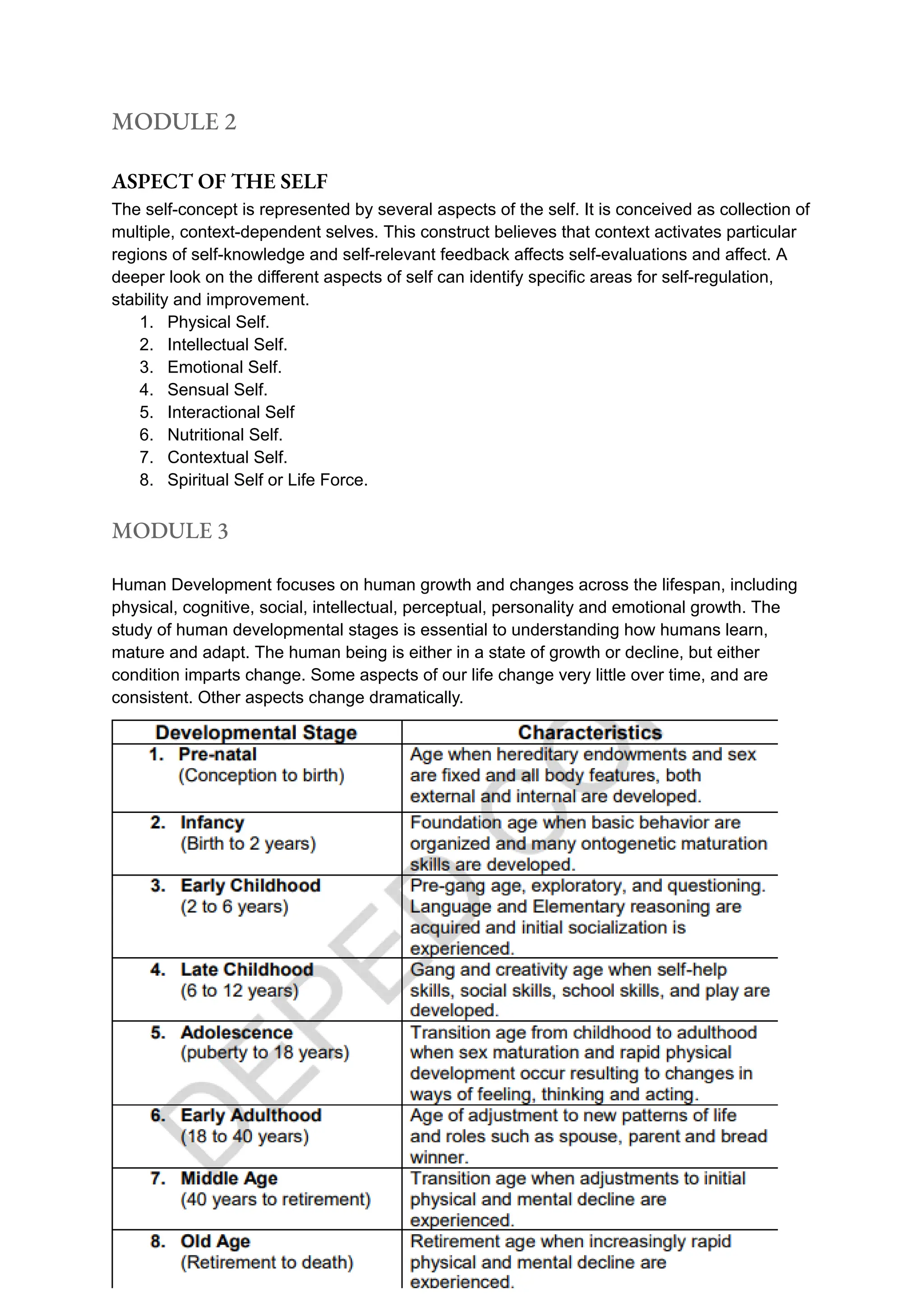
The document outlines concepts of the ideal self and actual self, emphasizing the importance of self-knowledge and personal alignment for mental well-being. It discusses personal effectiveness and essential skills in achieving life goals, contrasting three types of individuals: moviegoers, actors, and scriptwriters, in relation to life control. Additionally, it covers various aspects of the self and the continued nature of human development across the lifespan, based on the developmental tasks theory.