Recommended
PDF
Pyruvate dehydrogenase and tricarboxylic acid cycle/kreb’s cycle/citric acid ...
PPTX
PPTX
Krebs cycle/Citric acid cycle
PPTX
1051 carbohydrate metabolism lecture 3
PPTX
6 tricarboxylic acid cycle (2)
PPT
Pyruvate Dehydrogenase and Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle - PDH and TCA
PDF
PPTX
TRICARBOXYLIC ACID CYCLE (TCA CYCLE) Biochem II Unit 1.pptx
PDF
Genaral biology topic on krebs cyclce.pdf
PPTX
TCA CYCLE REGULATION $ SIGNIFICANCE.pptx
PDF
Lecture Note - Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle.pdf
PPTX
TCA cycle/Krebs cycle/Citric acid cycle
PPTX
The Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle
PPT
PPTX
TCA cycle in detail with all the mechanicsm
PPTX
KREBS CYCLE or Tricitric Acid in mitochondria1.pptx
PPTX
Tri Carboxylic acid cycle or Kreb cycle .pptx
PPTX
Krebs cycle- significance,steps,energetics,inhibitors,amphibolic
PPTX
Citric acid cycle ( TCA )
PPTX
Krebs cycle and enzymes final 12 OCT 23.pptx
PPT
PPTX
tca-151218061418.pptxhsheujdjejejejhdhee
PPT
TCA (Tricarboxylic Acid/ Krebs Cycle/ Citric Acid Cycle
PPTX
Citric acid cycle, krebs cycle, by Dr atindra pandey
PPTX
Citric acid cycle, krebs cycle, by atindra pandey
PPTX
PPTX
TCA.pptxkbkgjgjgjvssusjsjejfnrnfnfnnfnfkcf
PPTX
the presentation on pyruvate dehydrogenase complex (PDH).pptx
PPTX
Lumbar Facet Joint Pain – A Pain Generator Based Diagnostic & Treatment Approach
PDF
Gastrointestinal Infection PCR Panel Diagnostic Screen
More Related Content
PDF
Pyruvate dehydrogenase and tricarboxylic acid cycle/kreb’s cycle/citric acid ...
PPTX
PPTX
Krebs cycle/Citric acid cycle
PPTX
1051 carbohydrate metabolism lecture 3
PPTX
6 tricarboxylic acid cycle (2)
PPT
Pyruvate Dehydrogenase and Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle - PDH and TCA
PDF
PPTX
TRICARBOXYLIC ACID CYCLE (TCA CYCLE) Biochem II Unit 1.pptx
Similar to PDH_TCA_Cycle_Presentation.pptx citric acid cycle
PDF
Genaral biology topic on krebs cyclce.pdf
PPTX
TCA CYCLE REGULATION $ SIGNIFICANCE.pptx
PDF
Lecture Note - Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle.pdf
PPTX
TCA cycle/Krebs cycle/Citric acid cycle
PPTX
The Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle
PPT
PPTX
TCA cycle in detail with all the mechanicsm
PPTX
KREBS CYCLE or Tricitric Acid in mitochondria1.pptx
PPTX
Tri Carboxylic acid cycle or Kreb cycle .pptx
PPTX
Krebs cycle- significance,steps,energetics,inhibitors,amphibolic
PPTX
Citric acid cycle ( TCA )
PPTX
Krebs cycle and enzymes final 12 OCT 23.pptx
PPT
PPTX
tca-151218061418.pptxhsheujdjejejejhdhee
PPT
TCA (Tricarboxylic Acid/ Krebs Cycle/ Citric Acid Cycle
PPTX
Citric acid cycle, krebs cycle, by Dr atindra pandey
PPTX
Citric acid cycle, krebs cycle, by atindra pandey
PPTX
PPTX
TCA.pptxkbkgjgjgjvssusjsjejfnrnfnfnnfnfkcf
PPTX
the presentation on pyruvate dehydrogenase complex (PDH).pptx
Recently uploaded
PPTX
Lumbar Facet Joint Pain – A Pain Generator Based Diagnostic & Treatment Approach
PDF
Gastrointestinal Infection PCR Panel Diagnostic Screen
PPTX
Anaesthesia in Hypertension (anaesthesia in intercurrent diseases)
PPTX
BILIARY TREE RADIOLOGY ADVANCE IMAGING (USG, CT SCAN, MRI AND ERCP) OF ITS AN...
PPTX
HIGH FREQUENCY CURRENT ppt prepared by urvi
PDF
Pediatric neurodegenerative disorders and anesthesia considerations. Dalamagk...
PPTX
FETAL ALCOHOL SYNDROME PRESENTATION.pptx
PPTX
ppt on Cholangiocarcinoma.pptx PPT ON CHOLANGIOCARCINOMA EIOLOGY DIAGNOSIS AN...
PPTX
Lungs & Respiratory System (RIT): Mechanics of Breathing and Gas Exchange Exp...
PPTX
Biotransformation and Excretion
PDF
General Anesthetics. Dalamagka, Maria. Anaesthetist- physician
PPTX
Easy Peasy Gut: Complete Digestive Support
PPTX
Biostatistics- Data types and presentation
PPTX
Drug use evaluation and WHO drug use Indicators.pptx
PPTX
Nervous System: Organization & Functions
PPTX
Chemistry of Hemoglobin (Types, Derivatives and Disorders)
PDF
Scholar.postdoc - Anaesthesia: Dalamagka, Maria
PPTX
ppt on Cholangiocarcinoma.pptx BY DR MULATU ASFAW D GENERAL SURGEON
PDF
Key Steps to Success With CDK4/6 Inhibition in Early Through Metastatic Breas...
