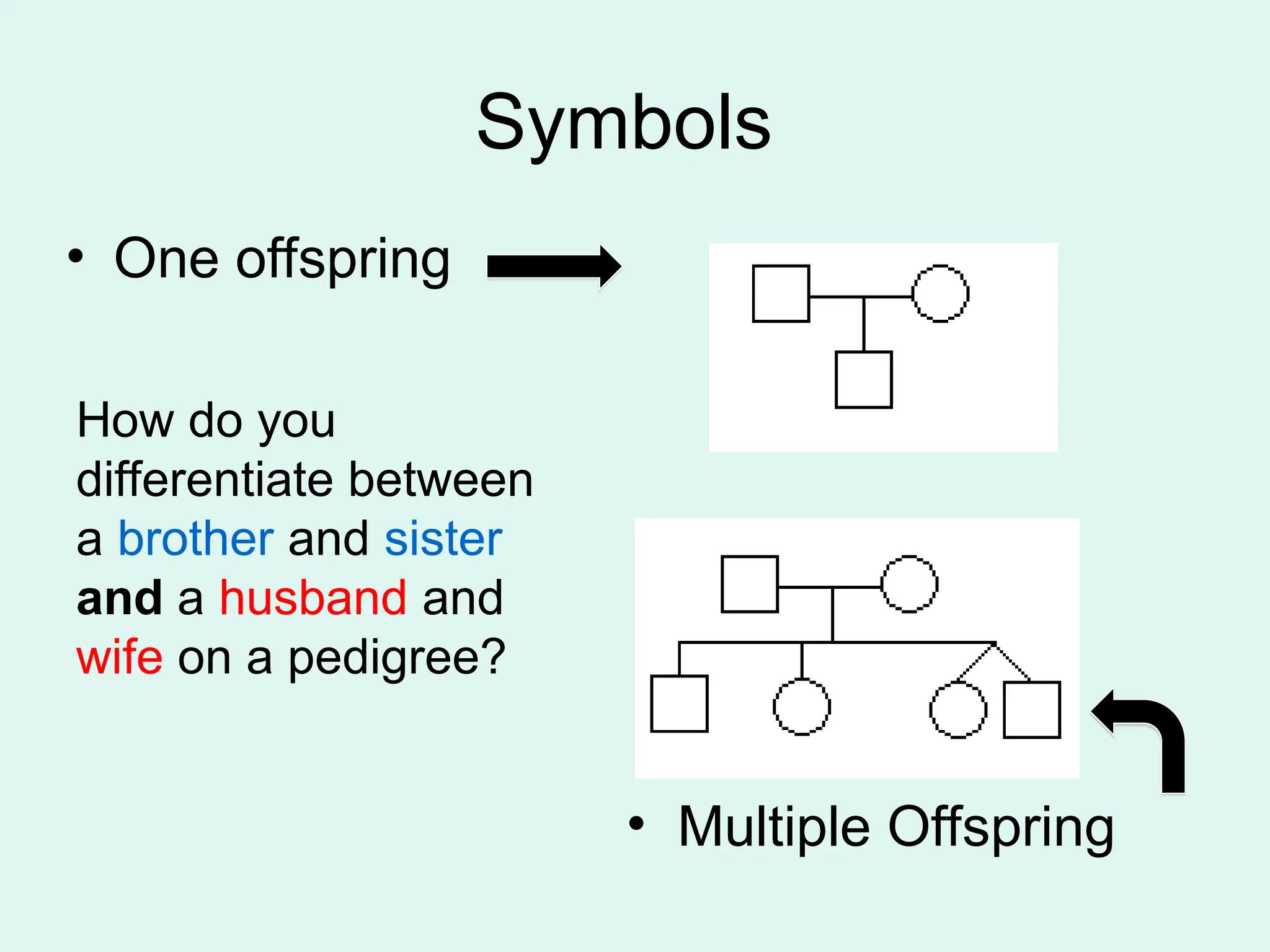
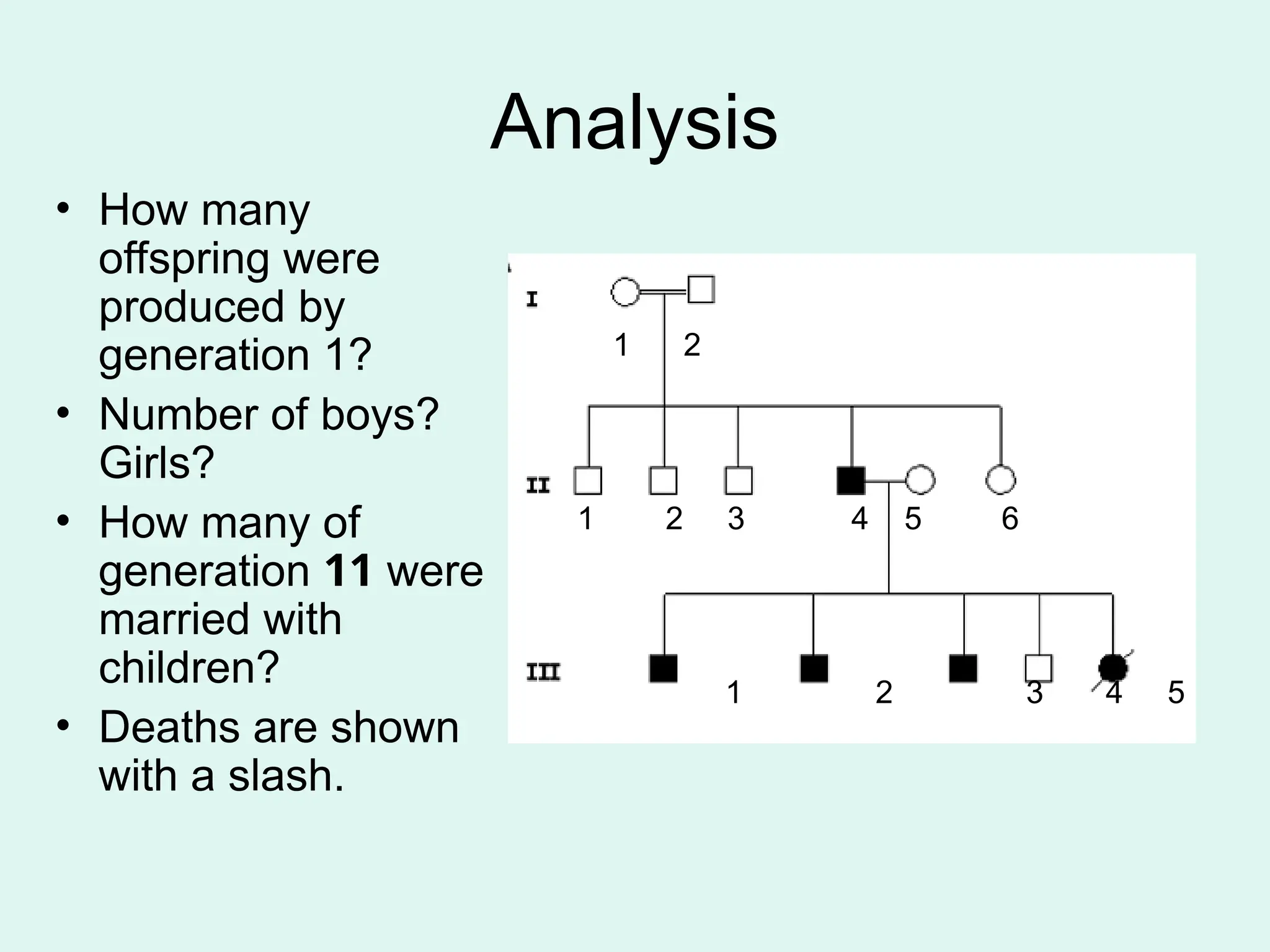
The document explains the use of pedigree charts in genetics to illustrate familial relationships and inheritance patterns of traits, such as albinism and polydactyly. It details the symbols used to represent individuals, the significance of shading, and how to analyze traits across generations. Additionally, it discusses identifying dominant and recessive traits based on the presence of carriers and generational patterns.