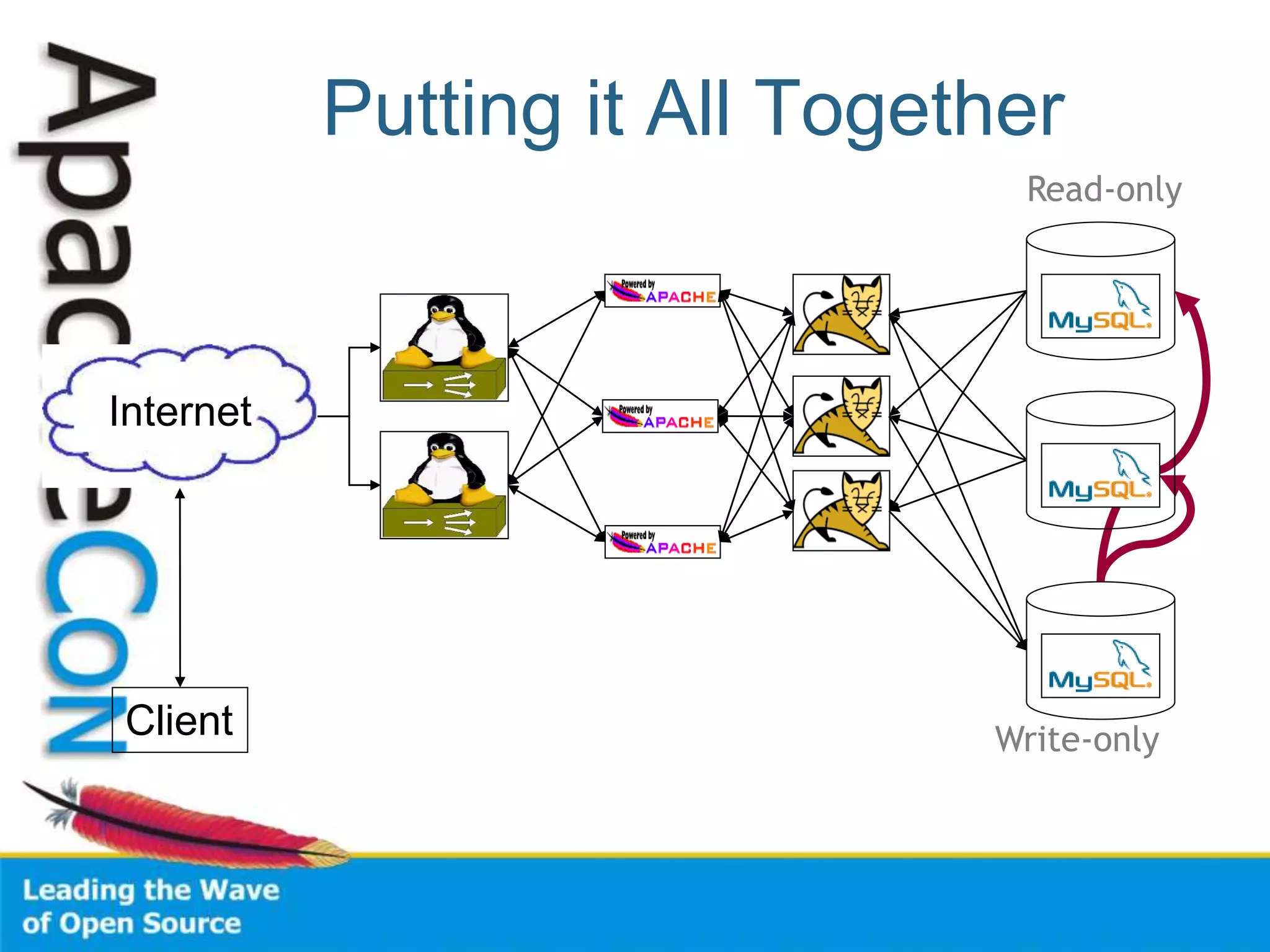
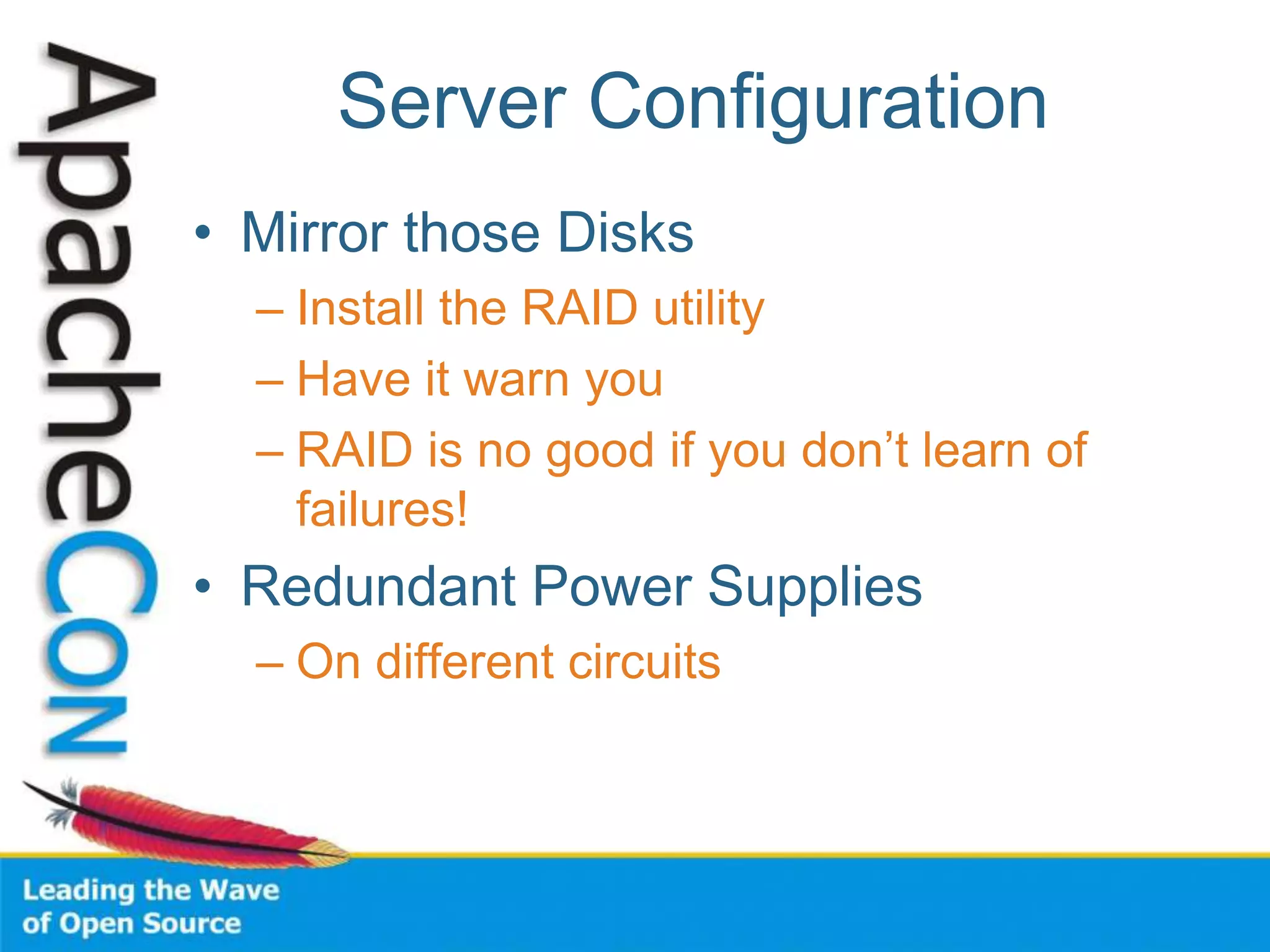
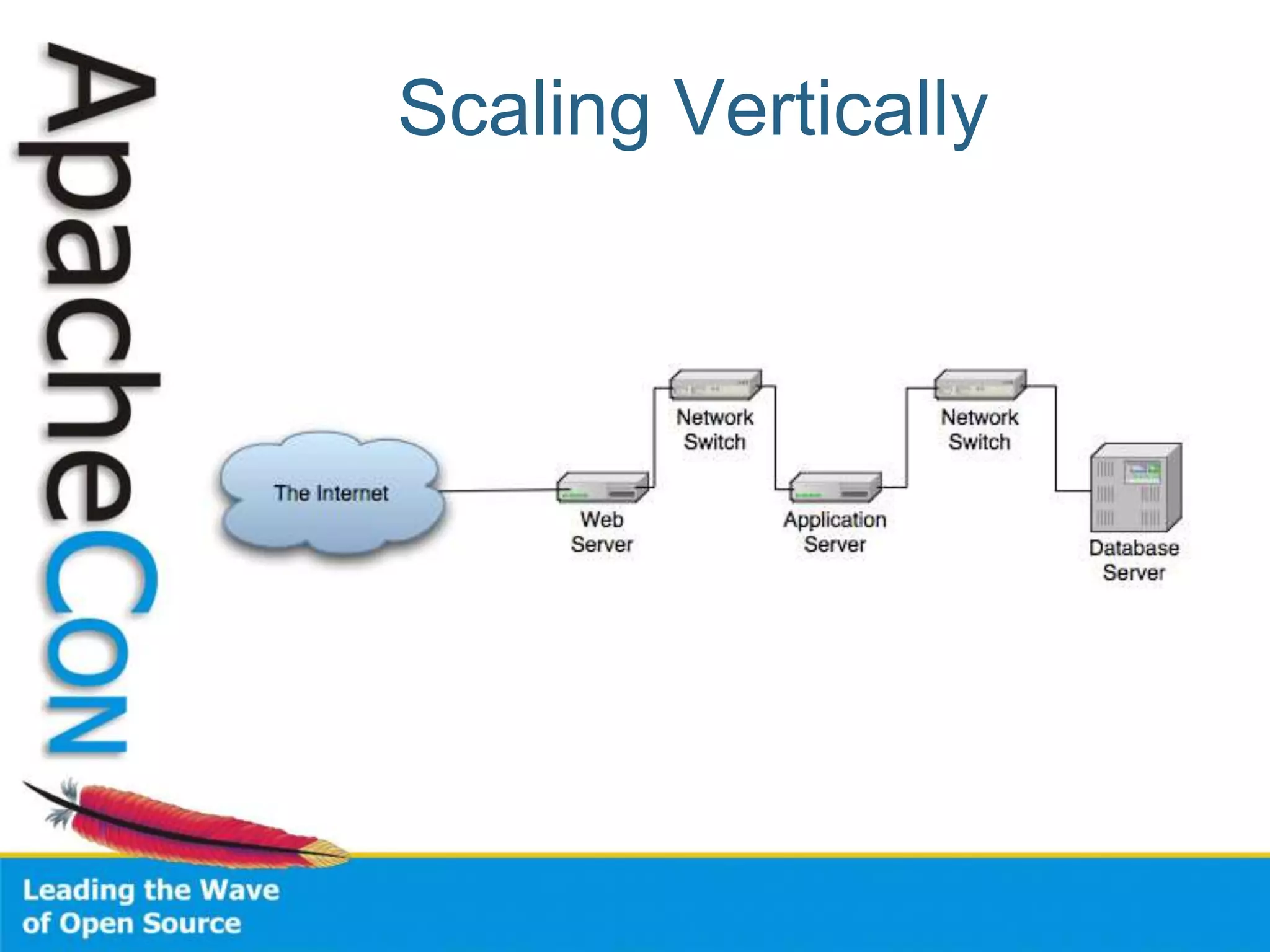
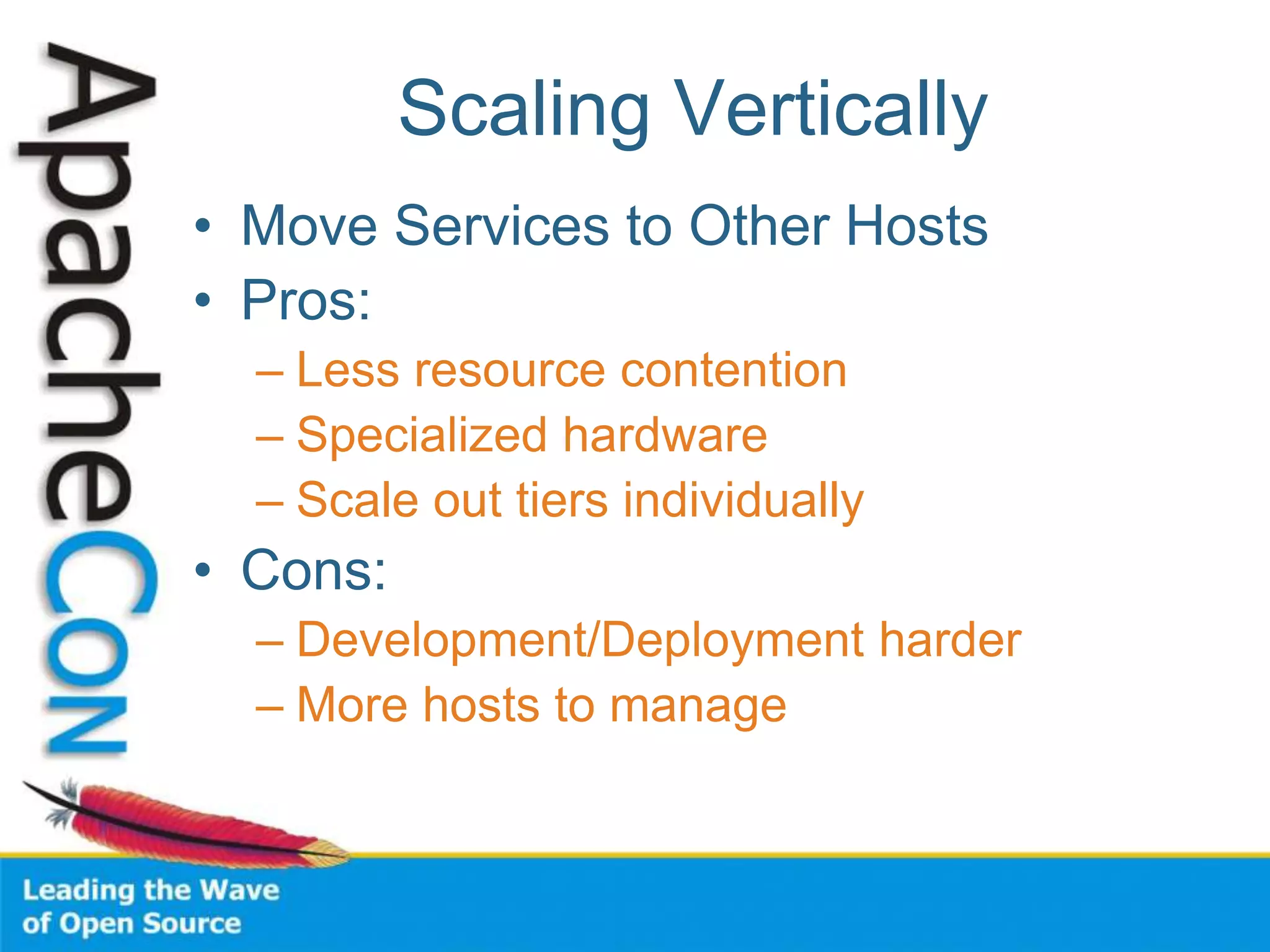
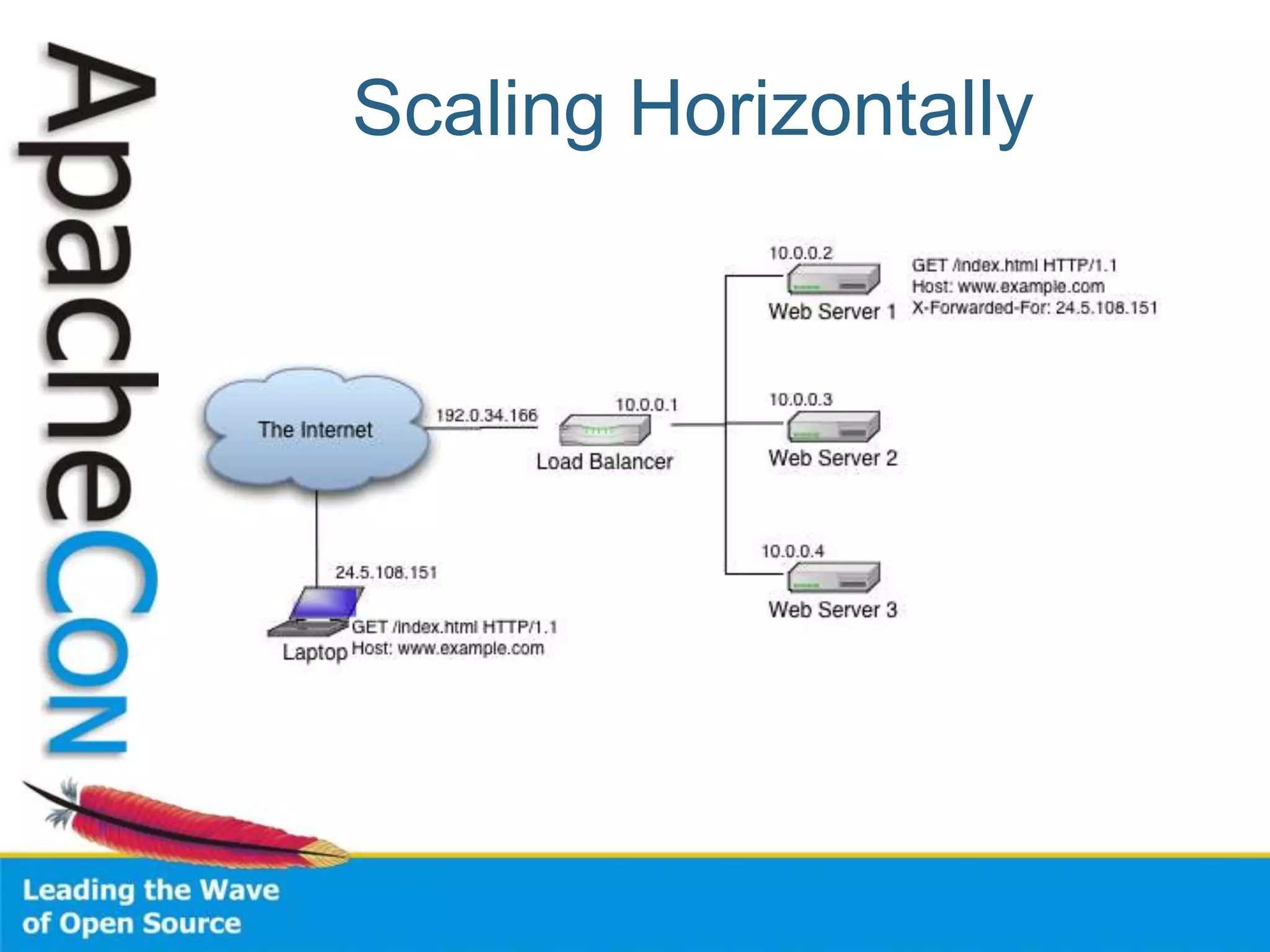
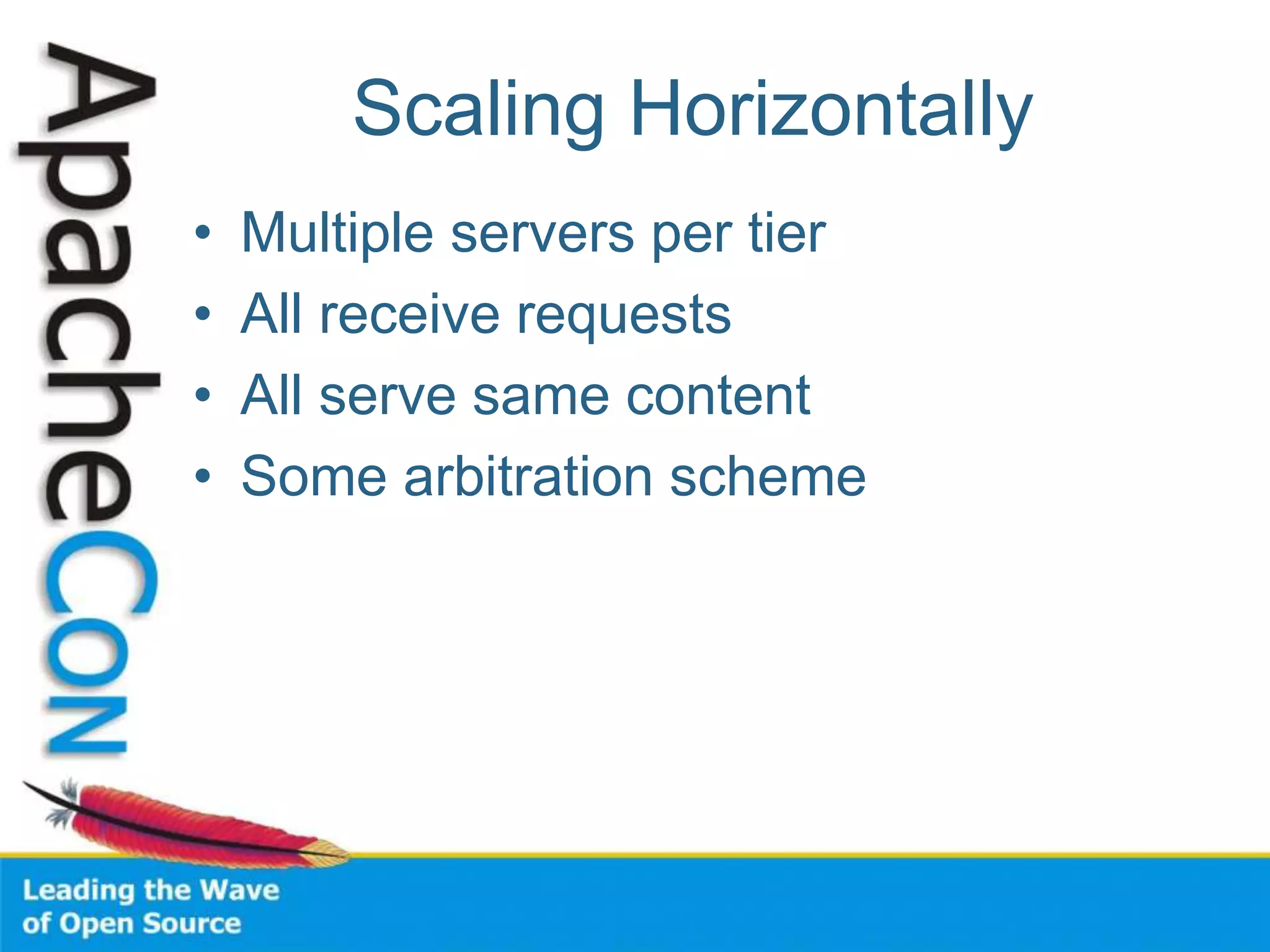
