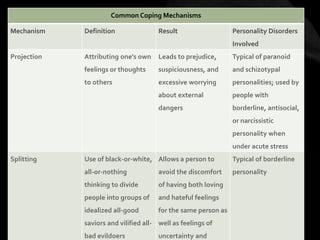
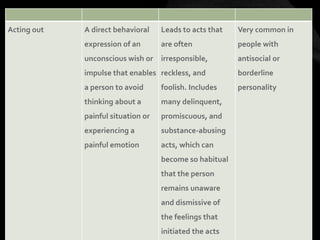
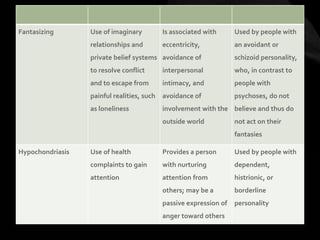
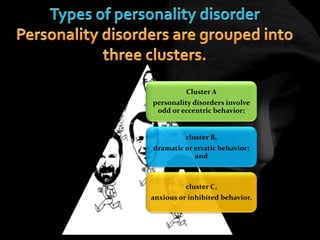
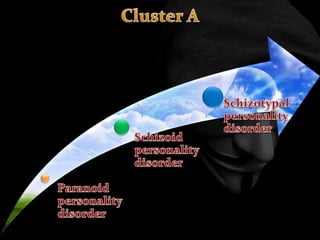
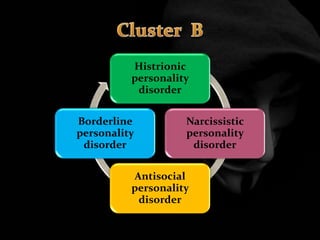
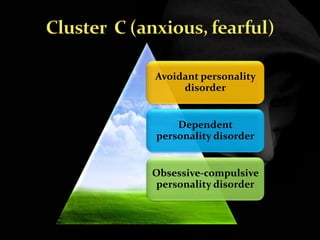
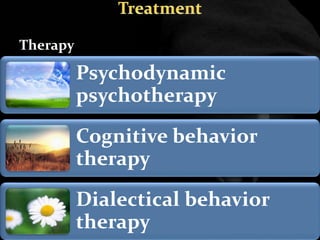
The document provides an overview of various personality disorders, highlighting their characteristics, typical behaviors, and potential coping mechanisms. It notes how these disorders can impact relationships and daily functioning, often beginning in adolescence or early adulthood, with individuals typically unaware of their maladaptive patterns. Additionally, it discusses treatment options and the difficulties faced by those living with someone who has a personality disorder.