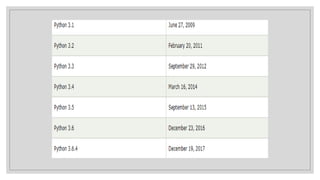
Python is a versatile, high-level, and easy-to-learn programming language founded by Guido van Rossum, supporting various programming paradigms, including object-oriented and functional programming. It features a dynamic typing system, extensive standard library, cross-platform compatibility, and is widely used for web applications, scientific computing, and more. The document outlines Python's history, its core concepts such as strings, tuples, dictionaries, and functions, as well as examples of basic syntax and operations.















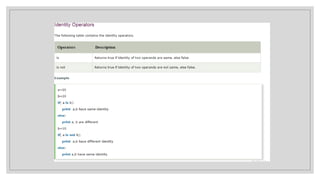
![>>> tuple=('rahul',100,60.4,'deepak')
>>> tuple1=('sanjay',10)
>>> tuple ('rahul', 100, 60.4, 'deepak')
>>> tuple[2:] (60.4, 'deepak')
>>> tuple1[0] 'sanjay'
>>> tuple+tuple1 ('rahul', 100, 60.4, 'deepak', 'sanjay', 10)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/13introtoit2-241218234215-d753170d/85/pengenalan-python-apa-itu-python-untuk-apa-pptx-18-320.jpg)
![Dictionary
Dictionary is a collection which works on a key-value pair.
It works like an associated array where no two keys can be same.
Dictionaries are enclosed by curly braces ({}) and values can be
retrieved by square bracket([]).
>>> dictionary={'name':'charlie','id':100,'dept':'it'}
>>> dictionary {'dept': 'it', 'name': 'charlie', 'id': 100}
>>> dictionary.keys()
['dept', 'name', 'id']
>>> dictionary.values() ['it', 'charlie',
100]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/13introtoit2-241218234215-d753170d/85/pengenalan-python-apa-itu-python-untuk-apa-pptx-19-320.jpg)

![List
List contain items of different data types. Lists are mutable i.e.,
modifiable.
The values stored in List are separated by commas(,) and enclosed
within a square brackets([]). We can store different type of data in a
List.
Value stored in a List can be retrieved using the slice operator([] and
[:]).
The plus sign (+) is the list concatenation and asterisk(*) is the
repetition operator.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/13introtoit2-241218234215-d753170d/85/pengenalan-python-apa-itu-python-untuk-apa-pptx-21-320.jpg)
![>>> list=[‘Maulik',678,20.4,‘Ravi']
>>> list1=[456,‘Kalpesh']
list ['aman', 678, 20.4, 'saurav
>>> list+list1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/13introtoit2-241218234215-d753170d/85/pengenalan-python-apa-itu-python-untuk-apa-pptx-22-320.jpg)