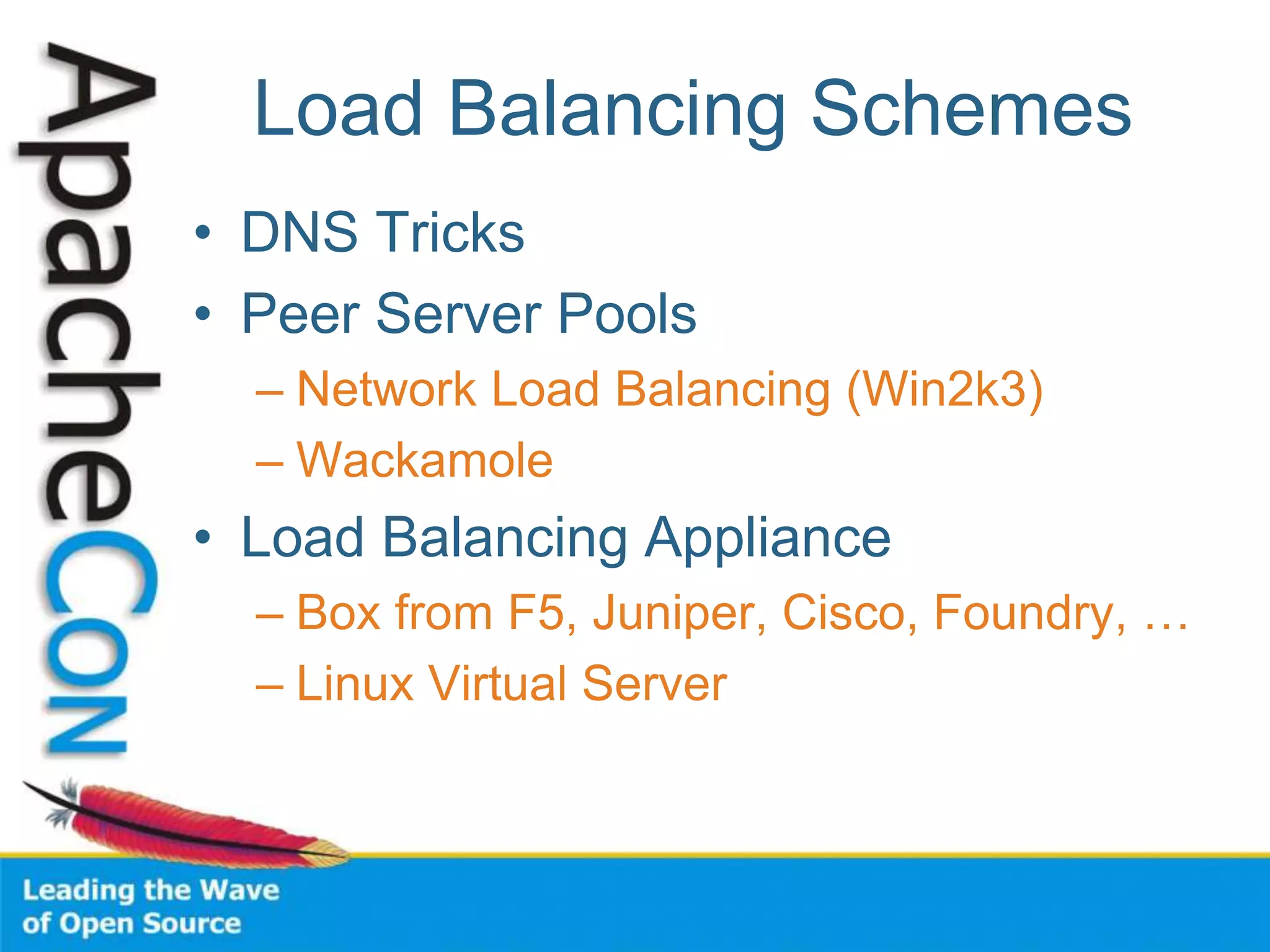
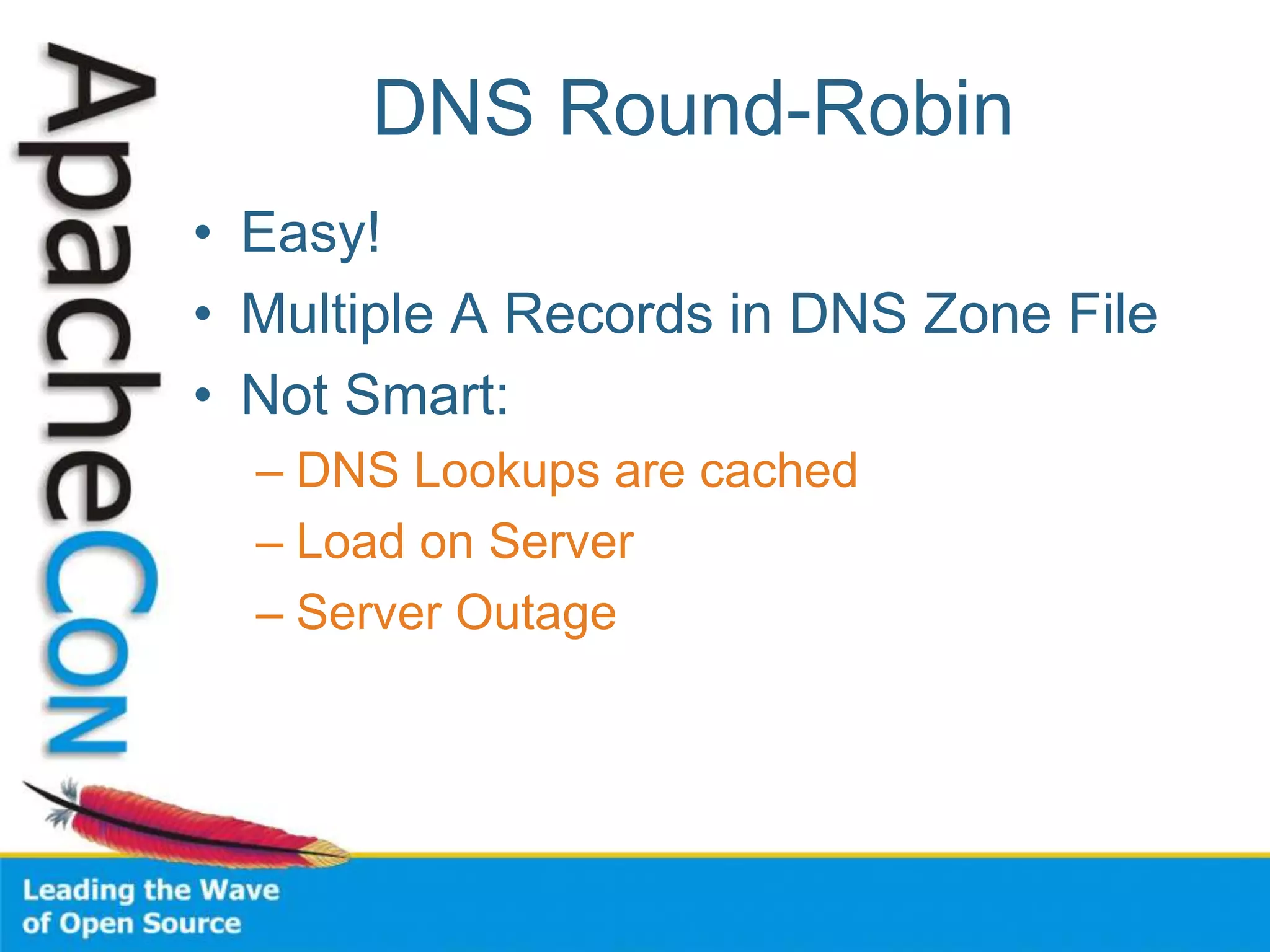
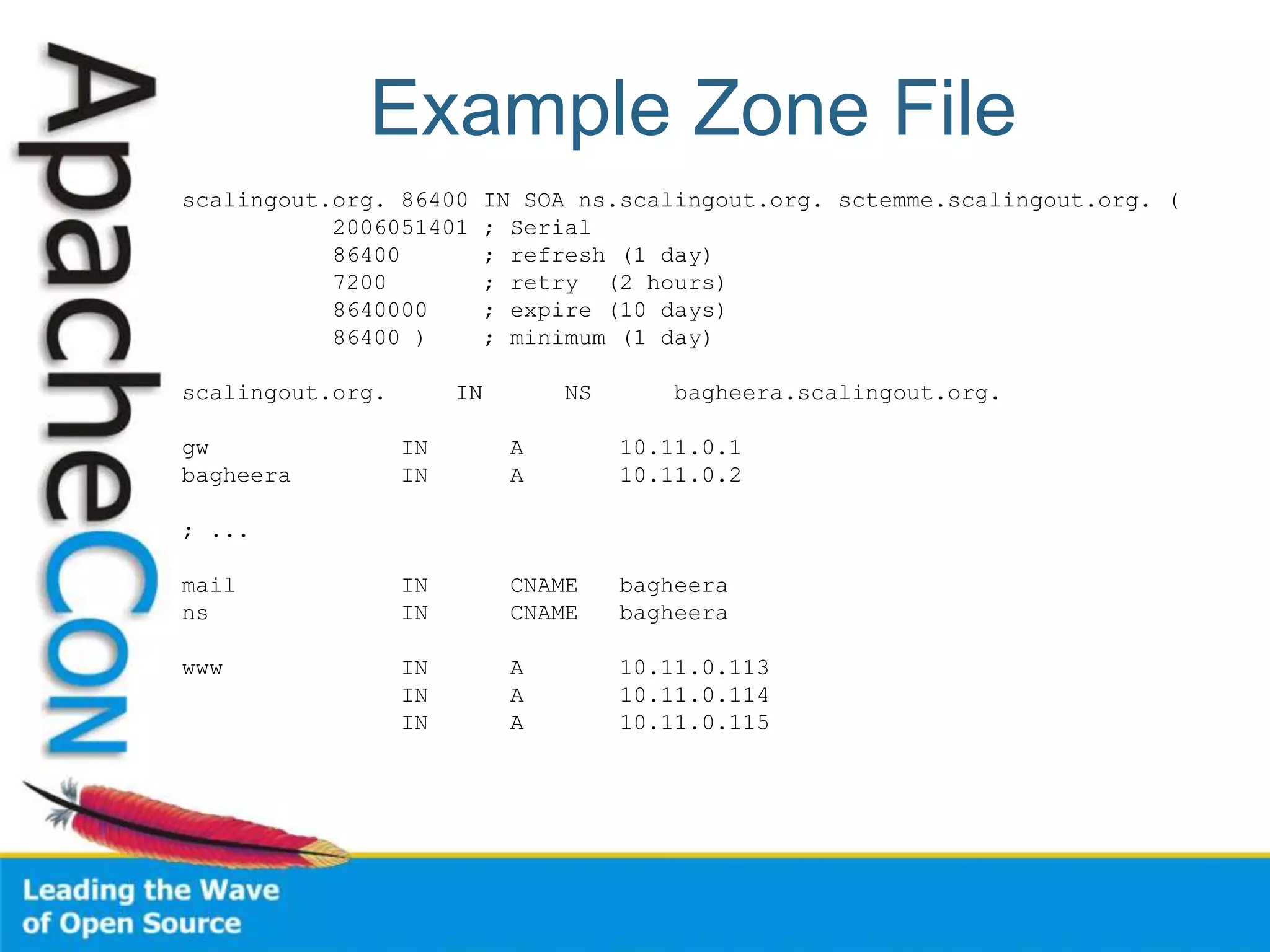
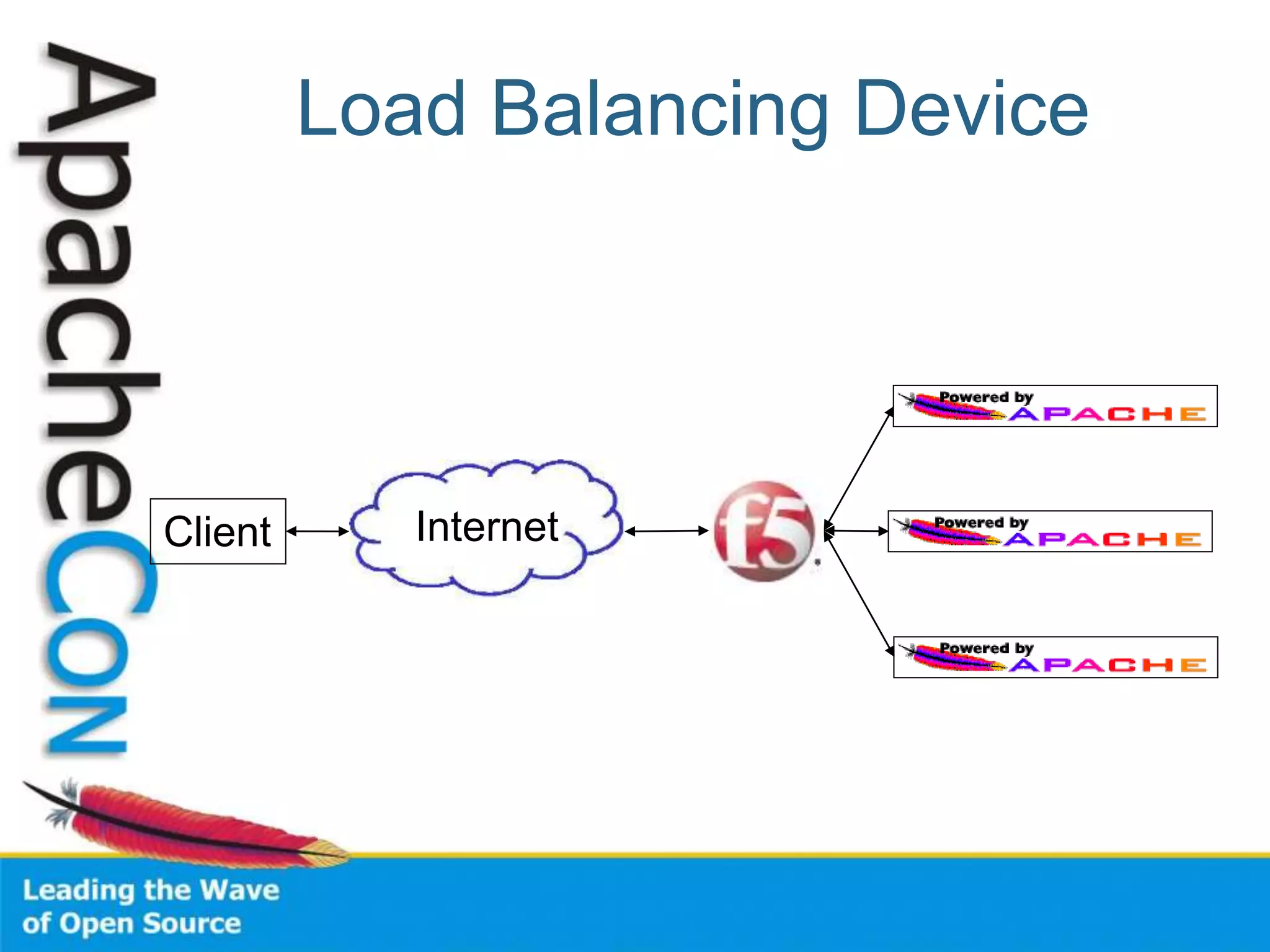
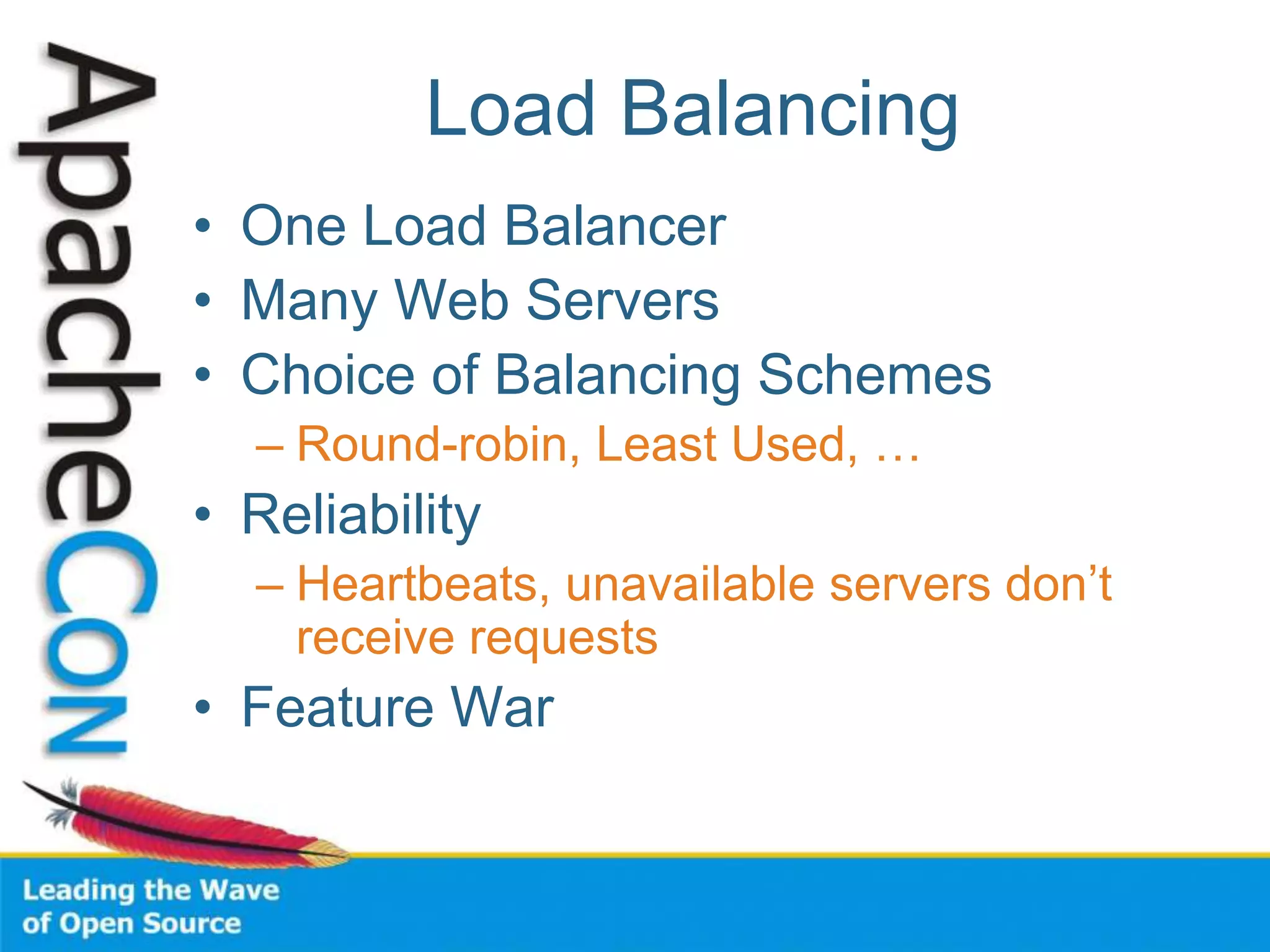