PDF
Ailanthone A novel potential drug ol-20-02-1489for Vestibular Schwannoma
PDH_TCA_Cycle_Presentation.pptx citric acid cycle 1. PDH Complex and TCA Cycle –
Inhibition & Regulation
Presented by: [Your Group Name]
Guided by: [Professor’s Name]
Institution: [Your College Name]
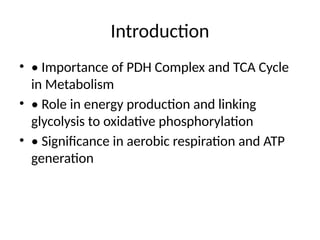
2. Introduction
• • Importance of PDH Complex and TCA Cycle
in Metabolism
• • Role in energy production and linking
glycolysis to oxidative phosphorylation
• • Significance in aerobic respiration and ATP
generation
3. Pyruvate Dehydrogenase (PDH)
Complex – Overview
• • Converts pyruvate to Acetyl-CoA
• • Location: Mitochondrial matrix
• • Reaction: Pyruvate + NAD⁺ + CoA → Acetyl-
CoA + CO₂ + NADH
• • Coenzymes: TPP, Lipoic Acid, CoA, FAD, NAD⁺
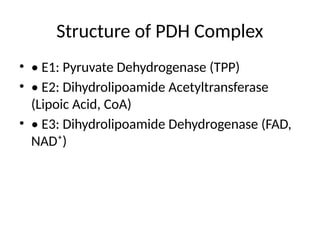
4. Structure of PDH Complex
• • E1: Pyruvate Dehydrogenase (TPP)
• • E2: Dihydrolipoamide Acetyltransferase
(Lipoic Acid, CoA)
• • E3: Dihydrolipoamide Dehydrogenase (FAD,
NAD⁺)
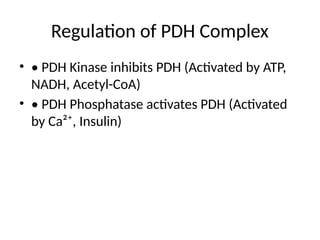
5. Regulation of PDH Complex
• • PDH Kinase inhibits PDH (Activated by ATP,
NADH, Acetyl-CoA)
• • PDH Phosphatase activates PDH (Activated
by Ca²⁺, Insulin)
6. Inhibition of PDH Complex
• • Thiamine Deficiency (Beriberi, Wernicke-
Korsakoff)
• • Heavy Metal Poisoning (Arsenic inhibits
Lipoic Acid)
• • Excess ATP, NADH, Acetyl-CoA (Negative
Feedback)
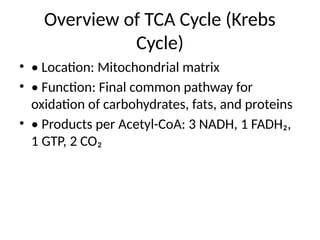
7. Overview of TCA Cycle (Krebs
Cycle)
• • Location: Mitochondrial matrix
• • Function: Final common pathway for
oxidation of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins
• • Products per Acetyl-CoA: 3 NADH, 1 FADH₂,
1 GTP, 2 CO₂
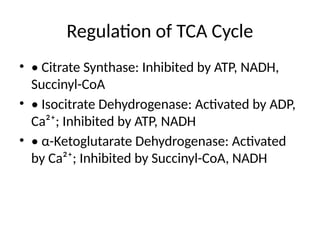
8. Regulation of TCA Cycle
• • Citrate Synthase: Inhibited by ATP, NADH,
Succinyl-CoA
• • Isocitrate Dehydrogenase: Activated by ADP,
Ca²⁺; Inhibited by ATP, NADH
• • α-Ketoglutarate Dehydrogenase: Activated
by Ca²⁺; Inhibited by Succinyl-CoA, NADH
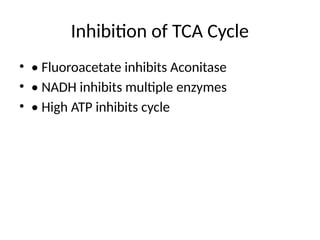
9. Inhibition of TCA Cycle
• • Fluoroacetate inhibits Aconitase
• • NADH inhibits multiple enzymes
• • High ATP inhibits cycle
10. Clinical Correlations
• • PDH Deficiency → Lactic Acidosis
• • Vitamin B1 Deficiency → Affects PDH & TCA
Cycle
• • Arsenic Poisoning → Inhibits Lipoic Acid
11. Summary
• • PDH Complex links glycolysis to TCA Cycle
• • TCA Cycle is the final oxidative pathway
• • Both pathways are tightly regulated by
energy status
• • Inhibitors include ATP, NADH, Acetyl-CoA,
heavy metals
• • Deficiencies can cause metabolic diseases
12. References
• • Vasudevan, D. M. – Textbook of
Biochemistry for Medical Students
• • Satyanarayana U. – Biochemistry
• • Harper’s Illustrated Biochemistry
• • Lippincott’s Illustrated Reviews:
Biochemistry
![PDH Complex and TCA Cycle –
Inhibition & Regulation
Presented by: [Your Group Name]
Guided by: [Professor’s Name]
Institution: [Your College Name]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pdhtcacyclepresentation-250501163824-895078b8/85/PDH_TCA_Cycle_Presentation-pptx-citric-acid-cycle-1-320.jpg)