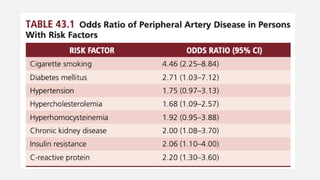
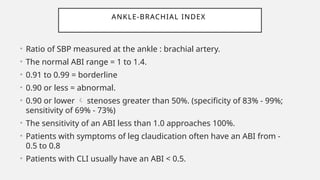
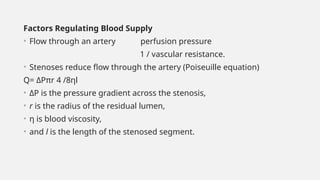
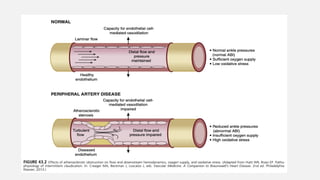
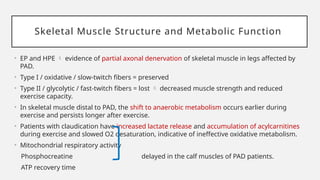
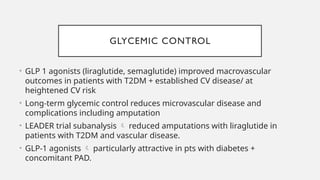
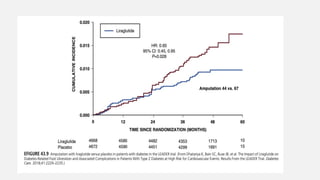
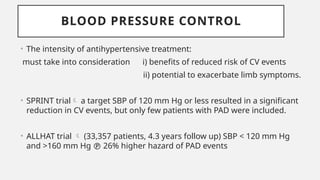
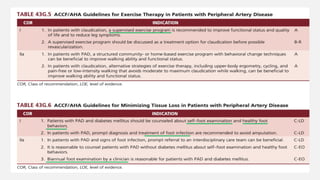
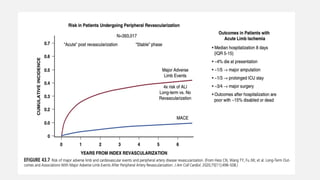
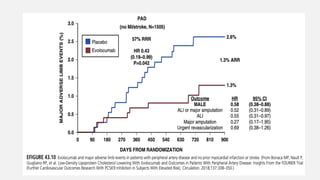
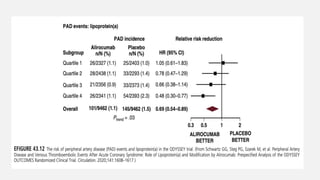
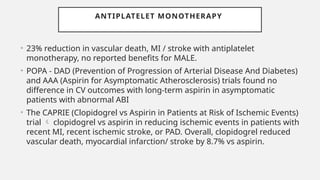
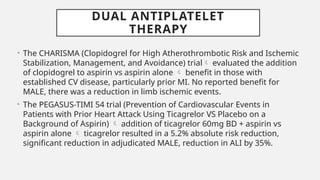
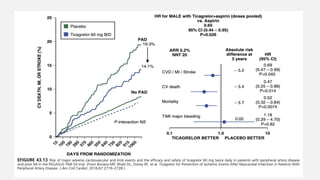
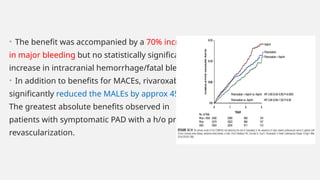
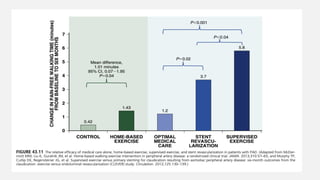
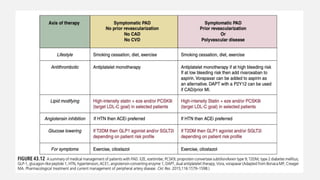
Peripheral arterial disease (PAD) leads to obstruction of arteries, primarily caused by atherosclerosis, resulting in ischemic complications and symptoms like intermittent claudication. The prevalence of PAD is significant among older adults, affecting over 200 million people globally, with various treatment options including pharmacotherapy, lifestyle changes, and supervised exercise programs to improve symptoms and reduce complications. Management strategies emphasize risk factor optimization, such as blood pressure and lipid control, while newer agents like GLP-1 agonists and combinations of anticoagulants and antiplatelet therapies show promise in improving patient outcomes.