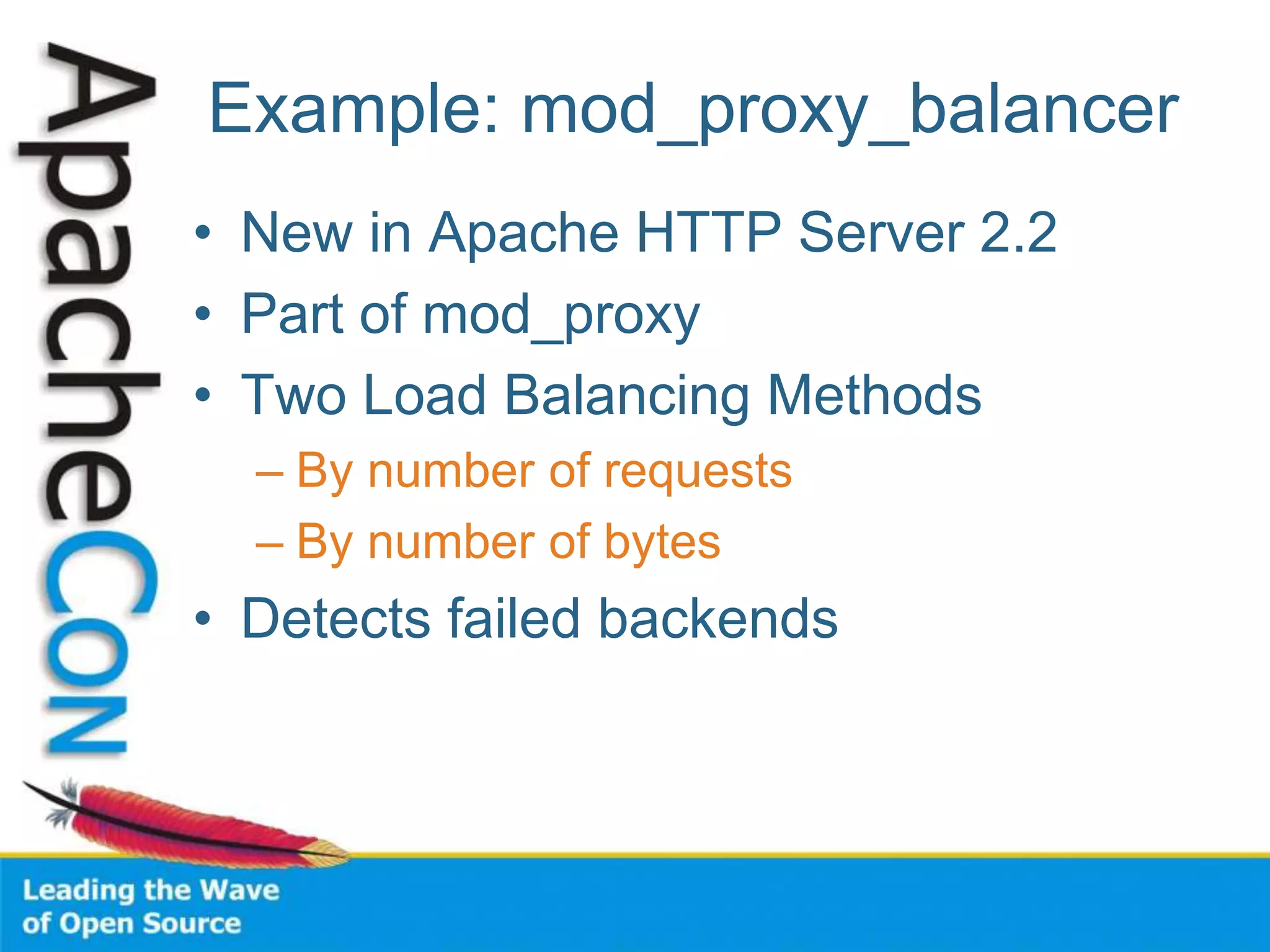
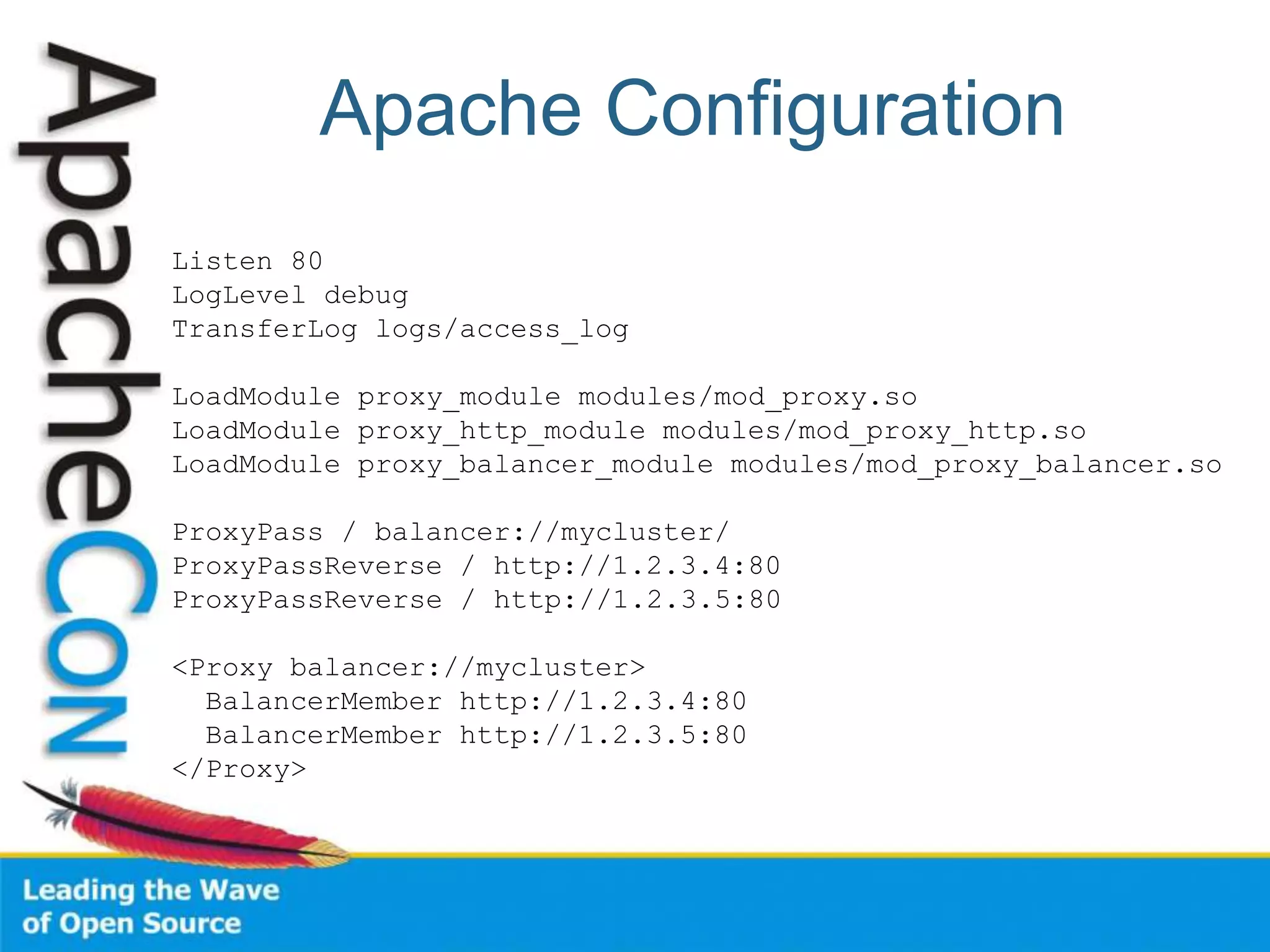
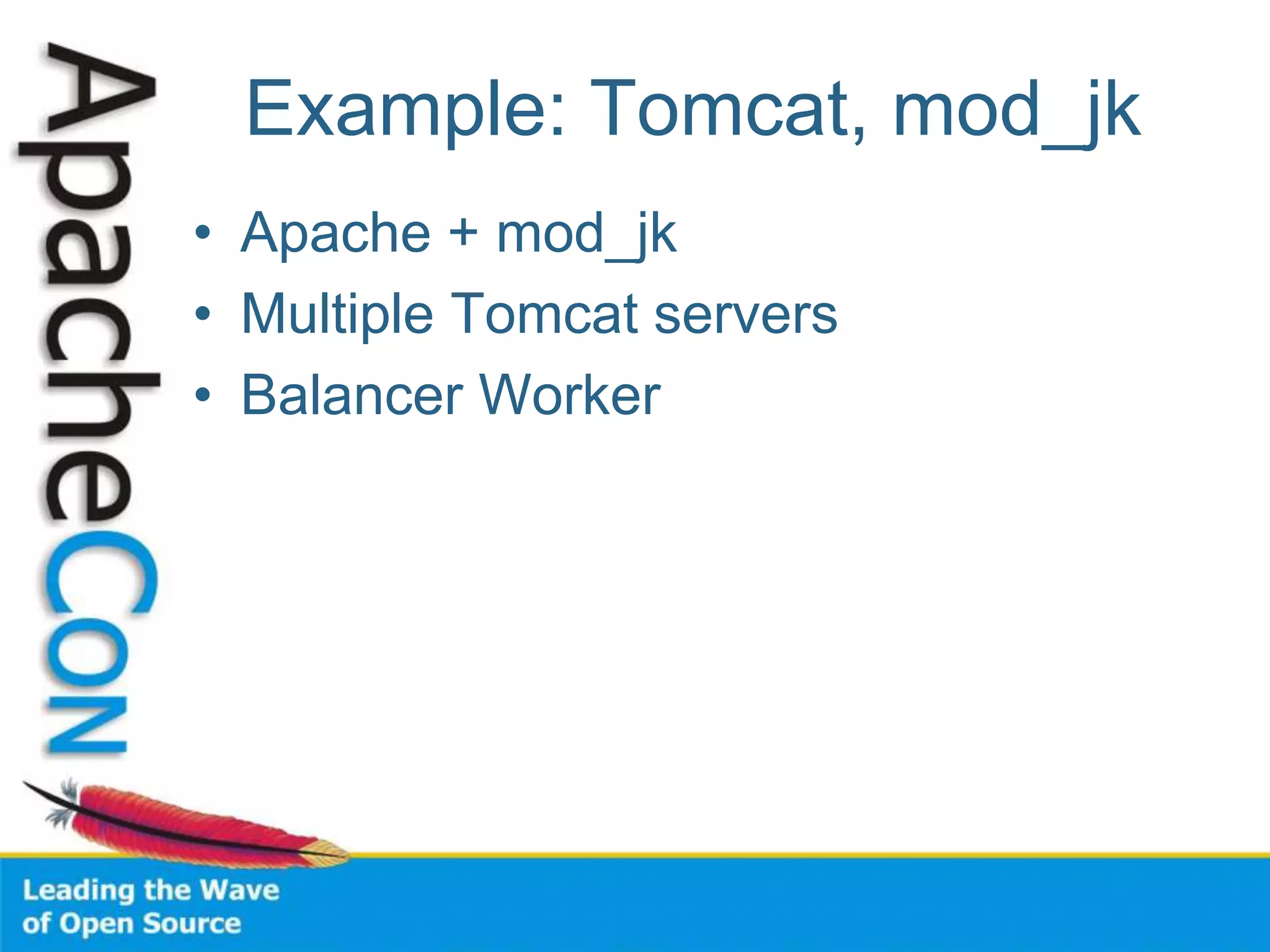
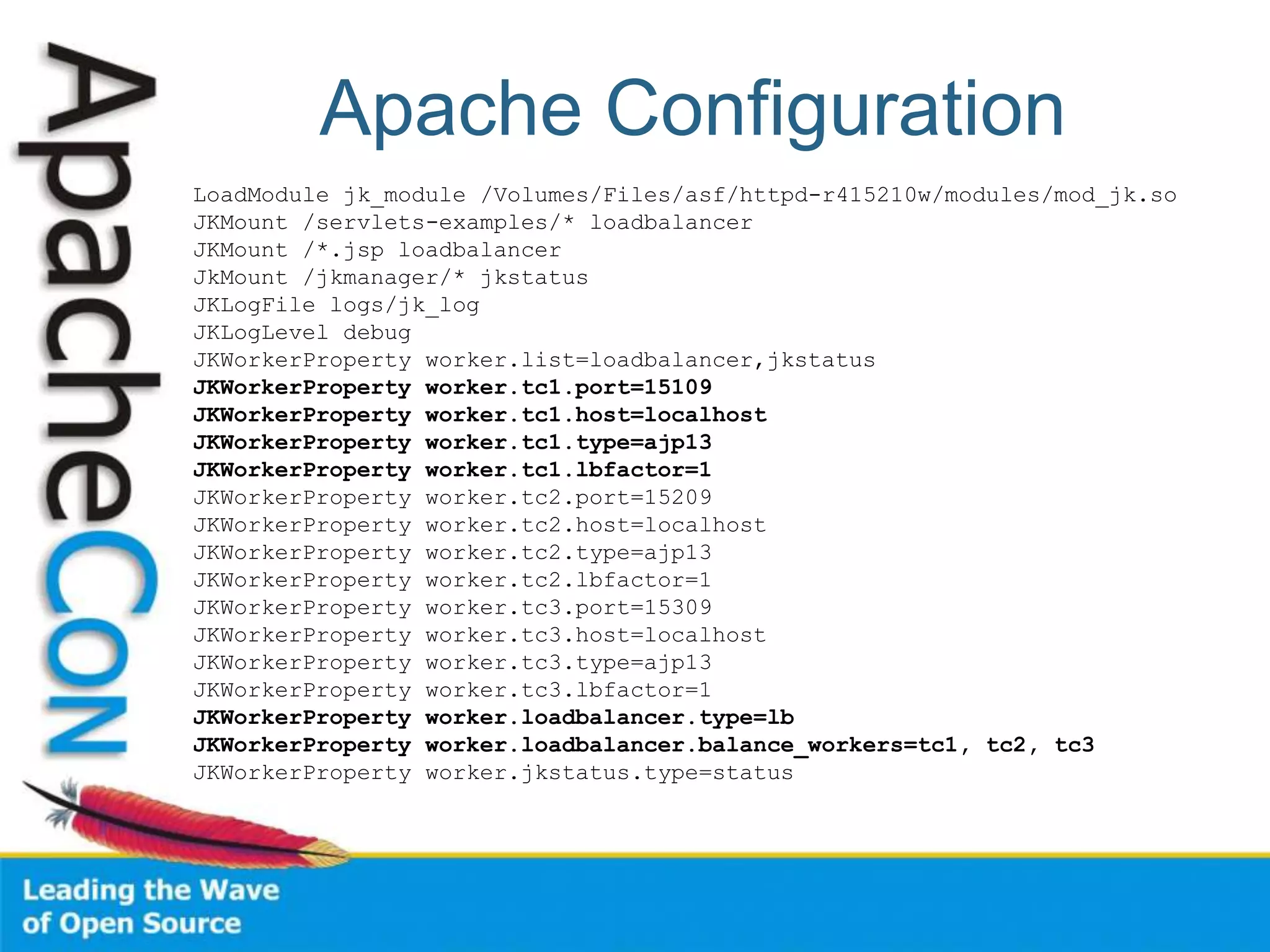
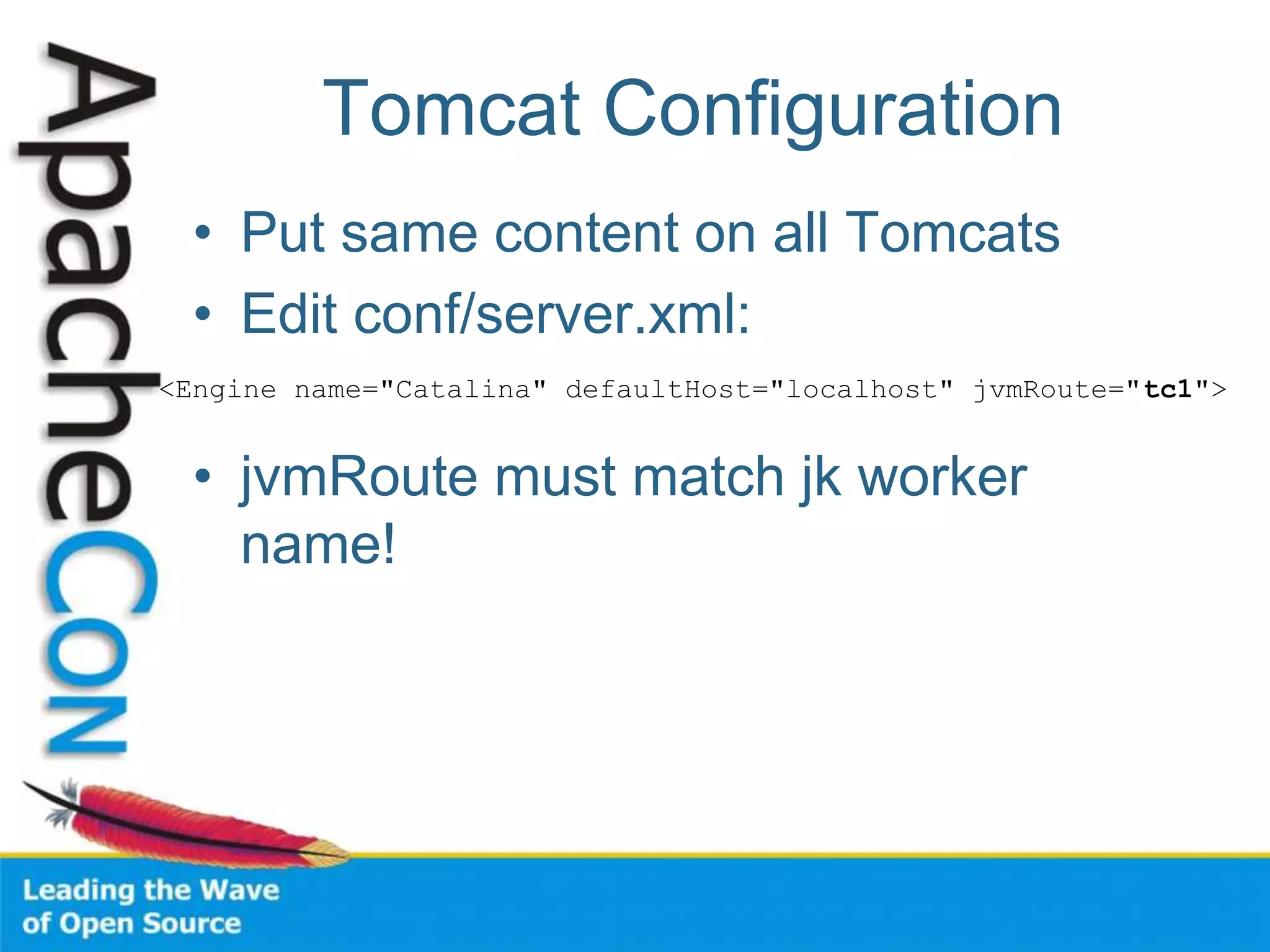
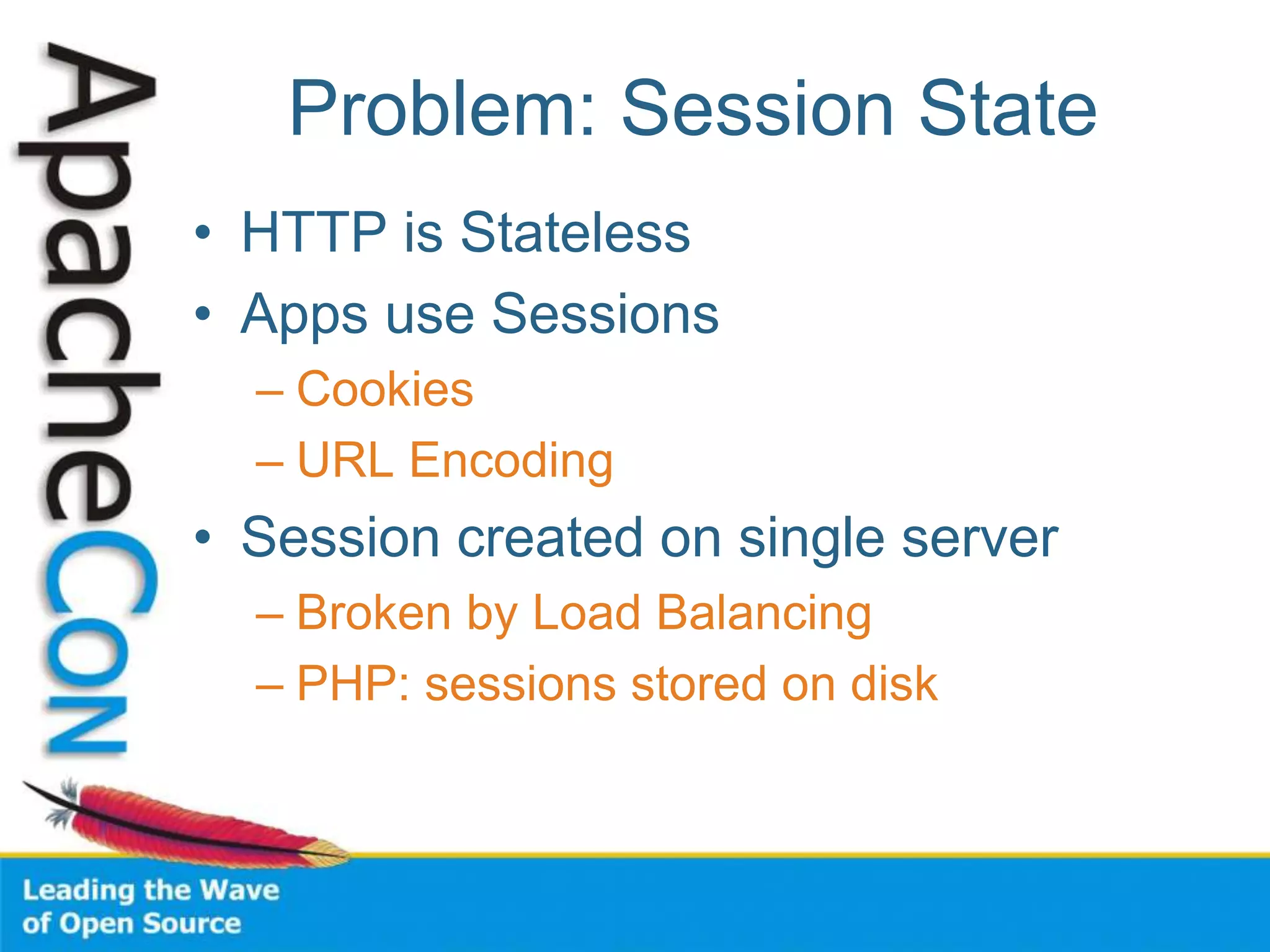
