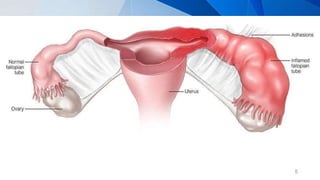
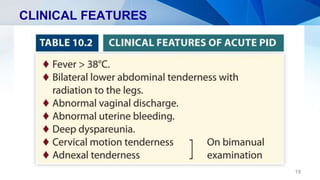
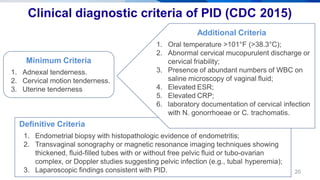
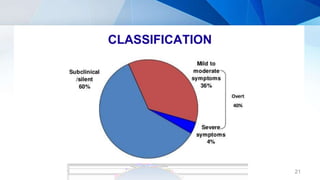
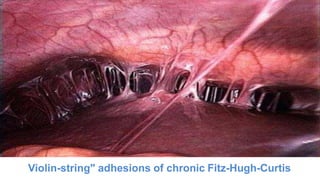
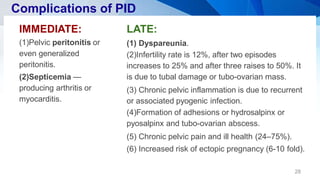
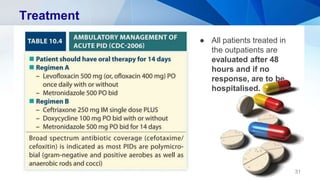
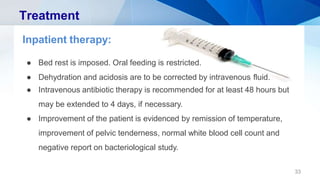
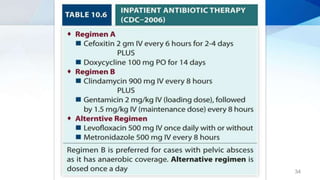
Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) is an infection of the upper female genital tract that is usually caused by bacteria spreading from the vagina and cervix. It is characterized by inflammation of the uterus, fallopian tubes, ovaries, and surrounding pelvic structures. Common symptoms include lower abdominal and pelvic pain, fever, abnormal vaginal discharge, and dyspareunia. Diagnosis is based on clinical criteria including cervical motion tenderness and adnexal tenderness. Treatment involves antibiotics, with hospitalization required if the infection is severe. Complications can include infertility, ectopic pregnancy, chronic pelvic pain, and recurrent infection if proper treatment and prevention measures are not followed.

























![REFERENCES
1. SALLY COLLINS, SABARATNAM ARULKUMARAN, KEVIN HAYES,
SIMON JACKSON, LAWRENCE IMPEY. Pelvic inflammatory disease.
Oxford Handbook of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, 2013, 3rd edition,
P.561-563.
2. HIRALAR KONAR. Pelvic inflammatory disease. Dc dutta’s textbook of
gynecology, 2013, 6th edition. P.127-133.
3. BARRY O’REILLY, CECILIA BOTTOMLEY, JANICE RYMER. Pelvic
Inflammatory
Disease. Essentials of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, 2012, 2nd edition,
P.130-133.
4. Pelvic Inflammatory Disease. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention,
June 4, 2015 [Viewed on 27 January 2018]. Available from :
https://www.cdc.gov/std/tg2015/pid.htm 40](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pid-201120043827/85/Pelvic-inflammatory-disease-39-320.jpg)
