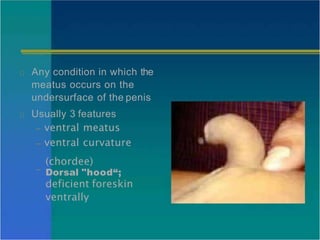
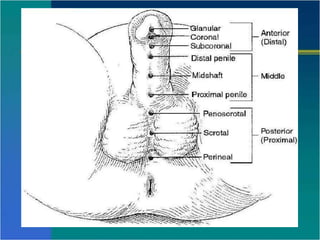
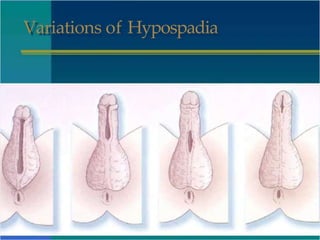
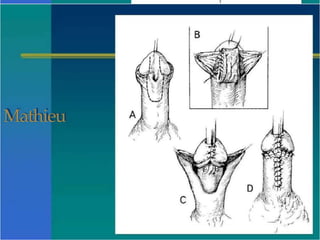
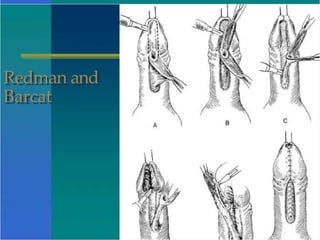
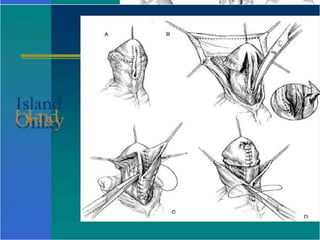
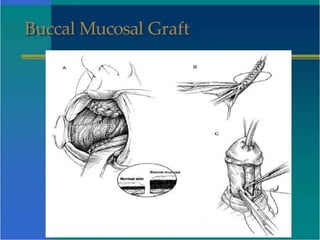
Hypospadias is a condition where the urethral opening is located on the underside of the penis. It occurs in about 1 in 300 male births. Risk factors include family history and certain genetic conditions. Associated anomalies include undescended testes and inguinal hernias. Evaluation for intersex conditions is recommended for severe or proximal hypospadias, especially with cryptorchidism. Over 150 surgical techniques have been described to repair hypospadias, depending on the location and severity. The goal of surgery is to relocate the urethral opening to the tip of the penis.