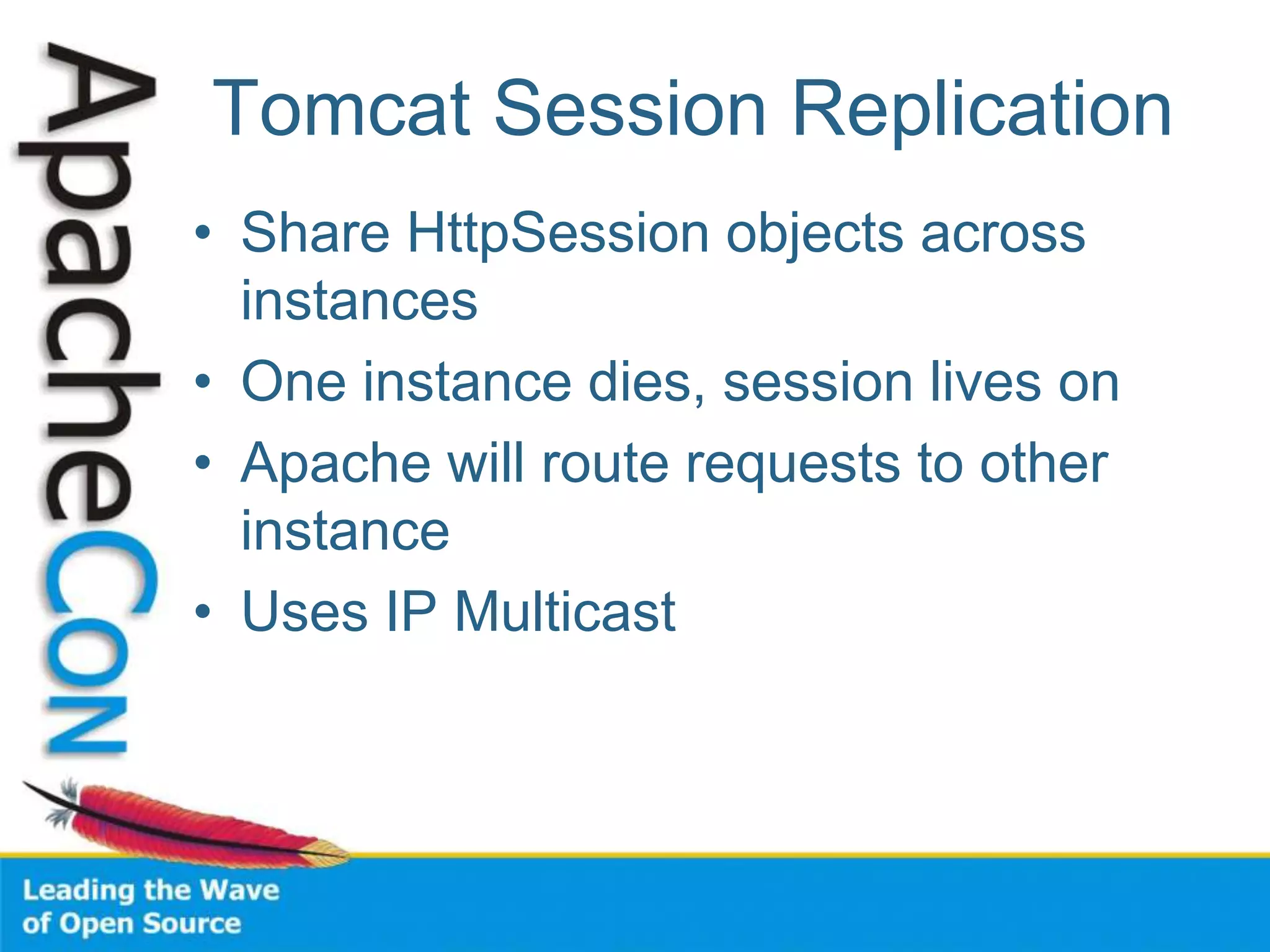
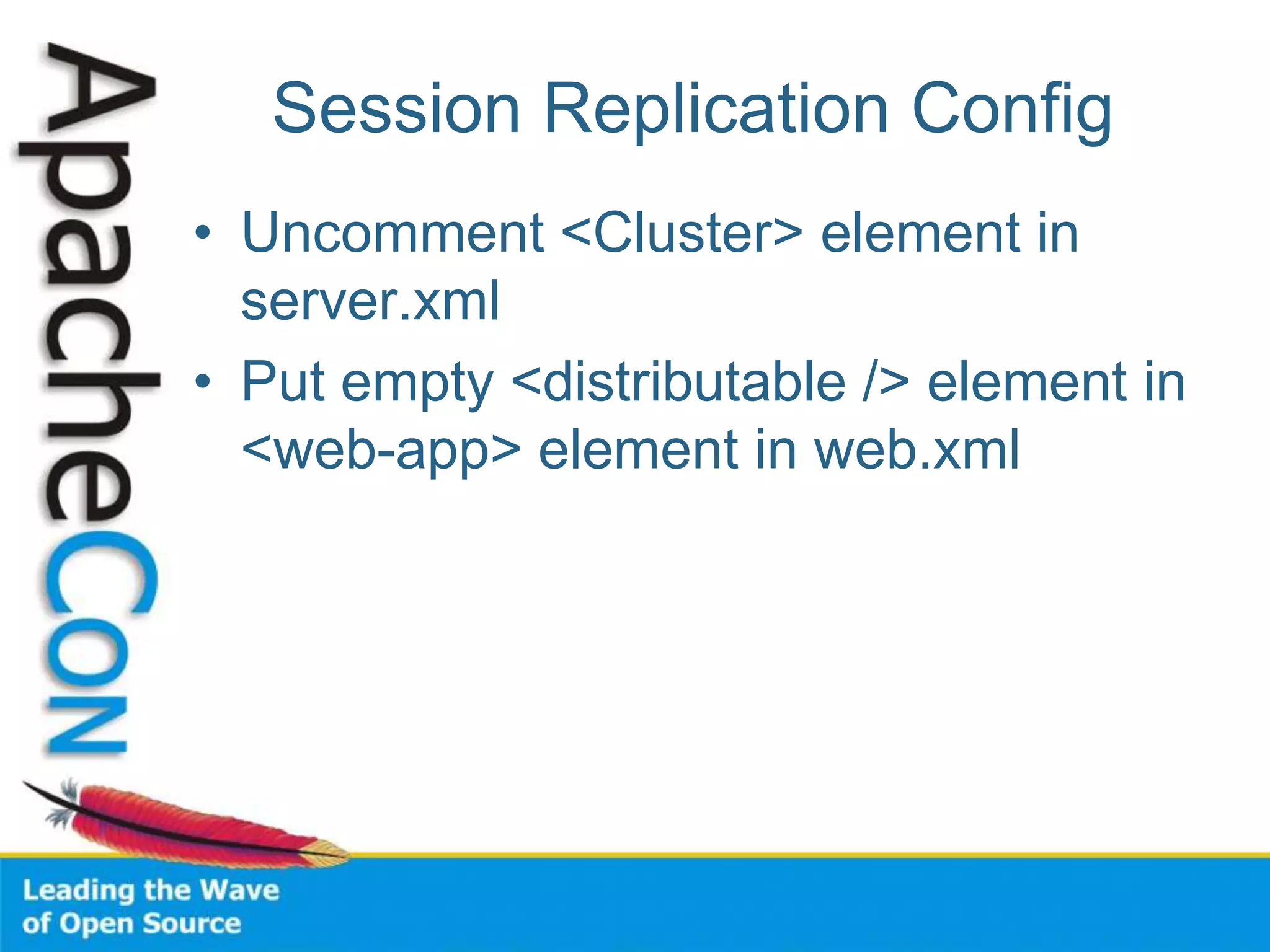
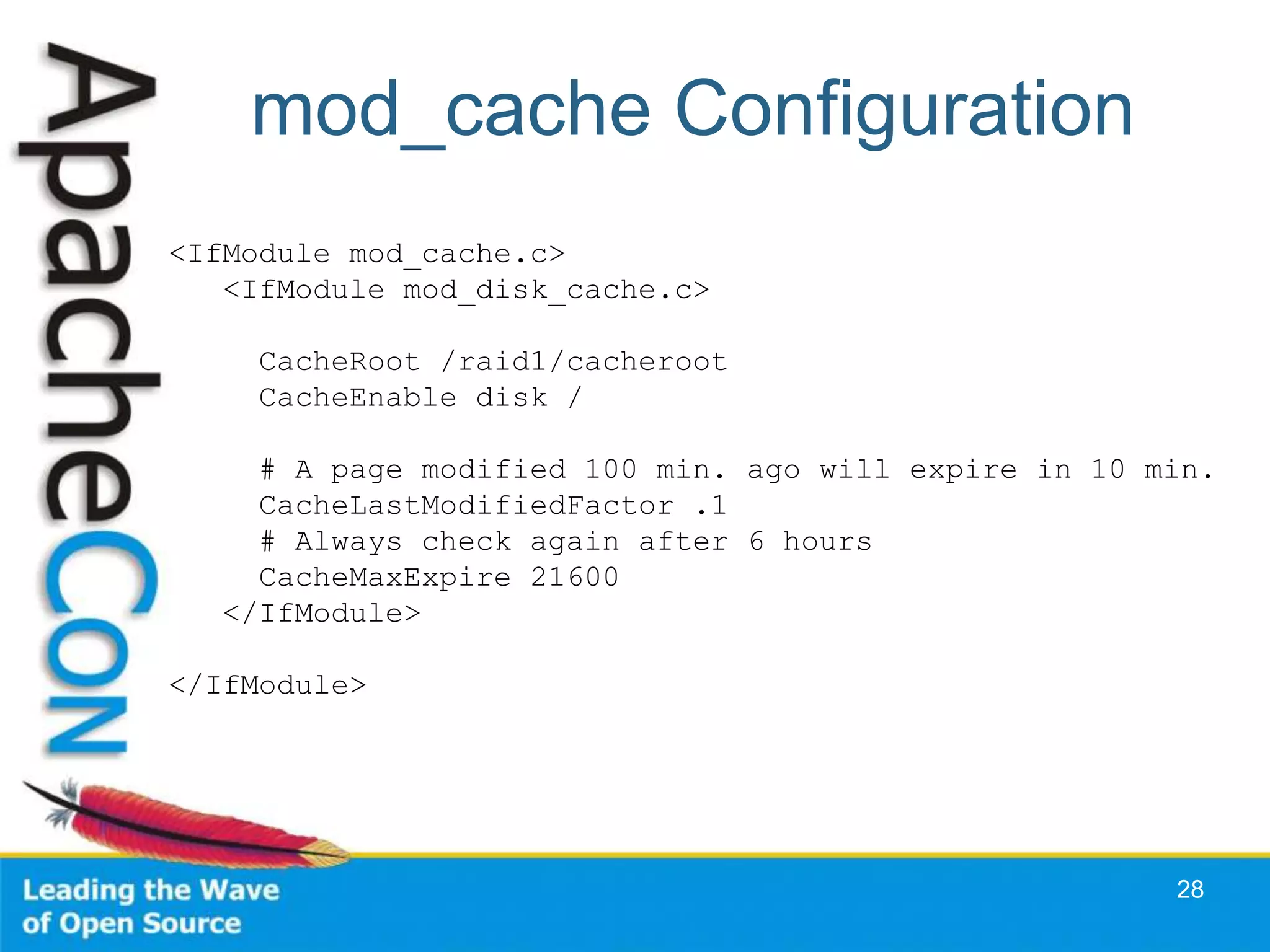
This document discusses techniques for scaling out Apache web servers to improve performance and reliability. It covers adding redundancy with hardware components like RAID disk mirroring and redundant power supplies. It also discusses scaling out the application tier vertically by moving services to separate hosts, and horizontally by load balancing traffic across multiple servers. Load balancing can be done with techniques like DNS round robin, network load balancers, and load balancing appliances. The document also addresses session state management across servers and caching static content to improve performance.







![Static Page Substitution
30
<Directory "/home/sctemme/inst/blog/httpd/htdocs">
Options +Indexes
Order allow,deny
Allow from all
RewriteEngine on
RewriteCond %{REQUEST_FILENAME} !-f
RewriteCond %{REQUEST_FILENAME} !-d
RewriteRule ^(.*)$ /cgi-bin/blosxom.cgi/$1 [L,QSA]
</Directory>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/performanceout-150114141857-conversion-gate02/75/Performance-out-30-2048.jpg)